
Concept explainers
Draw the influence lines for the reaction moment at support A, the vertical reactions at supports A and B and the shear at the internal hinge C.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Influence line for vertical reaction at support B.
Apply a 1 k unit moving load at a distance of x from left end B.
Sketch the free body diagram of frame as shown in Figure 1.
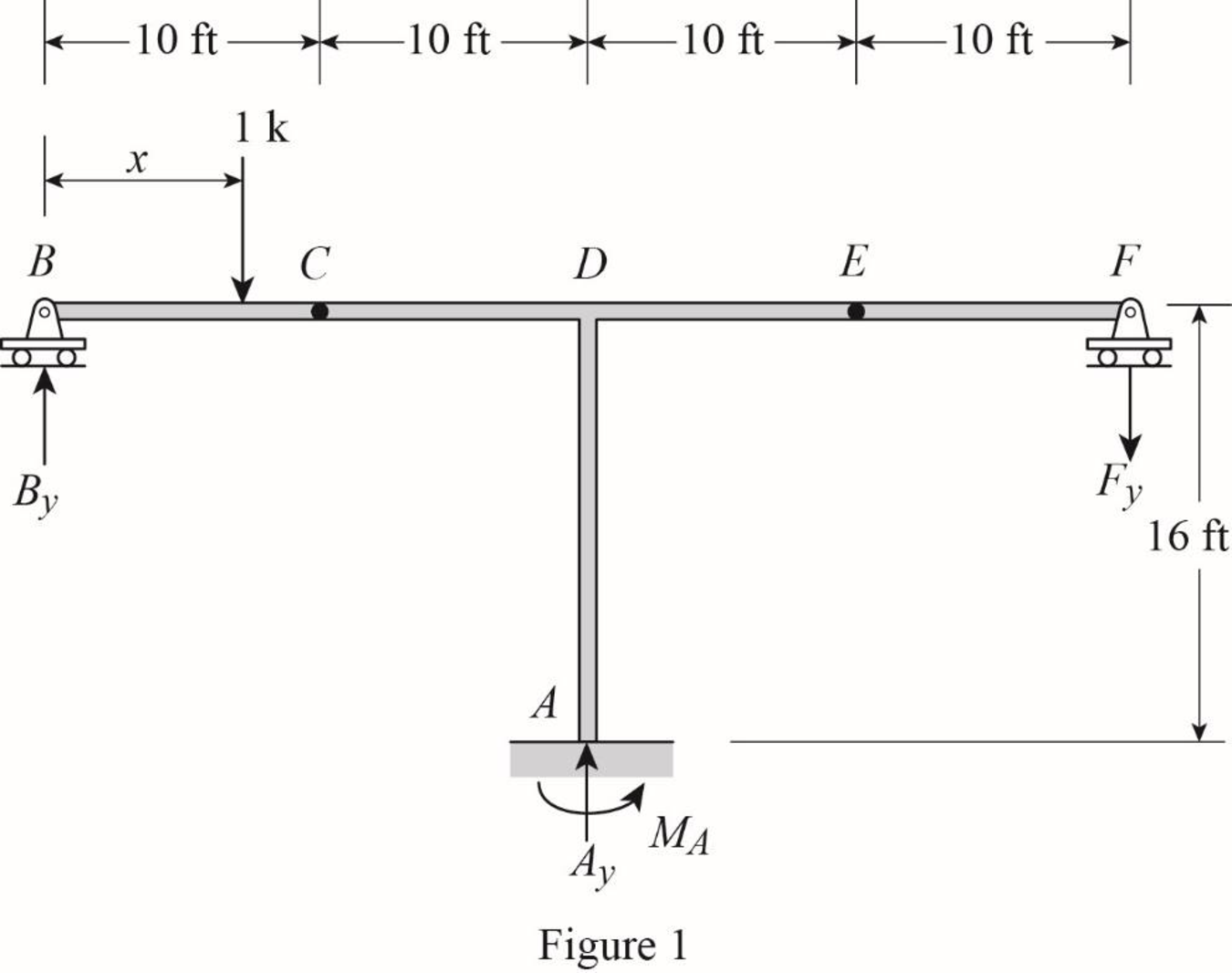
Refer Figure 1.
