
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The Lewis formula of
Concept Introduction:
Lewis Structure: A Lewis structure shows a covalent bond as pair of electrons shared between two atoms.
Procedure to write Lewis formulas:
- 1) The symbols of the atoms that are bonded together in the molecule next to one another are arranged.
- 2) The total number of valence electrons in the molecule is calculated by adding the number of valence electrons for all the atoms in the molecules. If the species is an ion, then the charge of ion into account by adding electrons, if it is a negative ion or subtracting electrons if it is a positive ion.
- 3) A two-electron covalent bond is represented by placing a line between the atoms, which are assumed to be bonded to each other.
- 4) The remaining valence electrons as lone pairs about each atom are arranged so that the octet rule is satisfied for each other.
Formal charge (F.C): The charges that assigned to each atom in a molecule or ion by a set of arbitrary rules and don not actually represent the actual charges on the atoms are called as formal charges.
The formal charge is calculated using the formula,
The Lewis structure with zero formal charge or least separated formal charges is the preferred structure of the molecule.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electrons in
Number of valence electrons in hydrogen=
Number of valence electrons in oxygen=
Number of valence electrons in sulphur=
The total number of valence electrons is thirty-two.
One sulphur atom forms four bonds oxygen and two oxygen forms a bond with hydrogen atoms that means twelve electrons are used to form that bonds and remaining twenty electrons are used to satisfy the octet rule of atoms.
The Lewis formula is,
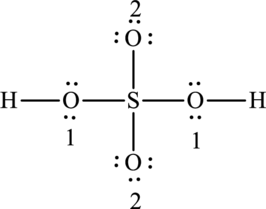
The formal charge for each atom is calculated as,
Formal charge on sulphur=
Formula charge on oxygen (1)=
Formula charge on oxygen (2)=
Formula charge on hydrogen=
The Lewis formula is,
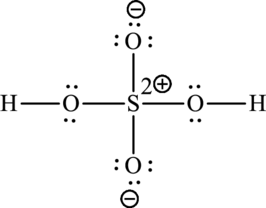
A large charge separation can be seen in the structure, this can be avoided by adding two pi bonds between oxygen and sulphur. The sulphur atom can expand the octet rule since it belongs to period three. The final Lewis structure is,
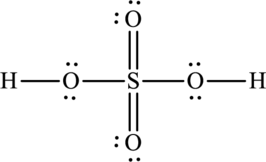
(b)
Interpretation:
The Lewis formula of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electrons in
Number of valence electrons in hydrogen=
Number of valence electrons in oxygen=
Number of valence electrons in sulphur=
The total number of valence electrons is thirty-two.
One sulphur atom forms one bond with other sulphur atom and three bonds oxygen and two oxygen forms a bond with hydrogen atoms that means twelve electrons are used to form that bonds and remaining twenty electrons are used to satisfy the octet rule of atoms.
The Lewis formula is,
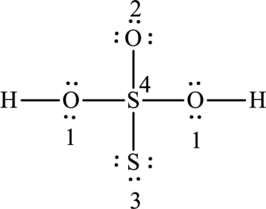
The formal charge for each atom is calculated as,
Formal charge on sulphur (3)=
Formal charge on sulphur (4)=
Formula charge on oxygen (1)=
Formula charge on oxygen (2)=
Formula charge on hydrogen=
The Lewis formula is,
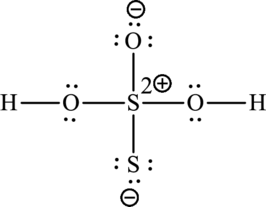
A large charge separation can be seen in the structure, this can be avoided by adding two pi bonds between oxygen and sulphur. The sulphur atom can expand the octet rule since it belongs to period three. The final Lewis structure is,
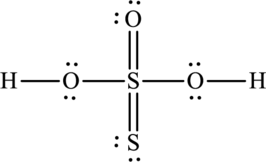
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis formula of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electrons in
Number of valence electrons in hydrogen=
Number of valence electrons in oxygen=
Number of valence electrons in sulphur=
The total number of valence electrons is fifty-six.
