
THERMODYNAMICS-SI ED. EBOOK >I<
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781307573022
Author: CENGEL
Publisher: MCG/CREATE
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 7.13, Problem 179RP
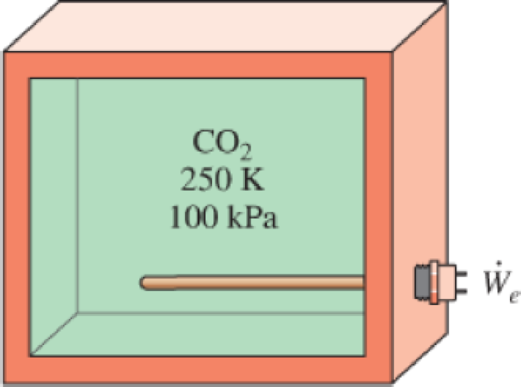
A 0.8-m3 rigid tank contains carbon dioxide (CO2) gas at 250 K and 100 kPa. A 500-W electric resistance heater placed in the tank is now turned on and kept on for 40 min, after which the pressure of CO2 is measured to be 175 kPa. Assuming the surroundings to be at 300 K and using constant specific heats, determine (a) the final temperature of CO2, (b) the net amount of heat transfer from the tank, and (c) the entropy generation during this process.
FIGURE P7–179
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A spring package with two springs and an external force, 200N. The short spring has a loin of 35 mm. Constantly looking for spring for short spring so that total compression is 35 mm (d). Known values: Long spring: Short spring:C=3.98 N/mm Lo=65mmLo=87.4mmF=c·fTotal compression is same for both spring. 200 = (3.98(c1) × 35) + (c₂ × 35)
200 = 139.3 + 35c₂
200 - 139.3 = 35c₂
60.7 = 35c₂
c₂ = 60.7/35
Short spring (c₂) = 1.73 N/mm
According to my study book, the correct answer is 4.82N/mm
What is wrong with the calculating?
What is the reason for this composition?
Homework: ANOVA Table for followed design
B
AB
Dr
-1
-1
1
(15.18,12)
1
-1
-1
(45.48.51)
-1
1
-1
(25,28,19)
1
1
(75.75,81)
Chapter 7 Solutions
THERMODYNAMICS-SI ED. EBOOK >I<
Ch. 7.13 - Does a cycle for which Q 0 violate the Clausius...Ch. 7.13 - Does the cyclic integral of heat have to be zero...Ch. 7.13 - Is a quantity whose cyclic integral is zero...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 4PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 5PCh. 7.13 - How do the values of the integral 12Q/T compare...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 7PCh. 7.13 - The entropy of a hot baked potato decreases as it...Ch. 7.13 - When a system is adiabatic, what can be said about...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 7.13 - A pistoncylinder device contains helium gas....Ch. 7.13 - A pistoncylinder device contains nitrogen gas....Ch. 7.13 - A pistoncylinder device contains superheated...Ch. 7.13 - The entropy of steam will (increase, decrease,...Ch. 7.13 - During a heat transfer process, the entropy of a...Ch. 7.13 - Steam is accelerated as it flows through an actual...Ch. 7.13 - Heat is transferred at a rate of 2 kW from a hot...Ch. 7.13 - A completely reversible air conditioner provides...Ch. 7.13 - Heat in the amount of 100 kJ is transferred...Ch. 7.13 - In Prob. 719, assume that the heat is transferred...Ch. 7.13 - During the isothermal heat addition process of a...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 22PCh. 7.13 - During the isothermal heat rejection process of a...Ch. 7.13 - Air is compressed by a 40-kW compressor from P1 to...Ch. 7.13 - Refrigerant-134a enters the coils of the...Ch. 7.13 - A rigid tank contains an ideal gas at 40C that is...Ch. 7.13 - A rigid vessel is filled with a fluid from a...Ch. 7.13 - A rigid vessel filled with a fluid is allowed to...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 29PCh. 7.13 - One lbm of R-134a is expanded isentropically in a...Ch. 7.13 - Two lbm of water at 300 psia fill a weighted...Ch. 7.13 - A well-insulated rigid tank contains 3 kg of a...Ch. 7.13 - Using the relation ds = (Q/T)int rev for the...Ch. 7.13 - The radiator of a steam heating system has a...Ch. 7.13 - A rigid tank is divided into two equal parts by a...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 36PCh. 7.13 - An insulated pistoncylinder device contains 5 L of...Ch. 7.13 - Onekg of R-134a initially at 600 kPa and 25C...Ch. 7.13 - Refrigerant-134a is expanded isentropically from...Ch. 7.13 - Refrigerant-134a at 320 kPa and 40C undergoes an...Ch. 7.13 - A rigid tank contains 5 kg of saturated vapor...Ch. 7.13 - A 0.5-m3 rigid tank contains refrigerant-134a...Ch. 7.13 - Steam enters a steady-flow adiabatic nozzle with a...Ch. 7.13 - Steam enters an adiabatic diffuser at 150 kPa and...Ch. 7.13 - R-134a vapor enters into a turbine at 250 psia and...Ch. 7.13 - Refrigerant-134a enters an adiabatic compressor as...Ch. 7.13 - The compressor in a refrigerator compresses...Ch. 7.13 - An isentropic steam turbine processes 2 kg/s of...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 52PCh. 7.13 - Twokg of saturated water vapor at 600 kPa are...Ch. 7.13 - A pistoncylinder device contains 5 kg of steam at...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 55PCh. 7.13 - In Prob. 755, the water is stirred at the same...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 57PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 58PCh. 7.13 - Determine the total heat transfer for the...Ch. 7.13 - Calculate the heat transfer, in kJ/kg. for the...