Apply 1 k load just left of C
Consider section BC.
Consider moment equilibrium at C.
Take moment at C from B.
Consider clockwise moment as positive and anticlockwise moment as negative.
Apply 1 k load just right of C
Consider section BC.
Consider moment equilibrium at C.
Take moment at C from B.
Consider clockwise moment as positive and anticlockwise moment as negative.
Thus, the equation of vertical support reaction at B as follows,
Find the influence line ordinate of
Substitute 0 for
Thus, the influence line ordinate of
Similarly calculate the influence line ordinate of
| x (ft) | Points | Influence line ordinate of |
| 0 | B | 1 |
| 10 | C | 0 |
| 20 | D | 0 |
| 30 | E | 0 |
| 40 | F | 0 |
Sketch the influence line diagram for vertical support reaction at B using Table 1 as shown in Figure 2.
Influence line for vertical reaction at support A.
Apply a 1 k unit moving load at a distance of x from left end C.
Refer Figure 1.
Find the vertical support reaction
Apply 1 k load just left of E
Consider section EF.
Consider moment equilibrium at point E.
Consider clockwise moment as positive and anticlockwise moment as negative
Apply 1 k load just right of E
Consider section EF.
Consider moment equilibrium at point E.
Consider clockwise moment as positive and anticlockwise moment as negative
Thus, the equation of vertical support reaction at F as follows,
Apply a 1 k unit moving load at a distance of x from left end B.
Refer Figure 1.
Apply vertical equilibrium in the system.
Consider upward force as positive and downward force as negative.
Find the equation of vertical support reaction
Substitute
Find the equation of vertical support reaction
Substitute
Find the equation of vertical support reaction
Substitute
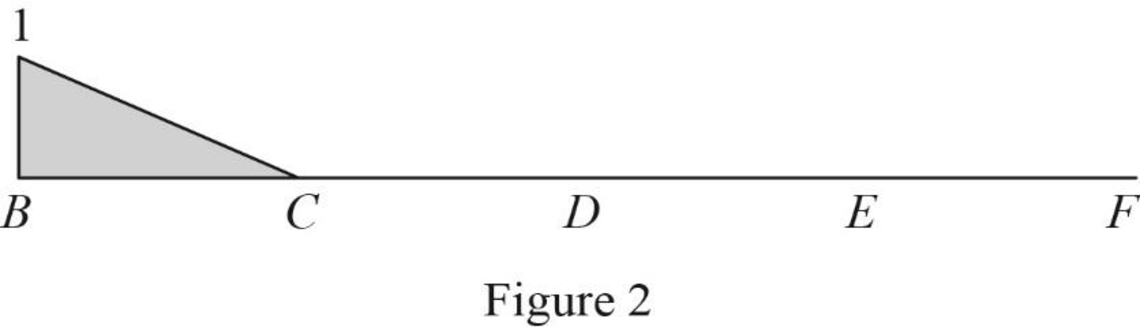
Thus, the equation of vertical support reaction at A as follows,
Find the influence line ordinate of
Substitute 40 ft for
Thus, the influence line ordinate of
Similarly calculate the influence line ordinate of
| x (ft) | Points | Influence line ordinate of |
| 0 | B | 0 |
| 10 | C | 1 |
| 20 | D | 1 |
| 30 | E | 1 |
| 40 | F | 0 |
Sketch the influence line diagram for the vertical reaction at support A using Table 3 as shown in Figure 3.
Influence line for moment at support A.
Apply a 1 k unit moving load at a distance of x from left end B.
Refer Figure 1.
Apply 1 k load just left of C
Take moment at A from B.
Consider clockwise moment as positive and anticlockwise moment as negative.
Substitute
Apply 1 k load just right of C to just left of D
Take moment at A from B.
Consider clockwise moment as positive and anticlockwise moment as negative.
Substitute
Apply 1 k load just right of D to just left of E
Take moment at A from F.
