
Concept explainers
Classify each of the structures shown as completely, partially, or improperly constrained; if completely constrained, further classify as determinate or indeterminate. (All members can act both in tension and in compression.)
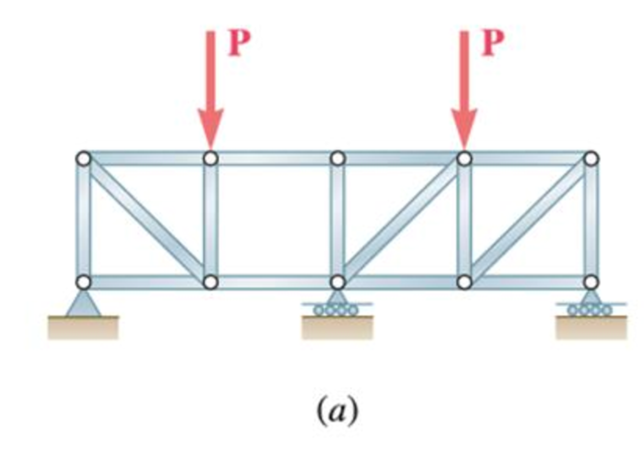
(a)
Classify the given structure as completely, partially, or improperly constrained and if completely constrained, further classify as determinate or indeterminate.
Answer to Problem 6.70P
The given structure is completely constrained and determinate.
Explanation of Solution
The structure is shown in Fig. P6.70 (a). The free-body diagram of the truss is given in Figure 1.
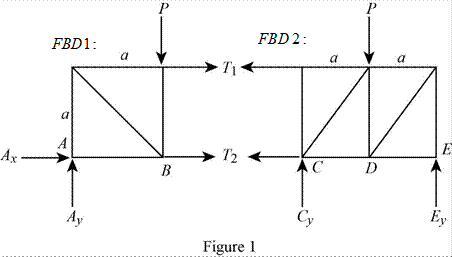 |
Write the condition for a truss to be completely constrained.
Here,
Write the condition for a truss to be partially constrained.
Write the expression for a truss to be indeterminate.
Write the expression for the condition for equilibrium.
Here,
Conclusion:
For the given truss,
Compute
Compute
So, for the given system,
Apply the condition for equilibrium in equation (IV) about various points of the structure in the free-body diagrams
Apply the condition for equilibrium in equation (V) about various points of the structure in the free-body diagrams
Since each section is a simple truss with reactions determined, the given structure is completely constrained and determinate.
Therefore, the given structure is completely constrained and determinate.
(b)
Classify the given structure as completely, partially, or improperly constrained and if completely constrained, further classify as determinate or indeterminate.
Answer to Problem 6.70P
The given structure is partially constrained.
Explanation of Solution
The structure is shown in Fig. P6.70 (b). It is a non-simple truss.
From equations (I), and (II), the conditions for the state of constrain of the structure is as follows,
Conclusion:
For the given truss,
Compute
Compute
So, for the given system,
Therefore, the given structure is partially constrained.
(c)
Classify the given structure as completely, partially, or improperly constrained and if completely constrained, further classify as determinate or indeterminate.
Answer to Problem 6.70P
The given structure is improperly constrained and indeterminate.
Explanation of Solution
The structure is shown in Fig. P6.70 (c). The free-body diagram of the truss is given in Figure 2.
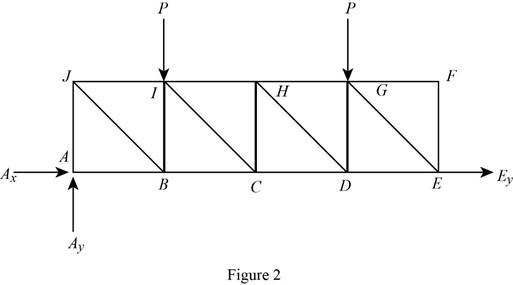
From equations (I), and (II), the conditions for the state of constrain of the structure is as follows,
Conclusion:
For the given truss,
Compute
Compute
It is clear that for the given system, the condition in equation (I) is satisfied, but the horizontal reaction forces
Therefore, the given structure is improperly constrained and indeterminate.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
VECTOR MECH. FOR EGR: STATS & DYNAM (LL
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
- If the 300-kg drum has a center of mass at point G, determine the horizontal and vertical components of force acting at pin A and the reactions on the smooth pads C and D. The grip at B on member DAB resists both horizontal and vertical components of force at the rim of the drum. P 60 mm; 60 mm: 600 mm A E 30° B C 390 mm 100 mm D Garrow_forwardThe design of the gear-and-shaft system shown requires that steel shafts of the same diameter be used for both AB and CD. It is further required that the angle D through which end D of shaft CD rotates not exceed 1.5°. Knowing that G = 77.2 GPa, determine the required diameter of the shafts. 40 mm 400 mm 100 mm 600 mm T-1000 N-m Darrow_forwardAssume a Space Launch System (Figure 1(a)) that is approximated as a cantilever undamped single degree of freedom (SDOF) system with a mass at its free end (Figure 1(b)). The cantilever is assumed to be massless. Assume a wind load that is approximated with a concentrated harmonic forcing function p(t) = posin(ωt) acting on the mass. The known properties of the SDOF and the applied forcing function are given below. • Mass of SDOF: m =120 kip/g • Acceleration of gravity: g = 386 in/sec2 • Bending sectional stiffness of SDOF: EI = 1015 lbf×in2 • Height of SDOF: h = 2000 inches • Amplitude of forcing function: po = 6 kip • Forcing frequency: f = 8 Hzarrow_forward