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 61PCh. 7.13 - An adiabatic pump is to be used to compress...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 63PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 64PCh. 7.13 - A 30-kg aluminum block initially at 140C is...Ch. 7.13 - A 50-kg copper block initially at 140C is dropped...Ch. 7.13 - A 30-kg iron block and a 40-kg copper block, both...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 69PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 70PCh. 7.13 - Can the entropy of an ideal gas change during an...Ch. 7.13 - An ideal gas undergoes a process between two...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 73PCh. 7.13 - Air is expanded from 200 psia and 500F to 100 psia...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 75PCh. 7.13 - Air is expanded isentropically from 100 psia and...Ch. 7.13 - Which of the two gaseshelium or nitrogenhas the...Ch. 7.13 - Which of the two gasesneon or airhas the lower...Ch. 7.13 - A 1.5-m3 insulated rigid tank contains 2.7 kg of...Ch. 7.13 - An insulated pistoncylinder device initially...Ch. 7.13 - A pistoncylinder device contains 0.75 kg of...Ch. 7.13 - A mass of 25 lbm of helium undergoes a process...Ch. 7.13 - One kg of air at 200 kPa and 127C is contained in...Ch. 7.13 - An insulated rigid tank is divided into two equal...Ch. 7.13 - Air at 27C and 100 kPa is contained in a...Ch. 7.13 - Air at 3.5 MPa and 500C is expanded in an...Ch. 7.13 - Air is compressed in a pistoncylinder device from...Ch. 7.13 - Helium gas is compressed from 90 kPa and 30C to...Ch. 7.13 - Nitrogen at 120 kPa and 30C is compressed to 600...Ch. 7.13 - Five kg of air at 427C and 600 kPa are contained...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 92PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 93PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 94PCh. 7.13 - The well-insulated container shown in Fig. P 795E...Ch. 7.13 - An insulated rigid tank contains 4 kg of argon gas...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 97PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 98PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 99PCh. 7.13 - It is well known that the power consumed by a...Ch. 7.13 - Calculate the work produced, in kJ/kg, for the...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 102PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 103PCh. 7.13 - Saturated water vapor at 150C is compressed in a...Ch. 7.13 - Liquid water at 120 kPa enters a 7-kW pump where...Ch. 7.13 - Water enters the pump of a steam power plant as...Ch. 7.13 - Consider a steam power plant that operates between...Ch. 7.13 - Saturated refrigerant-134a vapor at 15 psia is...Ch. 7.13 - Helium gas is compressed from 16 psia and 85F to...Ch. 7.13 - Nitrogen gas is compressed from 80 kPa and 27C to...Ch. 7.13 - Describe the ideal process for an (a) adiabatic...Ch. 7.13 - Is the isentropic process a suitable model for...Ch. 7.13 - On a T-s diagram, does the actual exit state...Ch. 7.13 - Argon gas enters an adiabatic turbine at 800C and...Ch. 7.13 - Steam at 100 psia and 650F is expanded...Ch. 7.13 - Combustion gases enter an adiabatic gas turbine at...Ch. 7.13 - Steam at 4 MPa and 350C is expanded in an...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 120PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 121PCh. 7.13 - Refrigerant-134a enters an adiabatic compressor as...Ch. 7.13 - The adiabatic compressor of a refrigeration system...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 125PCh. 7.13 - Argon gas enters an adiabatic compressor at 14...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 127PCh. 7.13 - Air enters an adiabatic nozzle at 45 psia and 940F...Ch. 7.13 - An adiabatic diffuser at the inlet of a jet engine...Ch. 7.13 - Hot combustion gases enter the nozzle of a...Ch. 7.13 - The exhaust nozzle of a jet engine expands air at...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 133PCh. 7.13 - Refrigerant-134a is expanded adiabatically from...Ch. 7.13 - A frictionless pistoncylinder device contains...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 136PCh. 7.13 - Steam enters an adiabatic turbine steadily at 7...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 138PCh. 7.13 - Oxygen enters an insulated 12-cm-diameter pipe...Ch. 7.13 - Water at 20 psia and 50F enters a mixing chamber...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 141PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 142PCh. 7.13 - In a dairy plant, milk at 4C is pasteurized...Ch. 7.13 - Steam is to be condensed in the condenser of a...Ch. 7.13 - An ordinary egg can be approximated as a...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 146PCh. 7.13 - In a production facility, 1.2-in-thick, 2-ft 2-ft...