
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781305501607
Author: Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher: CENGAGE L
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 7, Problem 7.33P
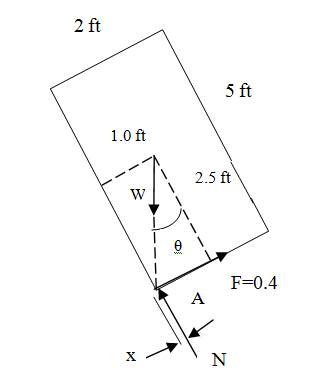
Determine the largest angle
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
%94 KB/S
Find : 1. dynamic load on each bearing due to the out-of-balance couple; and 2. kinetic energy of
the complete assembly.
[Ans. 6.12 kg: 8.7 N-m]
L
2.
3.
4.
5.
1.
2.
5.
DO YOU KNOW?
Why is balancing of rotating parts necessary for high speed engines?
Explain clearly the terms "static balancing' and 'dynamic balancing'. State the necessary conditions
to achieve them.
Discuss how a single revolving mass is balanced by two masses revolving in different planes.
Chapter 21: Balancing of Rotating Masses .857
Explain the method of balancing of different masses revolving in the same plane.
How the different masses rotating in different planes are balanced?
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
The balancing of rotating and reciprocating parts of an engine is necessary when it runs at
(a) slow speed
(b) medium speed (c) high speed
A disturbing mass, attached to a rotating shaft may be balanced by a single mass m, attached in
the same plane of rotation as that of my such that
(a)
(b) F
For static…
Provide a real-world usage example of the following:
Straightness
Circularity
Parallelism
What specific tools, jigs, and other devices are used to control the examples you provided?
856 Theory of Machines
5.
A shaft carries five masses A, B, C, D and E which revolve at the same radius in planes which are
equidistant from one another. The magnitude of the masses in planes A, C and D are 50 kg, 40 kg
and 80 kg respectively. The angle between A and C is 90° and that between C and D is 135°
Determine the magnitude of the masses in planes B and E and their positions to put the shaft in
complete rotating balance.
[Ans. 12 kg, 15 kg; 130° and 24° from mass A in anticlockwise direction]
Chapter 7 Solutions
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
Ch. 7 - Can the two blocks be in equilibrium in the...Ch. 7 - Determine the range of P for which the system of...Ch. 7 - Two identical chairs, each weighing 14 lb, are...Ch. 7 - The two homogeneous bars AB and BC are connected...Ch. 7 - The contact surface between the 36-lb block and...Ch. 7 - The uniform bar AB of weight W is leaning against...Ch. 7 - The center of gravity of the 50-kg spool is at G....Ch. 7 - The brake pads at C and D are pressed against the...Ch. 7 - The 200-lb homogenous cylinder of radius R is...Ch. 7 - The rear-wheel-drive pickup truck, with its center...
Ch. 7 - Solve Prob. 7.10 assuming that the pick-up truck...Ch. 7 - The 2-lb bar is pinned at A and rests on the 4-lb...Ch. 7 - The horizontal force P acts on the rim of the...Ch. 7 - The uniform bar and the homogeneous cylinder each...Ch. 7 - A stepladder consisting of two legs pinned...Ch. 7 - The mass of the unbalanced disk is m, and its...Ch. 7 - The two uniform sheets of plywood, each of length...Ch. 7 - Find the largest value of b/h at which the folding...Ch. 7 - The 3600-lb car with rear Wheel drive is...Ch. 7 - The 3600-lb car with rear wheel drive is...Ch. 7 - The man is trying to push the homogeneous 20-kg...Ch. 7 - A 1.1-kg disk A is placed on the inclined surface....Ch. 7 - The 40-lb spool is suspended from the hanger GA...Ch. 7 - A uniform plank is supported by a fixed support at...Ch. 7 - The uniform bar of weight W is supported by a...Ch. 7 - The uniform plank is initially at rest on the...Ch. 7 - The two homogeneous bars with the weights shown...Ch. 7 - The man pushes the 120-lb homogeneous crate with...Ch. 7 - The 80-kg crate has its center of gravity at G....Ch. 7 - Solve Prob. 7.29 if =0.Ch. 7 - The 120-lb door with its center of gravity at G is...Ch. 7 - Determine the largest force P for which the 16-kg...Ch. 7 - Determine the largest angle for which the...Ch. 7 - The cylinder and the block are connected by a...Ch. 7 - The weight of the cylindrical tank is negligible...Ch. 7 - The coeffient of static friction between the...Ch. 7 - The two homogenous boxes are stacked vertically....Ch. 7 - Two concrete blocks weighing 320 lb each form part...Ch. 7 - Derive the expression for the largest angle ? for...Ch. 7 - The 60-lb plank rests on a frictionless roller at...Ch. 7 - The 2000-lb weight of the trailer is distributed...Ch. 7 - Determine the smallest force P, applied to the...Ch. 7 - The homogenous cylinder of weight W is at rest...Ch. 7 - The uniform bar of length L and weight W is kept...Ch. 7 - The movable bracket of negligible weight is...Ch. 7 - The 200-lb man walks up the inclined plank of...Ch. 7 - Determine the smallest coefficient of static...Ch. 7 - Find the smallest distance d for which the hook...