
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
7th Edition
ISBN: 8220100257063
Author: BEER
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 7.2, Problem 64P
The Mohr's circle shown corresponds to the state of stress given in Fig. 7.5a and b. Noting that σx’ = OC + (CX') cos (2θp – 2θ) and that τx’y’ = (CX') sin (2θp – 2θ), derive the expressions for σx’ and τx’y’ given in Eqs. (7.5) and (7.6), respectively. [Hint: Use sin (A + B) = sin A cos B + cos A sin B and cos (A + B) = cos A cos B – sin A sin B.]
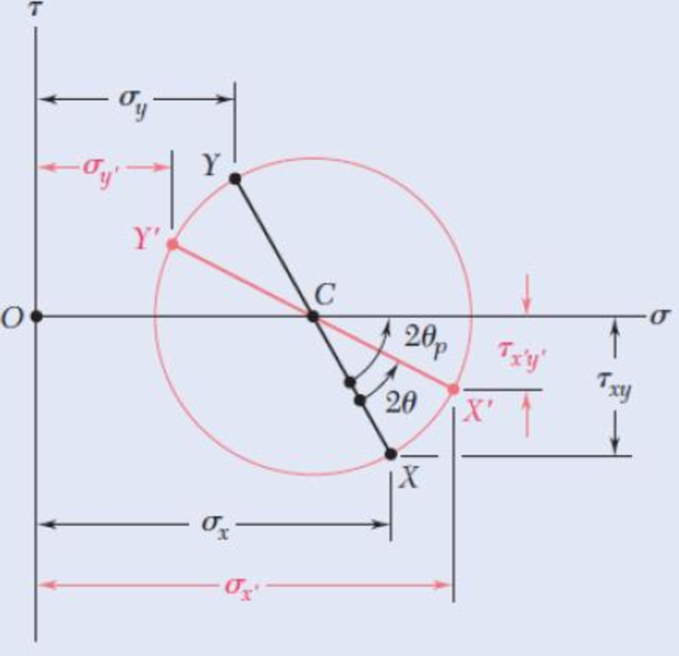
Fig. P7.64
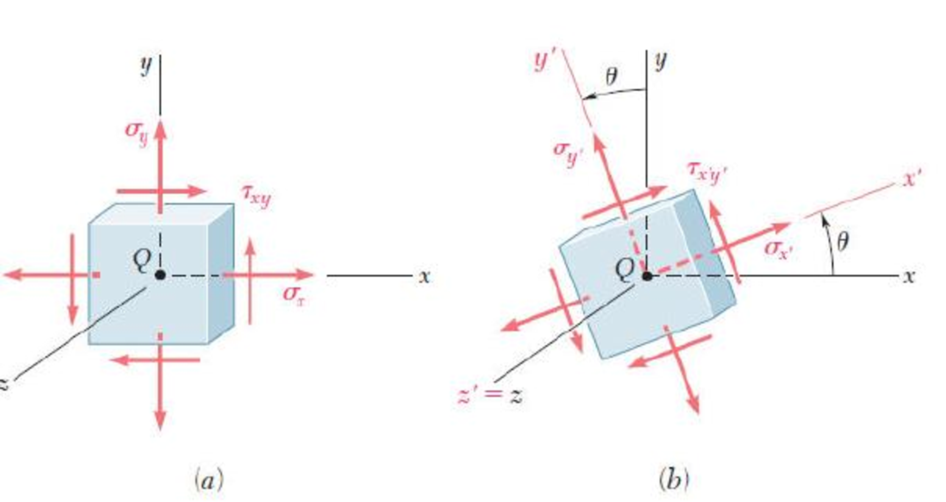
Fig. 7.5 (repeated) State of plane stress: (a) referred to {xyz}, (b) referred to {x’y’z’}.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
my ID# 016948724. Please solve this problem step by step
My ID# 016948724 please find the forces for Fx=0: fy=0: fz=0: please help me to solve this problem step by step
My ID# 016948724 please solve the proble step by step find the forces fx=o: fy=0; fz=0; and find shear moment and the bending moment diagran please draw the diagram for the shear and bending moment
Chapter 7 Solutions
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
Ch. 7.1 - 7.1 through 7.4 For the given state of stress,...Ch. 7.1 - 7.1 through 7.4 For the given state of stress,...Ch. 7.1 - 7.1 through 7.4 For the given state of stress,...Ch. 7.1 - 7.1 through 7.4 For the given state of stress,...Ch. 7.1 - 7.5 through 7.8 For the given state of stress,...Ch. 7.1 - 7.5 through 7.8 For the given state of stress,...Ch. 7.1 - 7.5 through 7.8 For the given state of stress,...Ch. 7.1 - 7.5 through 7.8 For the given state of stress,...Ch. 7.1 - 7.9 through 7.12 For the given state of stress,...Ch. 7.1 - 7.9 through 7.12 For the given state of stress,...