Consider clockwise moment as positive and anticlockwise moment as negative.
Substitute
Apply 1 k load just right of E
Take moment at A from F.
Consider clockwise moment as positive and anticlockwise moment as negative.
Substitute
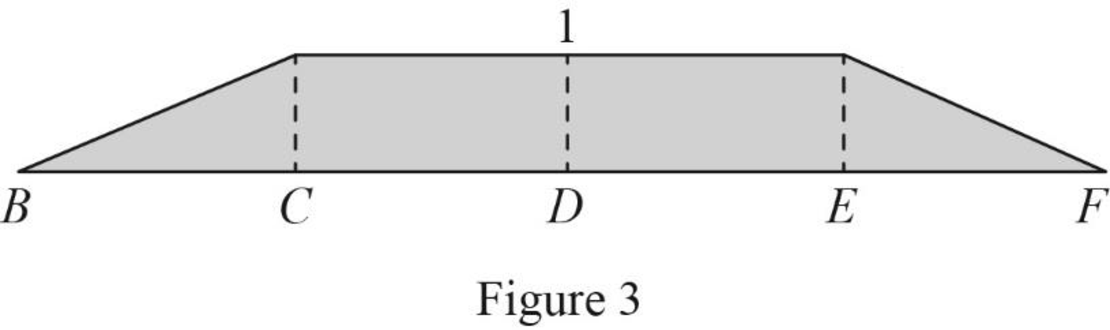
Thus, the equation of moment at A as follows,
Find the influence line ordinate of
Substitute 0 for
Thus, the influence line ordinate of
Similarly calculate the influence line ordinate of
| x (ft) | Points | Influence line ordinate of |
| 0 | B | 0 |
| 10 | C | ‑10 |
| 20 | D | 0 |
| 30 | E | 10 |
| 40 | F | 0 |
Sketch the influence line diagram for the moment at support A using Table 3 as shown in Figure 4.
Influence line for shear at point C.
Find the equation of shear force at C of portion BC
Sketch the free body diagram of the section BC when 1 k load placed between BC as shown in Figure 5.
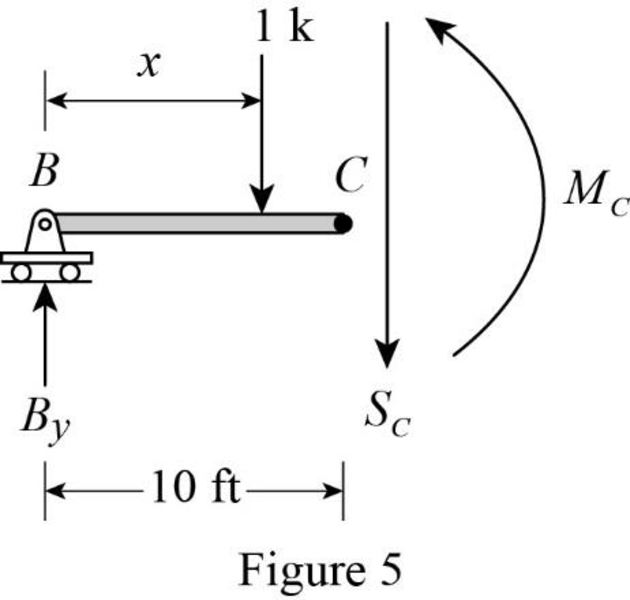
Refer Figure 5.
Apply equilibrium equation of forces.
Consider upward force as positive
Substitute
Find the equation of shear force at C of portion CF
Sketch the free body diagram of the section BC when 1 k load placed between CF as shown in Figure 6.
