
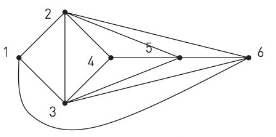
Getting greedy. (H) Suppose you are asked to color the vertices of this graph in the following way: You must color the vertices one-by-one in numerical order and no two vertices joined by an edge can be the same color. You are given the list of colors red, yellow, blue, green, purple, and orange. The coloring rule is to look at this ordered list of colors, and select the first color on the list that satisfies the criteria above. So, for example,
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
HEART OF MATHEMATICS
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Precalculus
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
- Q4*) (make sure you first understand question P5) Discuss the extremisation of the integral I = = √(2(y + 2) ³y' + (x − 7)) c You may find point (iv) in § 3.5 relevant. dx.arrow_forwardQ6*) Describe the plane paths of light in the two-dimensional media in which the light velocities are given respectively by (a) c = a/y, (b) c = a/√y, where a > 0, y > 0.arrow_forwardData Analysis DeltaMath Student Applical X Home $i$ Grades and Attendance x ent/3903821/26770486/bae6d3c1493d9868572f4878b5c163b6 y School St... Quizez And Tests Cancer reserch College Reserch Highschool Reserch Writing SCP Step Reason Statement ADBC 1 Given AD || BC 2 ACCA Reflexive Property try Type of Statement C B +> D A Feb 14arrow_forward
- lim 1 x→0x3 3 So²² 6 tln(1+t) t4 +4 .dt 2arrow_forward2. Suppose the population of Wakanda t years after 2000 is given by the equation f(t) = 45000(1.006). If this trend continues, in what year will the population reach 50,000 people? Show all your work, round your answer to two decimal places, and include units. (4 points)arrow_forward3. Solve the equation, give the answer exactly (no calculator approximations), and show all your work. (4 points) log5 2x = 3arrow_forward
- Examine the Variables: Carefully review and note the names of all variables in the dataset. Examples of these variables include: Mileage (mpg) Number of Cylinders (cyl) Displacement (disp) Horsepower (hp) Research: Google to understand these variables. Statistical Analysis: Select mpg variable, and perform the following statistical tests. Once you are done with these tests using mpg variable, repeat the same with hp Mean Median First Quartile (Q1) Second Quartile (Q2) Third Quartile (Q3) Fourth Quartile (Q4) 10th Percentile 70th Percentile Skewness Kurtosis Document Your Results: In RStudio: Before running each statistical test, provide a heading in the format shown at the bottom. “# Mean of mileage – Your name’s command” In Microsoft Word: Once you've completed all tests, take a screenshot of your results in RStudio and paste it into a Microsoft Word document. Make sure that snapshots are very clear. You will need multiple snapshots. Also transfer these results to the…arrow_forwardIf given is the graph of f(x), then how does the graph of modulus of f(x) will look like(roughly)?arrow_forwardpls helparrow_forward
- Let I = f(x) dx, where f is the function whose graph is shown. 4 2 y f X 1 2 3 4 (a) Use the graph to find L2, R2 and M2. R₂ M2 = = = (b) Are these underestimates or overestimates of I? O 42 is an underestimate. O 42 is an overestimate. ◇ R2 is an underestimate. OR2 is an overestimate. OM2 is an underestimate. ○ M2 is an overestimate. (c) Use the graph to find T2. T₂ =arrow_forwardExamine the Variables: Carefully review and note the names of all variables in the dataset. Examples of these variables include: Mileage (mpg) Number of Cylinders (cyl) Displacement (disp) Horsepower (hp) Research: Google to understand these variables. Statistical Analysis: Select mpg variable, and perform the following statistical tests. Once you are done with these tests using mpg variable, repeat the same with hp Mean Median First Quartile (Q1) Second Quartile (Q2) Third Quartile (Q3) Fourth Quartile (Q4) 10th Percentile 70th Percentile Skewness Kurtosis Document Your Results: In RStudio: Before running each statistical test, provide a heading in the format shown at the bottom. “# Mean of mileage – Your name’s command” In Microsoft Word: Once you've completed all tests, take a screenshot of your results in RStudio and paste it into a Microsoft Word document. Make sure that snapshots are very clear. You will need multiple snapshots. Also transfer these results to the…arrow_forwardVector u has a magnitude of 23 and vector v has a magnitude of 83. The angle between the two vectors is 126 degrees.a) Draw a fully-labelled vector diagram showing the two vectors and the resultant vector when they are added together.b) Find the magnitude of the resultant vector.c) Find the direction of the resultant vector relative to vector u. Solding by finding the x and y of the vectors and addingarrow_forward
 Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications ( 8th I...MathISBN:9781259676512Author:Kenneth H RosenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications ( 8th I...MathISBN:9781259676512Author:Kenneth H RosenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Mathematics for Elementary Teachers with Activiti...MathISBN:9780134392790Author:Beckmann, SybillaPublisher:PEARSON
Mathematics for Elementary Teachers with Activiti...MathISBN:9780134392790Author:Beckmann, SybillaPublisher:PEARSON
 Thinking Mathematically (7th Edition)MathISBN:9780134683713Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Thinking Mathematically (7th Edition)MathISBN:9780134683713Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Discrete Mathematics With ApplicationsMathISBN:9781337694193Author:EPP, Susanna S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Discrete Mathematics With ApplicationsMathISBN:9781337694193Author:EPP, Susanna S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)MathISBN:9781259985607Author:David Sobecki Professor, Brian A. MercerPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)MathISBN:9781259985607Author:David Sobecki Professor, Brian A. MercerPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