Ch. 7.1 - 7.9 through 7.12 For the given state of stress,...Ch. 7.1 - 7.9 through 7.12 For the given state of stress,...Ch. 7.1 - 7.13 through 7.16 For the given state of stress,...Ch. 7.1 - 7.13 through 7.16 For the given state of stress,...Ch. 7.1 - 7.13 through 7.16 For the given state of stress,...Ch. 7.1 - 7.13 through 7.16 For the given state of stress,...Ch. 7.1 - 7.17 and 7.18 The grain of a wooden member forms...Ch. 7.1 - 7.17 and 7.18 The grain of a wooden member forms...Ch. 7.1 - Two wooden members of 80 120-mm uniform...Ch. 7.1 - Two wooden members of 80 120-mm uniform...Ch. 7.1 - The centric force P is applied to a short post as...Ch. 7.1 - Two members of uniform cross section 50 80 mm are...Ch. 7.1 - The axle of an automobile is acted upon by the...Ch. 7.1 - A 400-lb vertical force is applied at D to a gear...Ch. 7.1 - A mechanic uses a crowfoot wrench to loosen a bolt...Ch. 7.1 - The steel pipe AB has a 102-mm outer diameter and...Ch. 7.1 - For the state of plane stress shown, determine the...Ch. 7.1 - For the state of plane stress shown, determine (a)...Ch. 7.1 - For the state of plane stress shown, determine (a)...Ch. 7.1 - Determine the range of values of x for which the...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Probs. 7.5 and 7.9, using Mohr's circle. 7.5...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Probs. 7.7 and 7.11, using Mohrs circle. 7.5...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.10, using Mohrs circle. 7.9 through...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.12, using Mohr's circle. 7.9 through...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.13, using Mohr's circle. 7.13...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.14, using Mohr's circle. 7.13...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.15, using Mohr's circle. 7.13...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.16, using Mohr's circle. 7.13...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.17, using Mohr's circle. 7.17 and...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.18, using Mohr's circle. 7.17 and...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.19, using Mohr's circle. 7.19 Two...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.20, using Mohr's circle. 7.20 Two...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.21, using Mohrs circle. 7.21 The...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.22, using Mohrs circle. 7.22 Two...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.23, using Mohr's circle. 7.23 The...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.24, using Mohr's circle 7.24 A...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.25, using Mohrs circle. 7.25 A...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.26, using Mohrs circle. 7.26 The...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.27, using Mohr's circle. 7.27 For...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.28, using Mohrs circle. 7.28 For the...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.29, using Mohr's circle. 7.29 For...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.30, using Mohrs circle. 7.30...Ch. 7.2 - Solve Prob. 7.29, using Mohr's circle and assuming...Ch. 7.2 - 7.54 and 7.55 Determine the principal planes and...Ch. 7.2 - 7.54 and 7.55 Determine the principal planes and...Ch. 7.2 - 7.56 and 7.57 Determine the principal planes and...Ch. 7.2 - 7.56 and 7.57 Determine the principal planes and...Ch. 7.2 - For the element shown, determine the range of...Ch. 7.2 - For the element shown, determine the range of...Ch. 7.2 - For the state of stress shown, determine the range...Ch. 7.2 - For the state of stress shown, determine the range...Ch. 7.2 - For the state of stress shown, determine the range...Ch. 7.2 - For the state of stress shown, it is known that...Ch. 7.2 - The Mohr's circle shown corresponds to the state...Ch. 7.2 - (a) Prove that the expression xy 2xywhere x,...Ch. 7.5 - For the state of plane stress shown, determine the...Ch. 7.5 - For the state of plane stress shown, determine the...Ch. 7.5 - For the state of stress shown, determine the...Ch. 7.5 - For the state of stress shown, determine the...Ch. 7.5 - 7.70 and 7.71 For the state of stress shown,...Ch. 7.5 - 7.70 and 7.71 For the state of stress shown,...Ch. 7.5 - 7.72 and 7.73 For the state of stress shown,...Ch. 7.5 - 7.72 and 7.73 For the state of stress shown,...Ch. 7.5 - For the state of stress shown, determine the value...Ch. 7.5 - For the state of stress shown, determine the value...Ch. 7.5 - Prob. 76PCh. 7.5 - For the state of stress shown, determine two...Ch. 7.5 - For the state of stress shown, determine the range...Ch. 7.5 - Prob. 79PCh. 7.5 - Prob. 80PCh. 7.5 - The state of plane stress shown occurs in a...Ch. 7.5 - Prob. 82PCh. 7.5 - The state of plane stress shown occurs in a...Ch. 7.5 - Solve Prob. 7.83, using the...Ch. 7.5 - The 38-mm-diameter shaft AB is made of a grade of...Ch. 7.5 - Solve Prob. 7.85, using the...Ch. 7.5 - The 1.5-in.