- 13.44 The end of a cylindrical liquid cryogenic propellant tank in free space is to be protected from external (solar) radiation by placing a thin metallic shield in front of the tank. Assume the view factor Fts between the tank and the shield is unity; all surfaces are diffuse and gray, and the surroundings are at 0 K. Tank T₁ Shield, T T₁ = 100 K E1 Solar irradiation Gs ε₁ = ε₂ = 0.05 ε₁ = 0.10 Gs = 1250 W/m² E2 Find the temperature of the shield T, and the heat flux (W/m²) to the end of the tank.arrow_forwardquestion 664 thank youarrow_forward13.38 Consider the attic of a home located in a hot climate. The floor of the attic is characterized by a width of L₁ = 8 m while the roof makes an angle of 0 = 30° from the horizontal direction, as shown in the schematic. The homeowner wishes to reduce the heat load to the home by adhering bright aluminum foil (ε = 0.07) onto the surfaces of the attic space. Prior to installation of the foil, the surfaces are of emissivity & = 0.90. Attic A2, 82, T2 0 = 30° A1, E1, T₁ 土 L₁ = 8 m (a) Consider installation on the bottom of the attic roof only. Determine the ratio of the radiation heat transfer after to before the installation of the foil. (b) Determine the ratio of the radiation heat transfer after to before installation if the foil is installed only on the top of the attic floor. (c) Determine the ratio of the radiation heat transfer if the foil is installed on both the roof bottom and the floor top.arrow_forward
- 13.1 Determine F2 and F2 for the following configura- tions using the reciprocity theorem and other basic shape factor relations. Do not use tables or charts. (a) Small sphere of area A, under a concentric hemi- sphere of area A₂ = 3A₁ A₂ A1 (a) (b) Long duct. Also, what is F₁₂? A₂ Αν (b) (c) Long inclined plates (point B is directly above the center of A₁) B 100 mm A₂ - 220 mm (c) (d) Long cylinder lying on infinite plane + A₁ Az (d) (e) Hemisphere-disk arrangement -A₂, hemisphere, diameter D A₂ A₁, disk, diameter D/2 (e) (f) Long, open channel 1 m AA₂ 2 m (f) (g) Long cylinders with A₁ = 4A₁. Also, what is F₁₂? -D₁ A1 -A₂ -D2 (e) (h) Long, square rod in a long cylinder. Also, what is F22? w=D/5 18 A₁ -A2 (h) -Darrow_forward13.9 Determine the shape factor, F12, for the rectangles shown. 6 m 1 3 m 6 m 1 m 2 6 m 1 0.5 m 2 1 m (a) Perpendicular rectangles without a common edge. -1 m. (b) Parallel rectangles of unequal areas.arrow_forwardI keep getting the wrong answer i have gotten 6519.87 and 319.71arrow_forward
- thank you for previous answer I apologize if the acceleration was unclear it is underlined now along with values in tablesarrow_forward११११११११ TABLE Much 160,000kg Croll 0,005 CD Ap Par ng При nchs 0.15 5m² 1.2kg/m³ 0.98 0.9 0,98 0,9 0,88 IF 20 10 to add The train is going to make several stops along its journey. It will be important for the train to accelerate quickdy to get back up to speed. In order to get Tesla Model S motors until we get the combined The Forque and power needed we are goins bined power and forque needed to accelerate from 0 to 324 km/hr in less than 5 Minutes. Tesla Prated 270 kW Tesla Trated Twheel ng Jaxle 440 NM 20 8.5kgm² 0.45M a) What is the minimum whole number of Tesla Motors required to achieve accelerate the train from 0 to 324 km/hr in less than 5 Nnutes? Seperate the acceleration into constant torque and constant power 0. b) How long does it take the train to accelerate from 0 to 324 km/hr with the number of Tesla motors from part a? c) Using Matlab plot the relocity profile as a function of time, Is this a constant acceleration profile? Barrow_forwardExample find f(t)? -4s F(s)= (s² + 4)²arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