One
The Lewis formula is,
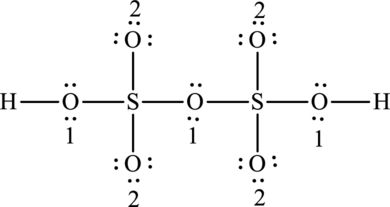
The formal charge for each atom is calculated as,
Formal charge on sulphur=
Formula charge on oxygen (1)=
Formula charge on oxygen (2)=
Formula charge on hydrogen=
The Lewis formula is,
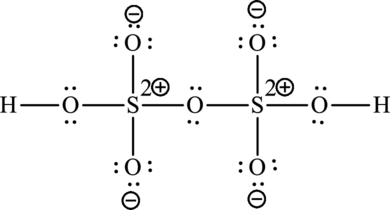
A large charge separation can be seen in the structure, this can be avoided by adding four pi bonds between oxygen and sulphur. The sulphur atom can expand the octet rule since it belongs to period three. The final Lewis structure is,
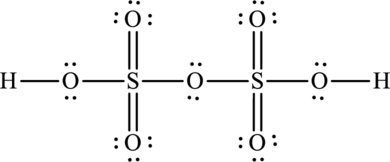
(d)
Interpretation:
The Lewis formula of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electrons in
Number of valence electrons in hydrogen=
Number of valence electrons in oxygen=
Number of valence electrons in sulphur=
The total number of valence electrons is fifty.
One S-S bonds is formed. One sulphur atom forms one bond with other sulphur. Each of two sulphur atom forms another three bonds with oxygen atoms and two oxygen atoms form a bond with hydrogen atom that means eighteen electrons form that bonds and the remaining thirty-two are used to satisfy the octet rule of atoms.
The Lewis formula is,
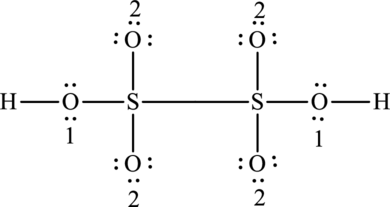
The formal charge for each atom is calculated as,
Formal charge on sulphur=
Formula charge on oxygen (1)=
Formula charge on oxygen (2)=
Formula charge on hydrogen=
The Lewis formula is,
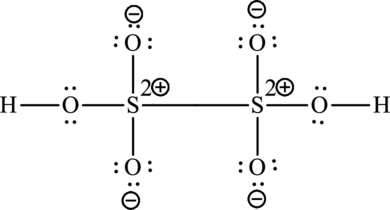
A large charge separation can be seen in the structure, this can be avoided by adding four pi bonds between oxygen and sulphur. The sulphur atom can expand the octet rule since it belongs to period three. The final Lewis structure is,
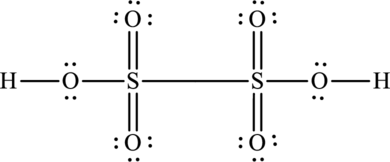
(e)
Interpretation:
The Lewis formula of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electrons in
Number of valence electrons in hydrogen=
Number of valence electrons in oxygen=
Number of valence electrons in sulphur=
The total number of valence electrons is sixty-two.
One O-O bond is formed from one oxygen atoms that forms one bond with other oxygen atom. Each of the oxygen atom forms one bond with one sulphur tom. Each of two sulphur forms another three bonds with oxygen atoms and two oxygen atoms form two bonds with hydrogen atom that means twenty-two electrons form that bonds and the remaining forty are used to satisfy the octet rule of atoms.
The Lewis formula is,
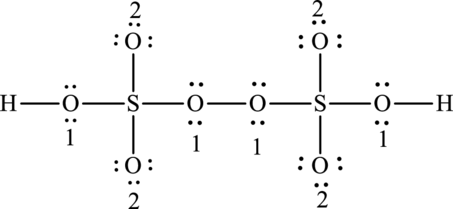
The formal charge for each atom is calculated as,
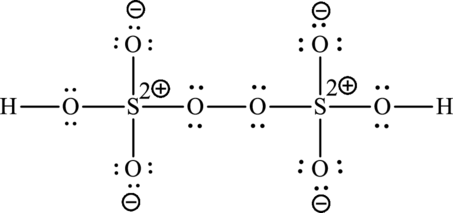
Formal charge on sulphur=
Formula charge on oxygen (1)=
Formula charge on oxygen (2)=
Formula charge on hydrogen=
The Lewis formula is,
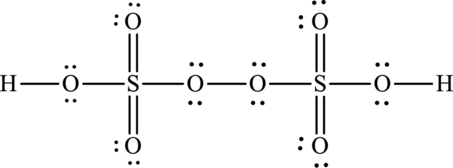
A large charge separation can be seen in the structure, this can be avoided by adding four pi bonds between oxygen and sulphur. The sulphur atom can expand the octet rule since it belongs to period three. The final Lewis structure is,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
General Chemistry
- What is the pH at the cathode for the following cell written in line notation at 25.0 oC with a Ecell = -0.2749 V? Ni(s)|Ni+2(aq, 1.00 M)||H+1(aq, ?M)|H2(g, 1.00 atm)|Pt(s)arrow_forwardCalculate Ecell for a hydrogen fuel cell at 95.0 oC using the following half-reactions with PH2 = 25.0 atm and PO2 = 25.0 atm. O2(g) + 4H+1(aq) + 4e-1 → 2H2O(l) Eo = 1.229 V 2H2(g) → 4H+1(aq) + 4e-1 Eo = 0.00 Varrow_forwardCalculate Ecell at 25.0 oC using the following half-reactions with [Ag+1] = 0.0100 M and [Sn+2] = 0.0200 M. Ag+1(aq) + 1e-1 Ag(s) Sn+2(aq) + 2e-1 Sn(s)arrow_forward