-diameter shaft AB is made of a grade...Ch. 7.5 - Prob. 88PCh. 7.5 - Prob. 89PCh. 7.5 - Prob. 90PCh. 7.5 - Prob. 91PCh. 7.5 - Prob. 92PCh. 7.5 - Prob. 93PCh. 7.5 - Prob. 94PCh. 7.5 - Prob. 95PCh. 7.5 - Prob. 96PCh. 7.5 - Prob. 97PCh. 7.6 - A spherical pressure vessel has an outer diameter...Ch. 7.6 - A spherical gas container having an inner diameter...Ch. 7.6 - The maximum gage pressure is known to be 1150 psi...Ch. 7.6 - Prob. 101PCh. 7.6 - Prob. 102PCh. 7.6 - A basketball has a 300-mm outer diameter and a...Ch. 7.6 - The unpressurized cylindrical storage tank shown...Ch. 7.6 - Prob. 105PCh. 7.6 - Prob. 106PCh. 7.6 - Prob. 107PCh. 7.6 - Prob. 108PCh. 7.6 - Prob. 109PCh. 7.6 - Prob. 110PCh. 7.6 - Prob. 111PCh. 7.6 - The cylindrical portion of the compressed-air tank...Ch. 7.6 - Prob. 113PCh. 7.6 - Prob. 114PCh. 7.6 - Prob. 115PCh. 7.6 - Square plates, each of 0.5-in. thickness, can be...Ch. 7.6 - The pressure tank shown has a 0.375-in. wall...Ch. 7.6 - Prob. 118PCh. 7.6 - Prob. 119PCh. 7.6 - A pressure vessel of 10-in. inner diameter and...Ch. 7.6 - Prob. 121PCh. 7.6 - A torque of magnitude T = 12 kN-m is applied to...Ch. 7.6 - The tank shown has a 180-mm inner diameter and a...Ch. 7.6 - The compressed-air tank AB has a 250-rnm outside...Ch. 7.6 - In Prob. 7.124, determine the maximum normal...Ch. 7.6 - Prob. 126PCh. 7.6 - Prob. 127PCh. 7.9 - 7.128 through 7.131 For the given state of plane...Ch. 7.9 - 7.128 through 7.131 For the given state of plane...Ch. 7.9 - Prob. 130PCh. 7.9 - 7.128 through 7.131 For the given state of plane...Ch. 7.9 - Prob. 132PCh. 7.9 - Prob. 133PCh. 7.9 - Prob. 134PCh. 7.9 - 7.128 through 7.131 For the given state of plane...Ch. 7.9 - 7.136 through 7.139 The following state of strain...Ch. 7.9 - Prob. 137PCh. 7.9 - Prob. 138PCh. 7.9 - Prob. 139PCh. 7.9 - Prob. 140PCh. 7.9 - 7.140 through 7.143 For the given state of plane...Ch. 7.9 - Prob. 142PCh. 7.9 - Prob. 143PCh. 7.9 - Prob. 144PCh. 7.9 - The strains determined by the use of the rosette...Ch. 7.9 - Prob. 146PCh. 7.9 - Prob. 147PCh. 7.9 - Show that the sum of the three strain measurements...Ch. 7.9 - Prob. 149PCh. 7.9 - Prob. 150PCh. 7.9 - Solve Prob. 7.150, assuming that the rosette at...Ch. 7.9 - Prob. 152PCh. 7.9 - Prob. 153PCh. 7.9 - Prob. 154PCh. 7.9 - Prob. 155PCh. 7.9 - The given state of plane stress is known to exist...Ch. 7.9 - The following state of strain has been determined...Ch. 7 - A steel pipe of 12-in. outer diameter is...Ch. 7 - Two steel plates of uniform cross section 10 80...Ch. 7 - Prob. 160RPCh. 7 - Prob. 161RPCh. 7 - For the state of stress shown, determine the...Ch. 7 - For the state of stress shown, determine the value...Ch. 7 - The state of plane stress shown occurs in a...Ch. 7 - The compressed-air tank AB has an inner diameter...Ch. 7 - For the compressed-air tank and loading of Prob....Ch. 7 - Prob. 167RPCh. 7 - Prob. 168RPCh. 7 - Prob. 169RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- My ID#016948724 please solve this problems and show me every step clear to follow pleasearrow_forwardMy ID# 016948724arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward
- Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward[Q2]: The cost information supplied by the cost accountant is as follows:Sales 20,00 units, $ 10 per unitCalculate the (a/ newsale guantity and (b) new selling price to earn the sameVariable cost $ 6 per unit, Fixed Cost $ 30,000, Profit $ 50,000profit ifi) Variable cost increases by $ 2 per unitil) Fixed cost increase by $ 10,000Ili) Variable cost increase by $ 1 per unit and fixed cost reduces by $ 10,000arrow_forward
- can you please help me perform Visual Inspection and Fractography of the attatched image: Preliminary examination to identify the fracture origin, suspected fatigue striation, and corrosion evidences.arrow_forwardcan you please help[ me conduct Causal Analysis (FTA) on the scenario attatched: FTA diagram which is a fault tree analysis diagram will be used to gain an overview of the entire path of failure from root cause to the top event (i.e., the swing’s detachment) and to identify interactions between misuse, material decay and inspection errors.arrow_forwardhi can you please help me in finding the stress intensity factor using a k-calcluator for the scenario attathced in the images.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Understanding Stress Transformation and Mohr's Circle; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_DH3546mSCM;License: Standard youtube license