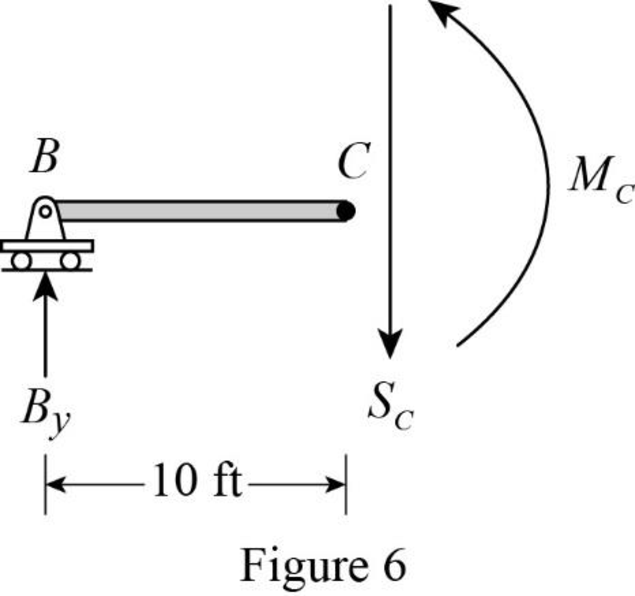
Refer Figure 5.
Apply equilibrium equation of forces.
Consider upward force as positive
Substitute
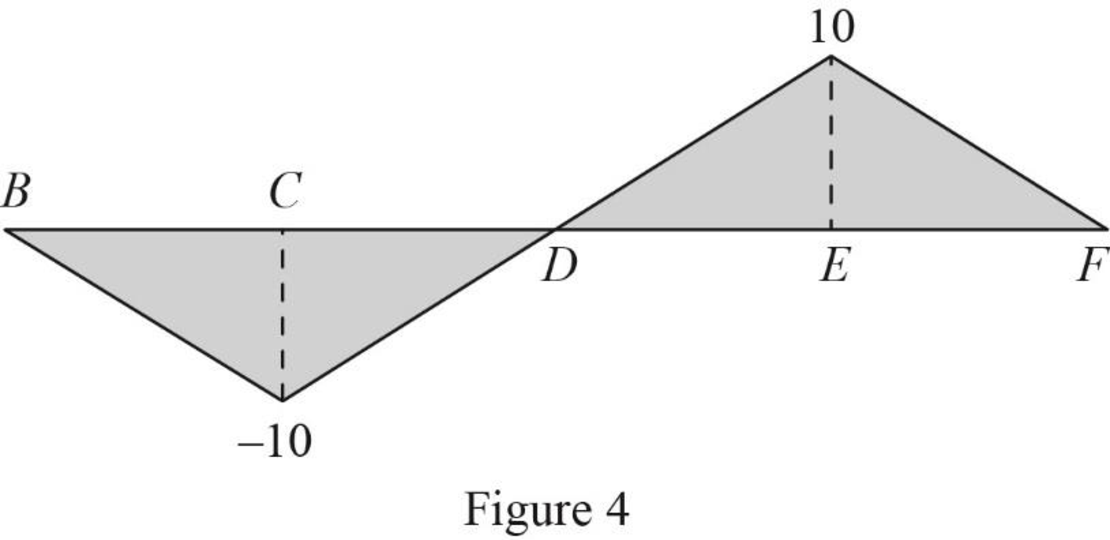
Thus, the equations of the influence line for
Find the influence line ordinate of
Substitute 10 m for
Thus, the influence line ordinate of
Find the shear force of
| x (ft) | Points | Influence line ordinate of |
| 0 | B | 0 |
| 10 | ‑1 | |
| 20 | 0 | |
| 30 | E | 0 |
| 40 | F | 0 |
Draw the influence lines for the shear force at point C using Table 4 as shown in Figure 7.