- Done 18:19 www-awu.aleks.com Chapter 12 HW Question 27 of 39 (5 points) | Question Attempt: 1 of Unlimited .. LTE סוי 9 ✓ 20 ✓ 21 × 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Answer the following questions about the given alkane. Part: 0 / 2 Part 1 of 2 Classify each carbon atom as a 1º, 2º, 3º, or 4°. Highlight in red any 1° carbons, highlight in blue any 2° carbons. highlight in green any 3° carbons, and leave any 4° carbons unhighlighted. Skip Part Check Save For Later © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center | Accessibility ☑ คarrow_forward< Done 19:22 www-awu.aleks.com Chapter 12 HW Question 4 of 39 (2 points) | Question Attempt: 5 of Unlimited : .. LTE סוי 1 ✓ 2 ✓ 3 = 4 ✓ 5 ✓ 6 ✓ 7 ✓ 8 ✓ 9 = 10 11 ✓ 12 Consider the molecule (CH3)2CHCH2CHCн for the following questions. Part 1 of 2 Which of the following molecules is/are constitutional isomer(s) to (CH3)2CHCH2CH2CH3? Check all that apply. Part 2 of 2 (CH3),C(CH2)2CH3 CH3 H,C-CH-CH-CH, CH 3 None of the above. ☑ Which of the following molecules is/are identical molecules to (CH3)2CHCH2CH2CH₁₂? Check all that apply. CH3 H,C-CH-CH₂-CH2-CH, CH3(CH2)2CH(CH3)2 CH2-CH2-CH3 HỌC-CH=CH, 乂 ☑ а None of the above Check Save For Later Submit Assignment © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Accessibilityarrow_forward18:11 LTE ا... US$50 off hotels is waiting for you Book now, hotels in Nashville are going fast QUTSLIVII 25 61 69 points) | QuestIVIT ALLēm... now Give the IUPAC name for each compound. Part 1 of 3 Part 2 of 3 X ☑ Х Check Save For Later Submit © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. TOMS CT US ...vacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forward
- Done 19:17 www-awu.aleks.com Chapter 12 HW Question 29 of 39 (6 points) | Question Attempt: 1 of Unlimited .III LTE סוי 27 28 = 29 30 31 32 = 33 34 35 Consider this structure. CH3CH2CH2 Part 1 of 3 3 CH2 CH2CH3 - C-CH2CH 3 H CH₂ Give the IUPAC name of this structure. 3-ethyl-3,4-dimethylheptane Part: 1/3 Part 2 of 3 Draw the skeletal structure. Skip Part < Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Save For Later Submit © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility Хarrow_forward18:57 .III LTE www-awu.aleks.com Chapter 12 HW Question 31 of 39 (8 points) | Question Attem... Give the IUPAC name of each compound. Part 1 of 4 Part 2 of 4 Х Х Check Save For Later Submit © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. TOMS OF US vacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? CH3-C-CH2-NH2 + R - CH3 O: 0 CH3-N-CH2-C-NH-CH2-C-CH3 + H2O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume no products other than those shown above are formed. Explanation Check Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Accesarrow_forward
- Done 18:17 • www-awu.aleks.com Chapter 12 HW Question 24 of 39 (4 points) | Question Attempt: 1 of Unlimited ▼ 20 ✓ 21 × 22 23 24 25 26 raw the structure corresponding to each IUPAC name. Part 1 of 2 .III LTE 22 27 28 סוי 29 29 3 A skeletal structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3-ethyl-4-methylhexane. Part 2 of 2 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. A condensed structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 2,2,4- trimethylpentane. Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. Check Save For Later Submit < Х ப: G © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility : Garrow_forwardDone 18:25 www-awu.aleks.com .III LTE Chapter 12 HW Question 29 of 39 (6 points) | Question Attempt: 1 of Unlimi... Oli 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Consider this structure. CH2 CH2CH2 CH2CH2CH₂ C -C. -CH2CH3 H CH Part: 0 / 3 Part 1 of 3 Give the IUPAC name of this structure. Skip Part < Check ☑ Save For Later © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility ....................arrow_forwardCalculate Ecell at 25.0 oC using the following line notation. Zn(s)|Zn+2(aq, 0.900 M)||Cu+2(aq, 0.000200 M)|Cu(s)arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