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 148PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 149PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 150PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 151PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 152PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 153PCh. 7.13 - Liquid water at 200 kPa and 15C is heated in a...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 155PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 157PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 158PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 159PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 160PCh. 7.13 - The compressed-air requirements of a plant are met...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 162PCh. 7.13 - The space heating of a facility is accomplished by...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 164PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 165PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 166PCh. 7.13 - Prob. 167RPCh. 7.13 - A refrigerator with a coefficient of performance...Ch. 7.13 - What is the minimum internal energy that steam can...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 170RPCh. 7.13 - What is the maximum volume that 3 kg of oxygen at...Ch. 7.13 - A 100-lbm block of a solid material whose specific...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 173RPCh. 7.13 - A pistoncylinder device initially contains 15 ft3...Ch. 7.13 - A pistoncylinder device contains steam that...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 176RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 177RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 178RPCh. 7.13 - A 0.8-m3 rigid tank contains carbon dioxide (CO2)...Ch. 7.13 - Air enters the evaporator section of a window air...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 181RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 182RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 183RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 184RPCh. 7.13 - Helium gas is throttled steadily from 400 kPa and...Ch. 7.13 - Determine the work input and entropy generation...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 187RPCh. 7.13 - Reconsider Prob. 7187. Determine the change in the...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 189RPCh. 7.13 - Air enters a two-stage compressor at 100 kPa and...Ch. 7.13 - Three kg of helium gas at 100 kPa and 27C are...Ch. 7.13 - Steam at 6 MPa and 500C enters a two-stage...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 193RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 194RPCh. 7.13 - Refrigerant-134a enters a compressor as a...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 196RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 197RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 198RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 199RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 200RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 201RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 202RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 203RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 204RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 205RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 206RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 207RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 208RPCh. 7.13 - (a) Water flows through a shower head steadily at...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 211RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 212RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 213RPCh. 7.13 - Consider the turbocharger of an internal...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 215RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 216RPCh. 7.13 - A 5-ft3 rigid tank initially contains...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 218RPCh. 7.13 - Show that the difference between the reversible...Ch. 7.13 - Demonstrate the validity of the Clausius...Ch. 7.13 - Consider two bodies of identical mass m and...Ch. 7.13 - Consider a three-stage isentropic compressor with...Ch. 7.13 - Prob. 223RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 224RPCh. 7.13 - Prob. 225RPCh. 7.13 - The polytropic or small stage efficiency of a...Ch. 7.13 - Steam is condensed at a constant temperature of...Ch. 7.13 - Steam is compressed from 6 MPa and 300C to 10 MPa...Ch. 7.13 - An apple with a mass of 0.12 kg and average...Ch. 7.13 - A pistoncylinder device contains 5 kg of saturated...Ch. 7.13 - Argon gas expands in an adiabatic turbine from 3...Ch. 7.13 - A unit mass of a substance undergoes an...Ch. 7.13 - A unit mass of an ideal gas at temperature T...Ch. 7.13 - Heat is lost through a plane wall steadily at