
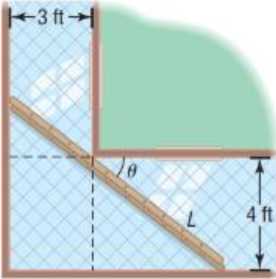
Carrying a Ladder around a Corner Two hallways, one of width 3 feet, the other of width 4 feet, meet at a right angle. See the illustration. It can be shown that the length of the ladder as a function of is .
a. In calculus, you will be asked to find the length of the longest ladder that can turn the comer by solving the equation Solve this equation for .
b. What is the length of the longest ladder that can be carried around the corner?
c. Graph , , and find the angle that minimizes the length .
d. Compare the result with the one found in part (a). Explain why the two answers are the same.
To find:
a. In calculus, you will be asked to find the length of the longest ladder that can turn the corner by solving the equation.
Solve this equation for .
Answer to Problem 108AYU
a.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Two hallways, one of width 3 feet, the other of width 4 feet, meet at a right angle. See the illustration. It can be shown that the length of the ladder as a function of is,
Calculation:
a.
Multiply by
To find:
b. What is the length of the longest ladder that can be carried around the corner?
Answer to Problem 108AYU
b. feet.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Two hallways, one of width 3 feet, the other of width 4 feet, meet at a right angle. See the illustration. It can be shown that the length of the ladder as a function of is,
Calculation:
b. The maximum happens when sub that back into the original equation to get the ladder length. Here is where you would use your calculator to get decimal approximations.
Without showing a crap-load of work, I can conclude that the maximum amount of "ladder" than can fit is exactly , which is approximately feet.
To find:
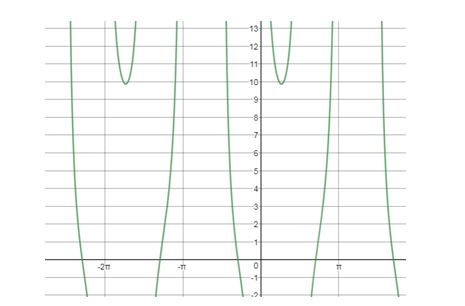
c. Graph and find the angle that minimizes the length .
Answer to Problem 108AYU
c.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
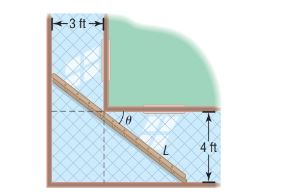
Two hallways, one of width 3 feet, the other of width 4 feet, meet at a right angle. See the illustration. It can be shown that the length of the ladder as a function of is,
Calculation:
c.

Minimum length is feet
To find:
d. Compare the result with the one found in part (a). Explain why the two answers are the same.
Answer to Problem 108AYU
d. Two answers are same, since both are angle of inclination.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Two hallways, one of width 3 feet, the other of width 4 feet, meet at a right angle. See the illustration. It can be shown that the length of the ladder as a function of is,
Calculation:
d. Two answers are same, since both are angle of inclination.
Chapter 7 Solutions
Precalculus Enhanced with Graphing Utilities
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Elementary Statistics
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Precalculus
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- 3. Consider the initial value problem 9y" +12y' + 4y = 0, y(0) = a>0: y′(0) = −1. Solve the problem and find the value of a such that the solution of the initial value problem is always positive.arrow_forward5. Euler's equation. Determine the values of a for which all solutions of the equation 5 x²y" + axy' + y = 0 that have the form (A + B log x) x* or Ax¹¹ + Bä” tend to zero as a approaches 0.arrow_forward4. Problem on variable change. The purpose of this problem is to perform an appropriate change of variables in order to reduce the problem to a second-order equation with constant coefficients. ty" + (t² − 1)y'′ + t³y = 0, 0arrow_forward4. Some psychologists contend that the number of facts of a certain type that are remembered after t hours is given by f(t)== 90t 951-90 Find the rate at which the number of facts remembered is changing after 1 hour and after 10 hours. Interpret.arrow_forward12:05 MA S 58 58. If f(x) = ci.metaproxy.org 25 2xon [0, 10] and n is a positive integer, then there is some Riemann sum Sthat equals the exact area under the graph of ƒ from x = Oto x = 10. 59. If the area under the graph of fon [a, b] is equal to both the left sum L, and the right sum Rfor some positive integer n, then fis constant on [a, b]. 60. If ƒ is a decreasing function on [a, b], then the area under the graph of fis greater than the left sum Land less than the right sum R₂, for any positive integer n. Problems 61 and 62 refer to the following figure showing two parcels of land along a river: River Parcel 2 Parcel 1 h(x) 500 ft 1,000 ft. Figure for 61 and 62 61. You want to purchase both parcels of land shown in the figure and make a quick check on their combined area. There is no equation for the river frontage, so you use the average of the left and right sums of rectangles covering the area. The 1,000-foot baseline is divided into 10 equal parts. At the end of each…arrow_forwardIf a snowball melts so that its surface area decreases at a rate of 10 cm²/min, find the rate (in cm/min) at which the diameter decreases when the diameter is 12 cm. (Round your answer to three decimal places.) cm/minarrow_forward1) let X: N R be a sequence and let Y: N+R be the squence obtained from x by di scarding the first meN terms of x in other words Y(n) = x(m+h) then X converges to L If and only is y converges to L- 11) let Xn = cos(n) where nyo prove D2-1 that lim xn = 0 by def. h→00 ii) prove that for any irrational numbers ther exsist asquence of rational numbers (xn) converg to S.arrow_forward4.2 Product and Quotient Rules 1. 9(x)=125+1 y14+2 Use the product and/or quotient rule to find the derivative of each function. a. g(x)= b. y (2x-3)(x-1) c. y== 3x-4 √xarrow_forward4.2 Product and Quotient Rules 1. Use the product and/or quotient rule to find the derivative of each function. 2.5 a. g(x)=+1 y14+2 √x-1) b. y=(2x-3)(x-:arrow_forward3. The total profit (in dollars) from selling x watches is P(x)=0.52x²-0.0002x². Find and interpret the following. a) P(100) b) P'(100)arrow_forward3. Find the slope and the equation of the tangent line to the graph of the given function at the given value of x. -4 f(x)=x-x³;x=2arrow_forward2. Find the equation of the tangent line to the graph of the given function at the given point. f(x)=(x+3)(2x²-6) at (1,-16)arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