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.49PCh. 7 - The block of weight W is pulled by the force P...Ch. 7 - The two 200-lb blocks are pushed apart by the 15...Ch. 7 - Determine the smallest horizontal force P that...Ch. 7 - The device shown is used to measure the kinetic...Ch. 7 - The single-threaded screw of the floor jack has a...Ch. 7 - A wedge is used to prop up the 6000-lb block of...Ch. 7 - The square-threaded screw 0f the C-clamp has a...Ch. 7 - The square-threaded screw with a pitch of 10 mm...Ch. 7 - The screw of the carjack has a pitch of 0.1 in....Ch. 7 - How many turns of rope around the capstan are...Ch. 7 - The force P applied to the brake handle enables...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.61PCh. 7 - The 120-kg block A is suspended from a rope that...Ch. 7 - The leather rein used to fasten the horse to the...Ch. 7 - The 30-lb weight is attached to a rope that runs...Ch. 7 - The rail AB of negligible weight is suspended from...Ch. 7 - The blocks A and B of weights WA and WB are joined...Ch. 7 - The 150-lb weight is attached to a rope that...Ch. 7 - The 50-lb homogeneous bar AB is suspended from a...Ch. 7 - The collar bearing carries the axial load P = 400...Ch. 7 - Solve Sample Problem 7.16 if the contact pressure...Ch. 7 - The 600-lb cable spool is placed on a frictionless...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.72PCh. 7 - The normal pressure acting on the disk of the...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.74PCh. 7 - The single-plate clutch transmits the torque C...Ch. 7 - The clutch described in Prob. 7.75 is to transmit...Ch. 7 - The cone clutch transmits the torque C through a...Ch. 7 - The figure shows a steel bar being processed by a...Ch. 7 - The coefficient of rolling resistance between the...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.80PCh. 7 - Calculate the horizontal force P required to push...Ch. 7 - The uniform pole BC of length L and weight W is...Ch. 7 - The homogeneous bar AB of weight W and length L is...Ch. 7 - Find the smallest angle for which the uniform...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.85RPCh. 7 - Determine the largest angle for which the uniform...Ch. 7 - Can the uniform bar of weight W remain at rest in...Ch. 7 - The panel of weight W with its center of gravity...Ch. 7 - The woman is trying to move the crate of weight W...Ch. 7 - The screw of the clamp has a square thread of...Ch. 7 - Find the largest clockwise couple C that can be...Ch. 7 - The test specimen AB is placed in the grip of a...Ch. 7 - The coefficient of static friction between the...Ch. 7 - The uniform bars AB and BC are connected with a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. 3. 4. clockwise from Four masses A, B, C and D revolve at equal radii and are equally spaced along a shaft. The mass B is 7 kg and the radii of C and D make angles of 90° and 240° respectively with the radius of B. Find the magnitude of the masses A, C and D and the angular position of A so that the system may be completely balanced. [Ans. 5 kg: 6 kg; 4.67 kg; 205° from mass B in anticlockwise direction] A rotating shaft carries four masses A, B, C and D which are radially attached to it. The mass centres are 30 mm, 38 mm, 40 mm and 35 mm respectively from the axis of rotation. The masses A, C and D are 7.5 kg. 5 kg and 4 kg respectively. The axial distances between the planes of rotation of A and B is 400 mm and between B and C is 500 mm. The masses A and C are at right angles to each other. Find for a complete balance, 1. the angles between the masses B and D from mass A, 2. the axial distance between the planes of rotation of C and D. 3. the magnitude of mass B. [Ans. 162.5%,…arrow_forward1. Four masses A, B, C and D are attached to a shaft and revolve in the same plane. The masses are 12 kg. 10 kg. 18 kg and 15 kg respectively and their radii of rotations are 40 mm, 50 mm, 60 mm and 30 mm. The angular position of the masses B, C and D are 60°, 135° and 270 from the mass A. Find the magnitude and position of the balancing mass at a radius of 100 mm. [Ans. 7.56 kg: 87 clockwise from A]arrow_forward3. The structure in Figure 3 is loaded by a horizontal force P = 2.4 kN at C. The roller at E is frictionless. Find the axial force N, the shear force V and the bending moment M at a section just above the pin B in the member ABC and illustrate their directions on a sketch of the segment AB. B P D A 65° 65° E all dimensions in meters Figure 3arrow_forward
