
Problems 79 and 80 require the following discussion: When granular materials are allowed to fall freely, they form conical (cone-shaped) piles. The naturally occurring angle of slope, measured from the horizontal, at which the loose material comes to rest is called the angle of repose and varies for different materials. The angle of repose is related to the height and base radius of the conical pile by the equation . See the illustration.
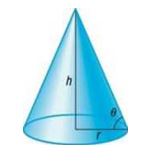
Angle of Repose: Bunker Sand The steepness of sand bunkers on a golf course is affected by the angle of repose of the sand (a larger angle of repose allows for steeper bunkers). A freestanding pile of loose sand from a United States Golf Association (USGA) bunker had a height of 4 feet and a base diameter of approximately feet.
(a) Find the angle of repose for USGA bunker sand.
(b) What is the height of such a pile if the diameter of the base is 8 feet?
(c) A 6-foot-high pile of loose Tour Grade 50/50 sand has a base diameter of approximately feet. Which type of sand (USGA or Tour Grade 50/50) would be better suited for steep bunkers?
To find:
A. The angle of repose for USGA bunker sand.
Answer to Problem 80AYU
Solution:
A. The angle of repose for the USGA bunker sand .
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Height of the freestanding pile of loose sand from USGA bunker .
Base diameter of the freestanding pile of loose sand from USGA bunker .
Radius of the freestanding pile of loose sand from USGA bunker .
Formula used:
The angle of repose .
Calculation:
To find , we need to find cos , because has the same range as except where undefined.
The angle of repose .
Here, .
Both and are positive, therefore lies in the I quadrant.
Equation of the circle .
Where .
Using the formula,
The angle of repose θ for the USGA bunker sand .
To find:
b. The height of conical USGA bunker sand pile.
Answer to Problem 80AYU
Solution:
b. The height of conical USGA bunker sand pile .
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The base diameter of conical pile .
Radius of the conical pile .
From 80 (a),
Angle of repose .
Formula used:
Calculation:
Using the formula,
Height of conical sand pile .
To find:
c. If USGA sand pile or tour grade sand is better choice for steep bunkers.
Answer to Problem 80AYU
Solution:
Angle of repose for tour grade sand is higher than USGA sand pile.
Tour grade sand is better choice for steep bunkers than USGA sand pile.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The height of the conical Tour grade sand pile .
Base diameter of conical Tour grade sand pile .
Base radius of conical Tour grade sand pile .
Formula used:
The angle of repose .
Calculation:
To find , we need to find cos , because has the same range as except where undefined.
The angle of repose .
Here, .
Both and are positive, therefore lies in the I quadrant.
Equation of the circle .
Where .
Using the formula,
The angle of repose for the tour grade sand .
The angle of repose for the USGA bunker sand .
Angle of repose for tour grade sand is higher than USGA sand pile.
Tour grade sand is better choice for steep bunkers than USGA sand pile.
Chapter 7 Solutions
Precalculus Enhanced with Graphing Utilities
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
- Solve please thanks!arrow_forwardSolve please and thank youarrow_forwardAccording to Newton's law of universal gravitation, the force F between two bodies of constant mass GmM m and M is given by the formula F = , where G is the gravitational constant and d is the d² distance between the bodies. a. Suppose that G, m, and M are constants. Find the rate of change of force F with respect to distance d. F' (d) 2GmM b. Find the rate of change of force F with gravitational constant G = 6.67 × 10-¹¹ Nm²/kg², on two bodies 5 meters apart, each with a mass of 250 kilograms. Answer in scientific notation, rounding to 2 decimal places. -6.67x10 N/m syntax incomplete.arrow_forward
- Solve please and thank youarrow_forwardmv2 The centripetal force of an object of mass m is given by F (r) = rotation and r is the distance from the center of rotation. ' where v is the speed of r a. Find the rate of change of centripetal force with respect to the distance from the center of rotation. F(r) b. Find the rate of change of centripetal force of an object with mass 500 kilograms, velocity of 13.86 m/s, and a distance from the center of rotation of 300 meters. Round to 2 decimal places. N/m (or kg/s²) F' (300)arrow_forwardSolve work shown please and thanks!arrow_forward
- Given the following graph of the function y = f(x) and n = = 6, answer the following questions about the area under the curve from x graph to enlarge it.) 1 (Round your answer to within two decimal places if necessary, but do not round until your final computation.) a. Use the Trapezoidal Rule to estimate the area. Estimate: T6 G b. Use Simpson's Rule to estimate the area. Estimate: S6 - ID = 0 to x = 6. (Click on aarrow_forward"Solve the following differential equation using the Operator Method and the Determinant Method:" Solve by dr no ai """'+3y"" + 3y+y=arrow_forward(4,4) M -4 2 2 -4 (-4,-4) 4 8 10 12 (8,-4) (12,-4) Graph of f The figure shows the graph of a piecewise-linear function f. For −4≤x≤12, the function g is x defined by g(x) = √ƒ (t)dt . . Find the value of g(6). Find the value of g'(6). |arrow_forward
- PREVIOUS ANSWERS ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER Find the derivative of the function. f'(x) = X x + √3x f(x) = 3x-5 (3√√3x+11√√x+5√3 2√√x (3x-5)² Need Help? Read It SUBMIT ANSWERarrow_forwardPREVIOUS ANSWERS ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE A Find the derivative of the function and evaluate f'(x) at the given val f(x) = (√√√x + 3x) (x3/2 - x); x = 1 f'(x) = 9x 412 (12x (13) 2 - 4x-3√√√x f'(1) = 2 Need Help? Read It Watch It SUBMIT ANSWERarrow_forwardConsider the following functions. g(x) = x + √3x h(x) = 3x-5 x + √3x f(x) = = 3x-5 Find the derivative of each function. g'(x) h'(x) = = f'(x) = 3 = +1 2√3x 3 (3√3x + 10√√x +5√√√3 2√√x (3x-5)² Need Help? Read It SUBMIT ANSWERarrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