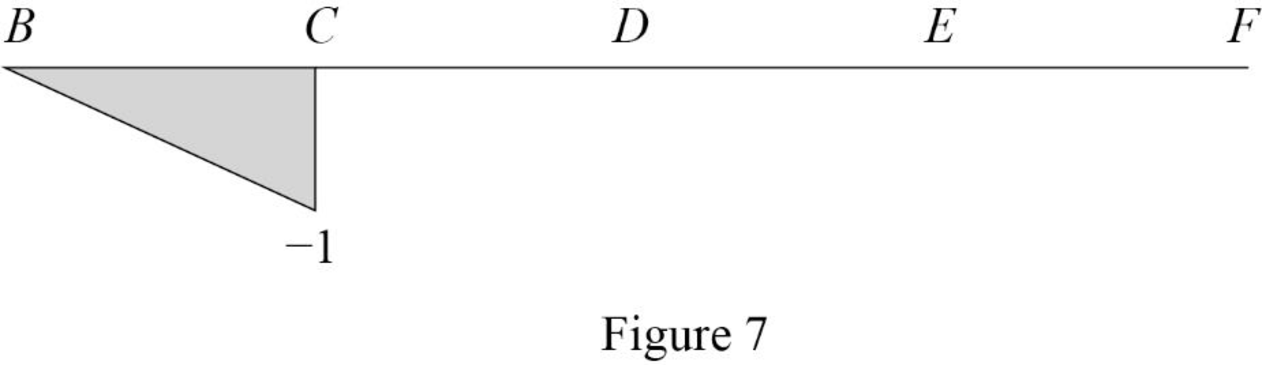
Therefore, the influence lines for the moment at support A and the vertical reactions at supports A and B and the influence lines for the shear hinge C are drawn.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Structural Analysis
- Calculate ALL nodal displacements and ALL the member forces in the truss. Please use the ID's noted in the truss diagramarrow_forwardQ3. In a water flood operation in reservoir A, water is being distributed to severalinjection wells from a common injection system; that is, water is supplied to all thewells at approximately the same well head pressure. Routine measurement of theindividual well injection rates by the team of field operators showed that one well wasreceiving approximately 45% more than its neighbours. The sum of the kh productsfor all of the injection wells were approximately the same depth. As a member of theteam, explain:What are the possible causes of the abnormally high injection rate in this well, andwhat production logs or other tests might be run to further diagnose the problem andplan remedial action?arrow_forwardQuestion 1 20 pts Test data on the bending strength of construction wood poles of various diameter are presented below assuming the same length. Kip- 1000 lbf. Using the following data with 2nd order Newton polynomial interpolation, we want to determine the strength of the material for x=4.5 in. Which data point will be used as x? After you found x0, enter the value of x-xo in the solution. Answer shall be in one decimal place. Distance (in) 2.6 1.5 8.3 2.8 5.7 Strength (kips) 100 200 300 400 500arrow_forward
- Solve pleasearrow_forwardsolve all of the last names from A-K to please for example use k=100k/in , m =1000lb/g . use el centro (2nd picture ) to solve the questions. Thank you for your help! for the following questions ignore that last name and just solve it pleae: Verify the modes that are orthogonal Normalize the first mode uisng electro with 2%damping, Determine Sa&Sd only for the first modearrow_forwardFor question 2 do 2% please. Use El centro spectrum to answer the secon question please. Thank you for your help!arrow_forward
- solve pleasearrow_forwardA mechanism for pushing small boxes from an assembly line onto a conveyor belt is shown with arm OD and crank CB in their vertical positions. For the configuration shown, crank CB has a constant clockwise angular velocity of 0.6π rad/s. Determine the acceleration QE of E (positive if to the right, negative if down). 450 mm 215 mm 565 mm A 185 mm 105 mm 110185. mm mm Answer: a = i B 40 mm E m/s²arrow_forwardPlease answer the following questions in the picture, use the second picture to answer some of the questions. I appreciate your help! Explain step by step, thank you!arrow_forward
- Question 5. Three pipes A, B, and C are interconnected as in Fig. 2. The pipe characteristics are given below. Find the rate at which water will flow in each pipe. Find also the pressure at point P. (Neglect minor losses) Pipe D (in) L (ft) f A 6 2000 0.020 B 4 1600 0.032 C 8 3000 0.02 -El. 200 ft P -El. 120 ft B Fig. 2 -El. 50 ft.arrow_forwardcalculate all nodal displacementts and all the member forces of the trussarrow_forwardNOTE: Use areal methods only for V,M,N diagrams(Do NOT use the equations) (also draw the N diagram(s) for the entire structure)arrow_forward
