
Concept explainers
a.
To use tables to give a numerical argument that
a.
Answer to Problem 57E
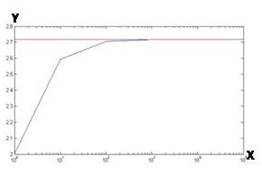
| x | y |
| 1 | 2 |
| 10 | 2.5937 |
| 100 | 2.7048 |
| 1000 | 2.7169 |
| 10000 | 2.7181 |
| 100000 | 2.7183 |
Graph is,
Explanation of Solution
Given Information: The function is,
Calculation:
As per the given problem,
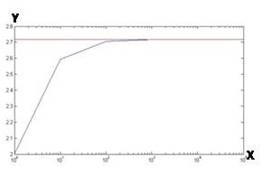
| x | y |
| 1 | 2 |
| 10 | 2.5937 |
| 100 | 2.7048 |
| 1000 | 2.7169 |
| 10000 | 2.7181 |
| 100000 | 2.7183 |
Graph is,
b.
For several different values of r, give numerical and graphical evidence that
b.
Answer to Problem 57E
The annuity will run out of fund at
Explanation of Solution
Given Information: The function is,
Calculation:
As per the given problem
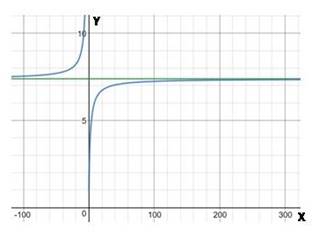
If
| 10 | 6.1917 |
| 100 | 7.2446 |
| 1000 | 7.3743 |
| 10000 | 7.3876 |
| 100000 | 7.389 |
| 1000000 | 7.3891 |
| 10000000 | 7.3891 |
To verify the limit graphically, input
If
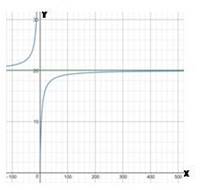
| 10 | 13.786 |
| 100 | 19.219 |
| 1000 | 19.996 |
| 10000 | 20.077 |
| 100000 | 20.085 |
| 1000000 | 20.086 |
| 10000000 | 20.086 |
To verify the limit graphically, input
If
| 10 | 1.6289 |
| 100 | 1.6467 |
| 1000 | 1.6485 |
| 10000 | 1.6487 |
| 100000 | 1.6487 |
To verify the limit graphically, input
c.
Explain why compounding interest over smaller and smaller periods of time leads to the concept of interest compounded continuously.
c.
Answer to Problem 57E
See calculation part.
Explanation of Solution
Given Information: Compounding interest over smaller and smaller periods of time leads to the concept of interest compounded continuously.
Calculation:
As per the given problem,
The compound interest formula is
Chapter 7 Solutions
Calculus 2012 Student Edition (by Finney/Demana/Waits/Kennedy)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
- Points z1 and z2 are shown on the graph.z1 is at (4 real,6 imaginary), z2 is at (-5 real, 2 imaginary)Part A: Identify the points in standard form and find the distance between them.Part B: Give the complex conjugate of z2 and explain how to find it geometrically.Part C: Find z2 − z1 geometrically and explain your steps.arrow_forwardA polar curve is represented by the equation r1 = 7 + 4cos θ.Part A: What type of limaçon is this curve? Justify your answer using the constants in the equation.Part B: Is the curve symmetrical to the polar axis or the line θ = pi/2 Justify your answer algebraically.Part C: What are the two main differences between the graphs of r1 = 7 + 4cos θ and r2 = 4 + 4cos θ?arrow_forwardA curve, described by x2 + y2 + 8x = 0, has a point A at (−4, 4) on the curve.Part A: What are the polar coordinates of A? Give an exact answer.Part B: What is the polar form of the equation? What type of polar curve is this?Part C: What is the directed distance when Ø = 5pi/6 Give an exact answer.arrow_forward
- New folder 10. Find the area enclosed by the loop of the curve (1- t², t-t³)arrow_forward1. Graph and find the corresponding Cartesian equation for: t X== y = t +1 2 te(-∞, ∞) 42,369 I APR 27 F5 3 MacBook Air stv A Aa T 4 DIIarrow_forwardMiddle School GP... Echo home (1) Addition and su... Google Docs Netflix Netflix New folder 9. Find the area enclosed by x = sin²t, y = cost and the y-axis.arrow_forward
- 2. Graph and find the corresponding Cartesian equation for: (4 cos 0,9 sin 0) θ ε [0, 2π) 42,369 I APR 27 3 MacBook Air 2 tv A Aaarrow_forward30 Page< 3. Find the equation of the tangent line for x = 1+12, y = 1-3 at t = 2 42,369 APR A 27 M . tv NA 1 TAGN 2 Aa 7 MacBook Air #8arrow_forwardEvaluate the following integrals as they are writtenarrow_forward
- Calculus lll May I please have the blank lines completed, and final statement defined as a result? Thank you for the support!arrow_forward3. Consider the polynomial equation 6-iz+7z² - iz³ +z = 0 for which the roots are 3i, -2i, -i, and i. (a) Verify the relations between this roots and the coefficients of the polynomial. (b) Find the annulus region in which the roots lie.arrow_forwardForce with 800 N and 400 N are acting on a machine part at 30° and 60°, respectively with the positive x axisarrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





