
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The IUPAC names of each of the given compounds are to be given by using
Concept introduction:
The priority of groups in nomenclature is assigned according to Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (CIP Rule) convention rules:
The higher the
If priority cannot be assigned according to atomic mass, then assign the priority according to first point of difference.
If both the priority groups are on the same side of double-bonded carbon atom, then it is known as
But, if both the priority groups are diagonal to each other, then it is
Rule for R/S Nomenclature:
4B(+)3B(-)2B(+)1B(-)
4B(+) means if 4th priority group is below then from 1 to 2 to 3 if leads a clockwise rotation then its R and if anticlockwise then it is S.
3B(-) means if 3rd priority group is below then from 1 to 2 to 4 if leads a clockwise rotation then its S and if anticlockwise then it is R.
Answer to Problem 1PP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
a)
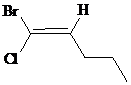
The IUPAC name with
Assign the priority to four groups, –Br gets first priority, pentyl group gets second, –Cl gets third, and –H gets fourth. Since both the priority groups are diagonal to each other, it is
Select the longest carbon chain. The parent hydrocarbon chain is pentane and hence pent- will be used and double bond is at the second position. Therefore, pent-1-ene is used.
Chloro and bromo groups are at first position. So, 1-bromo-1-chloropent-1-ene will be used.
Hence, the IUPAC name of the compound will be
b)
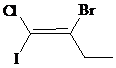
The IUPAC name with
Assign the priority to four groups, –I gets first priority, –Br gets second, –Cl gets third, and ethyl group gets fourth. Since both the priority groups are diagonal to each other, it is
Select the longest carbon chain. The parent hydrocarbon chain is butyl and hence but- will be used and double bond is at the first position. Therefore, but-1-ene is used.
Chloro and iodo groups are at first position and bromo group is at second position. So, 2-bromo-1-chloro-1-iodobut-1-ene will be used.
Hence, the IUPAC name of the compound will be
c)
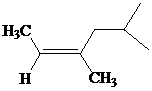
The IUPAC name with
Assign the priority to four groups, 2-methylpropyl gets first priority, both methyl groups get second, and –H gets third. Since both the priority groups are on the same side, it is
Select the longest carbon chain. The parent hydrocarbon chain is hexyl and hence hex- will be used and double bond is at the second position. Therefore, hex-2-ene is used.
There are two methyl groups at third and fifth positions. So, 3,5-dimethylhex-2-ene will be used.
Hence, the IUPAC name of the compound will be
d)
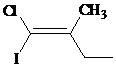
The IUPAC name with
Assign the priority to four groups, –I gets first priority, –Cl gets second, ethyl group gets third, and methyl group gets fourth. Since both the priority groups are on the same side, it is
Select the longest carbon chain. The parent hydrocarbon chain is butyl and hence but- will be used and double bond is at the first position. Therefore, but-1-ene is used.
There is one methyl group at second position, and chloro and iodo groups at first position. So, 1-chloro-1-iodo-2 methylbut-1-ene will be used.
Hence, the IUPAC name of the compound will be
e)
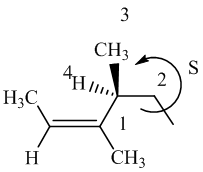
The IUPAC name with
Assign the priority to four groups, 1-methylpropyl gets first priority, both methyl groups get second, and –H gets third. Since both the priority groups are on the same side, it is
Select the longest carbon chain. The parent hydrocarbon chain is hexyl and hence hex- will be used and double bond is at the second position. Therefore, hex-2-ene is used.
There are two methyl groups at third and fourth position. So, 3,4-dimethylhex-2-ene will be used.
Carbon-4 is a chiral carbon. Assigning priority to the groups, 2-butene gets first priority, ethyl gets second, methyl gets third, and hydrogen gets fourth.
Move 1-2-3, it is in anticlockwise direction. So, it is
Hence, the IUPAC name of the compound will be
f)
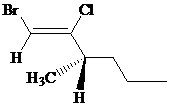
The IUPAC name can be done using the following steps:
Assign the priority to four groups, –Br gets first priority, –Cl gets second, 1-methylbutyl gets third, and –H gets fourth. Since both the priority groups are on the same side, it is
Select the longest carbon chain. The parent hydrocarbon chain is hexyl and hence hex- will be used and double bond is at the first position. Therefore, hex-1-ene is used.
There is one methyl group at third position, and chloro at second and bromo at first position. So, 1-bromo-2-chloro-3-methylhex-1-ene will be used.
Carbon-3 is a chiral carbon. Assigning priority to the groups, 1-bromo-2-chloroethene gets first priority, propyl gets second, methyl gets third, and hydrogen gets fourth.
Rotate the molecule such that –H is at a horizontal position and then move 1-2-3, it is in anticlockwise direction. So, it is
Hence, the IUPAC name of the compound will be
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- What is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forwardWhat would be the reagents and conditions above and below the arrow that will complete the proposed acetoacetic ester synthesis? If it cannot be done efficiently, then I will choose that answer. There could be 2 or 4 reagents involved. Please provide a detailed explanation and drawings showing how it would proceed with the correct reagents.arrow_forward
- For benzene, the ∆H° of vaporization is 30.72 kJ/mol and the ∆S° of vaporization is 86.97 J/mol・K. At 1.00 atm and 228.0 K, what is the ∆G° of vaporization for benzene, in kJ/mol?arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reaction. it is spontaneous only at High T, it is spontaneous at low T it is nonspontaneous at all T it is spontanrous at all T. it is non spontaneous only at low T.arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reactionarrow_forward
- Which of the following has the largest standard molar entropy, S° (298.15 K) He H2 NaCl KBr Hgarrow_forwardWhich of the following is true for a particular reaction if ∆G° is -40.0 kJ/mol at 290 K and –20.0 kJ/mol at 390 K?arrow_forwardWhat is the major product of the following reaction? O O OH OH 1. BH 2. H₂O₂, NaOH OH OHarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





