
(a)
To find
(a)
Answer to Problem 18E
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The matrices
Concept used:
Operations like addition and subtraction of matrices are only possible when they are of same dimension.
Dimension of matrix with a rows and b columns is given by
If a matrix is multiplied by a scalar then each element of the matrix is multiplied by the same scalar.
Calculation:
Add the matrix A and Bas follows:
Thus, the value of
Now, by graphing utility of matrix capability,
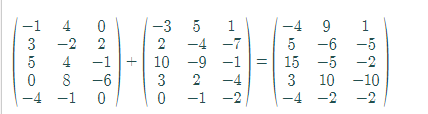
Hence, the result is verified.
(b)
To find
(b)
Answer to Problem 18E
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The matrices
Concept used:
Operations like addition and subtraction of matrices are only possible when they are of same dimension.
Dimension of matrix with a rows and b columns is given by
If a matrix is multiplied by a scalar then each element of the matrix is multiplied by the same scalar.
Calculation:
Subtract the matrices A and Bas follows:
Thus, the value of
Now, by graphing utility of matrix capability,
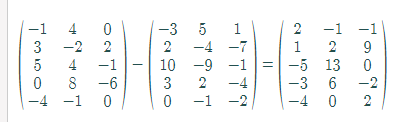
Hence, the result is verified.
(c)
To find
(c)
Answer to Problem 18E
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The matrix is
Concept used:
Operations like addition and subtraction of matrices are only possible when they are of same dimension.
Dimension of matrix with a rows and b columns is given by
If a matrix is multiplied by a scalar then each element of the matrix is multiplied by the same scalar.
Calculation:
Multiply all the elements of matrix A by 3 as follows:
Thus, the value of
Now, by graphing utility of matrix capability,
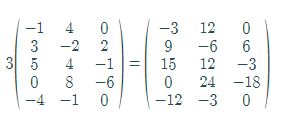
Hence, the result is verified.
(d)
To find
(d)
Answer to Problem 18E
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The matrices
Concept used:
Operations like addition and subtraction of matrices are only possible when they are of same dimension.
Dimension of matrix with a rows and b columns is given by
If a matrix is multiplied by a scalar then each element of the matrix is multiplied by the same scalar.
Calculation:
The value of
Thus, the value of
Now, by graphing utility of matrix capability,
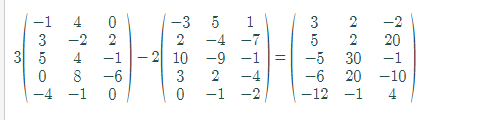
Hence, the result is verified.
Chapter 7 Solutions
PRECALCULUS W/LIMITS:GRAPH.APPROACH(HS)
- Find the tangent line approximation 7 to the graph of f at the given point. T(x) = f(x) = csc(x), (8, csc(8)) Complete the table. (Round your answers to four decimal places.) x f(x) T(x) 7.9 7.99 8 8.01 8.1arrow_forwardCan you solve it numerical methodarrow_forwardUse the information to find and compare Ay and dy. (Round your answers to four decimal places.) Function x-Value Differential of x Ду = dy = y = x² + 2 x = -4 Ax = dx = 0.01arrow_forward
- Calculus lll May I please have the statements with blank lines completed; furthermore, may I please have the text box completed? Thank youarrow_forwardCalculus lll May I please have the statements completed for the following text lines and box? Thank you so much,arrow_forwardCalculus lll May I please have the solution for the following exercise? Thank you so mucharrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