- 4. The distributed load in Figure 4 varies linearly from 3wo per unit length at A to wo per unit length at B and the beam is built in at A. Find expressions for the shear force V and the bending moment M as functions of x. 3W0 Wo A L Figure 4 2 Barrow_forward1. The beam AB in Figure 1 is subjected to a uniformly distributed load wo = 100 N/m. Find the axial force N, the shear force V and the bending moment M at the point D which is midway between A and B and illustrate their directions on a sketch of the segment DB. wo per unit length A D' B all dimensions in metersarrow_forward5. Find the shear force V and the bending moment M for the beam of Figure 5 as functions of the distance x from A. Hence find the location and magnitude of the maximum bending moment. w(x) = wox L x L Figure 5 Barrow_forward
- Dry atmospheric air enters an adiabatic compressor at a 20°C, 1 atm and a mass flow rate of 0.3kg/s. The air is compressed to 1 MPa. The exhaust temperature of the air is 70 degrees hottercompared to the exhaust of an isentropic compression.Determine,a. The exhaust temperature of the air (°C)b. The volumetric flow rate (L/s) at the inlet and exhaust of the compressorc. The power required to accomplish the compression (kW)d. The isentropic efficiency of the compressore. An accounting of the exergy entering the compressor (complete Table P3.9) assuming that thedead state is the same as State 1 (dry atmospheric air)f. The exergetic efficiency of the compressorarrow_forwardA heat pump is operating between a low temperature reservoir of 270 K and a high temperaturereservoir of 340 K. The heat pump receives heat at 255 K from the low temperature reservoir andrejects heat at 355 K to the high temperature reservoir. The heating coefficient of performance ofthe heat pump is 3.2. The heat transfer rate from the low temperature reservoir is 30 kW. The deadstate temperature is 270 K. Determine,a. Power input to the heat pump (kW)b. Heat transfer rate to the high-temperature reservoir (kW)c. Exergy destruction rate associated with the low temperature heat transfer (kW)d. Exergy destruction rate of the heat pump (kW)e. Exergy destruction rate associated with the high temperature heat transfer (kW)f. Exergetic efficiency of the heat pump itselfarrow_forwardRefrigerant 134a (Table B6, p514 of textbook) enters a tube in the evaporator of a refrigerationsystem at 132.73 kPa and a quality of 0.15 at a velocity of 0.5 m/s. The R134a exits the tube as asaturated vapor at −21°C. The tube has an inside diameter of 3.88 cm. Determine the following,a. The pressure drop of the R134a as it flows through the tube (kPa)b. The volumetric flow rate at the inlet of the tube (L/s)c. The mass flow rate of the refrigerant through the tube (g/s)d. The volumetric flow rate at the exit of the tube (L/s)e. The velocity of the refrigerant at the exit of the tube (m/s)f. The heat transfer rate to the refrigerant (kW) as it flows through the tubearrow_forward
- Water enters the rigid, covered tank shown in Figure P3.2 with a volumetric flow rate of 0.32L/s. The water line has an inside diameter of 6.3 cm. The air vent on the tank has an inside diameterof 4.5 cm. The water is at a temperature of 30°C and the air in the tank is at atmospheric pressure(1 atm) and 30°C. Determine the air velocity leaving the vent at the instant shown in the figurearrow_forwardUsing method of sections, determine the force in member BC, HC, and HG. State if these members are in tension or compression. 2 kN A 5 kN 4 kN 4 kN 3 kN H B C D E 3 m F 2 m -5 m 5 m- G 5 m 5 m-arrow_forwardDetermine the normal stresses σn and σt and the shear stress τnt at this point if they act on the rotated stress element shownarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
EVERYTHING on Axial Loading Normal Stress in 10 MINUTES - Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jQ-fNqZWrNg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY