
Saturated steam at a gauge pressure of 2.0 bar is to be used to heat a stream of ethane. The ethane enters a heat exchanger at 16°C and 1.5 bar gauge at a rate of 795 m3/min and is heated at constant pressure to 93°C. The steam condenses and leaves the exchanger as a liquid at 27°C. The speci?c enthalpy of ethane at the given pressure is 941 kJ/kg at 16°C and 1073 kJ/kg at 93°C.
(a) How much energy (kW) must be transferred to the ethane to heat it from 16°C to 93°C?
(b) Assuming that all the energy transferred from the steam goes to heat the ethane, at what rate in m3/s must steam be supplied to the exchanger? If the assumption is incorrect, would the calculated value be too high or too low?
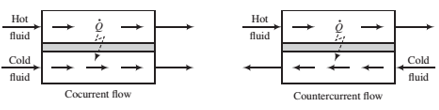
(c) Should the heat exchanger be set up for cocurrent or countercurrent ?ow (see the following schematic diagram)? Explain. (Hint: One of them will not work at all.)
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
ELEM.PRIN.OF CHEM.PROCESS-ACCESS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- Please answer handwritten, no chatgbt..arrow_forward#2 The isothermal gas-phase degradation reaction is given below. Pure ethane enters a flow reactor at 6 atm and 1100 K, with the pressure drop can be negligible. This reaction follows an elementary rate law. C2H6 → C2H4 + H2 a) Express the concentration of each species solely as a function of conversion. b) Write the reaction rate (the unit is mol/L-s) solely as a function of conversion (*rate constant k will be used in this mathematical expression). What is the unit of k. c) If this reaction is carried out in a constant volume batch reactor now, how to express the concentration of each species solely as a function of conversion?arrow_forward#1 For the following liquid phase reaction, ethylene oxide reacts with water to form ethylene glycol in a CSTR. The entering concentrations of ethylene oxide and water are 16.13 mol/L and 55.5 mol/L, respectively. The reaction rate constant k = 0.1 L/mol·s at 300 K. This reaction follows an elementary rate law. Taking ethylene oxide as the limiting species (i.e., basis of the calculation). ན CH₂-OH | H2SO4 CH2-CH₂+H₂O CH₂-OH a) Express the concentration of each species solely as a function of conversion. b) Write the reaction rate solely as a function of conversion at 300 K.arrow_forward
- #4 The gas phase reaction, as given below is carried out isothermally in a PFR with no pressure drop. The feed is equal molar in A and B, and the entering concentration of A is 0.1 mol/L. 2A + B → C a) What is the entering concentration of B? b) What are the concentrations of A, B, and C at 25% conversion of A? c) If at a particular conversion, the rate of formation of C is 2 mol/L-min, what is the rate of consumption of A at the same conversion?arrow_forward#3 Orthonitroanaline (an important intermediate in dyes - called fast orange) is formed from the reaction of orthonitroanaline (ONCB) and aqueous ammonia. This liquid phase reaction is first order in both ONCB and ammonia with k = 0.0017 m³/kmol·min at 188 °C. The initial entering concentration of ONCB and ammonia are 1.8 kmol/m³ and 6.6 kmol/m³, respectively. ONCB is used as the basis of calculation. NO2 CI NO2 NH₂ + NHCI +2NH₂ a) Express the concentration of each species solely as a function of conversion.arrow_forward4. (15 pts)A chemical project with a fixed capital investment without land of $250,000. The operation of the chemical project starts at the end of year 1 with 8-years of project lifetime. The estimated revenue per year is $90,000, the estimated cost of manufacture without depreciation over the project lifetime is $30,000/yr, and the taxation rate is 40%. a. Please determine the yearly depreciation values using the standard MACRS method assuming surplus value of $5,000. b. Please determine the net profit for operation year 1, 5, and 8.arrow_forward
- 2. (10 pts) You got a loan of $300,000 from a bank for your new house at a yearly interest rate of 6%, compounded monthly. How much do you pay total to the bank if the loan is 15 years? How much do you pay total to the bank if the loan is 30 years? 3. (10 pts) You got a 5-year loan of $50,000 to buy a BMW car at a yearly interest rate of 6% Please calculate your monthly payment if it is compounded monthly? Please calculate your quarterly payment if it is compounded quarterly?arrow_forwardA buffer solution is made by mixing 0.1 M acetic acid (HA) and 0.05 M sodium acetate (A⁻). The pKa of acetic acid is 4.76. Due to an experimental error, the actual pH was not recorded, and we need to solve for the concentration of the conjugate base (A⁻) given that the desired pH should be 4.90. Use the Bisection Method to find the concentration of A.arrow_forward1. (15) John had an loan plan shown in the following discrete cash flow diagram: $4,000 $6,000 GI $2,000 5 7 1 2 3 4 $3,000 $4,000 ? Years a. Please describe this diagram in terms of borrowing and payback. b. How much does John need to pay to totally payoff the loan at the end of year 8 if the interest rate is 8%? c. If John pays the sam amount of money at year 8, how much can John borrow at year 0 without paying back in between with the same interest rate?arrow_forward
- A buffer solution is made by mixing 0.1 M acetic acid (HA) and 0.05 M sodium acetate (A⁻). The pKa of acetic acid is 4.76. Due to an experimental error, the actual pH was not recorded, and we need to solve for the concentration of the conjugate base (A⁻) given that the desired pH should be 4.90. Use the Bisection Method to find the concentration of A.arrow_forward1. Liquid heptane is stored in a 100,000-L storage vessel that is vented directly to air. The heptane is stored at 25°C and 1 atm pressure. The liquid is drained from the storage vessel and all that remains in the vessel is the air saturated with heptane vapor. a. Is the vapor in the storage vessel flammable? b. What is the TNT equivalent for the vapor remaining in the vessel? c. If the vapor explodes, what is the overpressure 50 m from the vessel? d. What damage can be expected at 50 m?arrow_forward2. You have decided to use a vacuum purging technique to purge oxygen from a reactor vessel to reduce the concentration to 2.0% (mol). The reactor is 18 ft diameter and 40 ft tall. The temperature is 80°F. Assume that the vacuum purge goes from atmospheric pressure to 10.0 psia. How many purge cycles are required and how many total moles of nitrogen must be used? Assume the purge is done with pure nitrogen. 3. If the purging described in problem 2 takes place using nitrogen that has 1% (mol) oxygen in it, how many vacuum purge cycles are required? How many total moles of the inert gas must be used? 4. If the purging described in problem 2 is done by way of a "sweep-through" purge instead of a vacuum purge, for how long (in minutes) must the inert gas flow through the vessel if there is a 20 psig supply of pure nitrogen available at 150 CFM (ft³/min)? How much nitrogen must be used (lbm)?arrow_forward
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The