a...Ch. 7.13 - Air is compressed steadily and adiabatically from...Ch. 7.13 - Argon gas expands in an adiabatic turbine steadily...Ch. 7.13 - Water enters a pump steadily at 100 kPa at a rate...Ch. 7.13 - Air is to be compressed steadily and...Ch. 7.13 - Helium gas enters an adiabatic nozzle steadily at...Ch. 7.13 - Combustion gases with a specific heat ratio of 1.3...Ch. 7.13 - Steam enters an adiabatic turbine steadily at 400C...Ch. 7.13 - Liquid water enters an adiabatic piping system at...Ch. 7.13 - Liquid water is to be compressed by a pump whose...Ch. 7.13 - Steam enters an adiabatic turbine at 8 MPa and...Ch. 7.13 - Helium gas is compressed steadily from 90 kPa and...Ch. 7.13 - Helium gas is compressed from 1 atm and 25C to a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 20. [Ans. 9; 71.8 mm] A semi-elliptical laminated spring is made of 50 mm wide and 3 mm thick plates. The length between the supports is 650 mm and the width of the band is 60 mm. The spring has two full length leaves and five graduated leaves. If the spring carries a central load of 1600 N, find: 1. Maximum stress in full length and graduated leaves for an initial condition of no stress in the leaves. 2. The maximum stress if the initial stress is provided to cause equal stress when loaded. [Ans. 590 MPa ; 390 MPa ; 450 MPa ; 54 mm] 3. The deflection in parts (1) and (2).arrow_forwardQ6/ A helical square section spring is set inside another, the outer spring having a free length of 35 mm greater than the inner spring. The dimensions of each spring are as follows: Mean diameter (mm) Side of square section (mm) Active turns Outer Inner Spring Spring 120 70 8 7 20 15 Determine the (1) Maximum deflection of the two springs and (2) Equivalent spring rate of the two springs after sufficient load has been applied to deflect the outer spring 60 mm. Use G = 83 GN/m².arrow_forwardQ2/ The bumper springs of a railway carriage are to be made of rectangular section wire. The ratio of the longer side of the wire to its shorter side is 1.5, and the ratio of mean diameter of spring to the longer side of wire is nearly equal to 6. Three such springs are required to bring to rest a carriage weighing 25 kN moving with a velocity of 75 m/min with a maximum deflection of 200 mm. Determine the sides of the rectangular section of the wire and the mean diameter of coils when the shorter side is parallel to the axis of the spring. The allowable shear stress is not to exceed 300 MPa and G = 84 kN/mm². Q6/ A belicalarrow_forward
- 11. A load of 2 kN is dropped axially on a close coiled helical spring, from a height of 250 mm. The spring has 20 effective turns, and it is made of 25 mm diameter wire. The spring index is 8. Find the maximum shear stress induced in the spring and the amount of compression produced. The modulus of rigidity for the material of the spring wire is 84 kN/mm². [Ans. 287 MPa; 290 mm]arrow_forwardWhat is the reason for this composition?arrow_forwardHomework: ANOVA Table for followed design B AB Dr -1 -1 1 (15.18,12) 1 -1 -1 (45.48.51) -1 1 -1 (25,28,19) 1 1 (75.75,81)arrow_forward
- S B Pin 6 mm Garrow_forwardMid-Term Exam 2024/2025 Post graduate/Applied Mechanics- Metallurgy Q1/ State the type of fault in the following case, and state the structure in which it will appear. АВСАВСВАСВАСАВСАВСarrow_forwardالثانية Babakt Momentum equation for Boundary Layer S SS -Txfriction dray Momentum equation for Boundary Layer What laws are important for resolving issues 2 How to draw. 3 What's Point about this.arrow_forward
- R αι g The system given on the left, consists of three pulleys and the depicted vertical ropes. Given: ri J₁, m1 R = 2r; απ r2, J2, m₂ m1; m2; M3 J1 J2 J3 J3, m3 a) Determine the radii 2 and 3.arrow_forwardB: Solid rotating shaft used in the boat with high speed shown in Figure. The amount of power transmitted at the greatest torque is 224 kW with 130 r.p.m. Used DE-Goodman theory to determine the shaft diameter. Take the shaft material is annealed AISI 1030, the endurance limit of 18.86 kpsi and a factor of safety 1. Which criterion is more conservative? Note: all dimensions in mm. 1 AA Motor 300 Thrust Bearing Sprocket 100 9750 เอarrow_forwardQ2: The plate material of a pressure vessel is AISI 1050 QT 205 °C. The plate is rolled to a diameter of 1.2 m. The two sides of the plate are connected via a riveted joint as shown below. If the rivet material is G10500 with HB=197 and all rivet sizes M31. Find the required rivet size when the pressure vessel is subjected to an internal pressure of 500 MPa. Take safety factor = 2. 1.2m A B' A Chope olm 10.5 0.23 hopearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
The Refrigeration Cycle Explained - The Four Major Components; Author: HVAC Know It All;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zfciSvOZDUY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY