
Single Variable Calculus: Early Transcendentals, Books a la Carte, and MyLab Math with Pearson eText -- Title-Specific Access Card Package (3rd Edition)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780134996103
Author: William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 6.2, Problem 15E
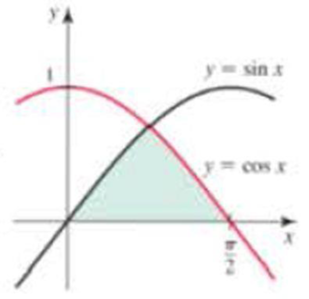
Finding area Determine the area of the shaded region in the following figures.
15.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A function is defined on the interval (-π/2,π/2) by this multipart rule:
if -π/2 < x < 0
f(x) =
a
if x=0
31-tan x
+31-cot x
if 0 < x < π/2
Here, a and b are constants. Find a and b so that the function f(x) is continuous at x=0.
a=
b= 3
Use the definition of continuity and the properties of limits to show that the function is continuous at the given number a.
f(x) = (x + 4x4) 5,
a = -1
lim f(x)
X--1
=
lim
x+4x
X--1
lim
X-1
4
x+4x
5
))"
5
))
by the power law
by the sum law
lim (x) + lim
X--1
4
4x
X-1
-(0,00+(
Find f(-1).
f(-1)=243
lim (x) +
-1 +4
35
4 ([
)
lim (x4)
5
x-1
Thus, by the definition of continuity, f is continuous at a = -1.
by the multiple constant law
by the direct substitution property
1. Compute
Lo
F⚫dr, where
and C is defined by
F(x, y) = (x² + y)i + (y − x)j
r(t) = (12t)i + (1 − 4t + 4t²)j
from the point (1, 1) to the origin.
Chapter 6 Solutions
Single Variable Calculus: Early Transcendentals, Books a la Carte, and MyLab Math with Pearson eText -- Title-Specific Access Card Package (3rd Edition)
Ch. 6.1 - A police officer leaves his station on a...Ch. 6.1 - Describe a possible motion of an object along a...Ch. 6.1 - Is the position s(t) a number or a function? For...Ch. 6.1 - Without doing further calculations, what are the...Ch. 6.1 - Prob. 5QCCh. 6.1 - Prob. 6QCCh. 6.1 - Explain the meaning of position, displacement, and...Ch. 6.1 - Suppose the velocity of an object moving along a...Ch. 6.1 - Given the velocity function v of an object moving...Ch. 6.1 - Prob. 4E
Ch. 6.1 - Prob. 5ECh. 6.1 - What is the result of integrating a population...Ch. 6.1 - Displacement and distance from velocity Consider...Ch. 6.1 - Displacement and distance from velocity Consider...Ch. 6.1 - Velocity graphs The figures show velocity...Ch. 6.1 - Prob. 10ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 11ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 12ECh. 6.1 - Displacement from velocity Consider an object...Ch. 6.1 - Displacement from velocity Consider an object...Ch. 6.1 - Displacement from velocity Consider an object...Ch. 6.1 - Displacement from velocity Assume t is time...Ch. 6.1 - Position from velocity Consider an object moving...Ch. 6.1 - Prob. 18ECh. 6.1 - Position from velocity Consider an object moving...Ch. 6.1 - Prob. 20ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 21ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 22ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 23ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 24ECh. 6.1 - Flying into a headwind The velocity (in mi/hr) of...Ch. 6.1 - Day hike The velocity (in mi/hr) of a hiker...Ch. 6.1 - Piecewise velocity The velocity of a (fast)...Ch. 6.1 - Probe speed A data collection probe is dropped...Ch. 6.1 - Position and velocity from acceleration Find the...Ch. 6.1 - Position and velocity from acceleration Find the...Ch. 6.1 - Prob. 31ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 32ECh. 6.1 - Position and velocity from acceleration Find the...Ch. 6.1 - Prob. 34ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 35ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 36ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 37ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 38ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 39ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 40ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 41ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 42ECh. 6.1 - Population growth 43. A culture of bacteria in a...Ch. 6.1 - Prob. 44ECh. 6.1 - Oil production An oil refinery produces oil at a...Ch. 6.1 - Prob. 46ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 47ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 48ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 49ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 50ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 51ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 52ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 53ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 54ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 55ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 56ECh. 6.1 - Marginal cost Consider the following marginal cost...Ch. 6.1 - Prob. 58ECh. 6.1 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 6.1 - Prob. 60ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 61ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 62ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 63ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 64ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 65ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 66ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 67ECh. 6.1 - Variable gravity At Earths surface, the...Ch. 6.1 - Prob. 69ECh. 6.1 - Prob. 70ECh. 6.1 - Another look at the Fundamental Theorem 71. Use...Ch. 6.1 - Prob. 72ECh. 6.2 - In the area formula for a region between two...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 2QCCh. 6.2 - Prob. 3QCCh. 6.2 - Prob. 4QCCh. 6.2 - Set up a sum of two integrals that equals the area...Ch. 6.2 - Set up an integral that equals the area of the...Ch. 6.2 - Make a sketch to show a case in which the area...Ch. 6.2 - Make a sketch to show a case in which the area...Ch. 6.2 - Find the area of the region (see figure) in two...Ch. 6.2 - Find the area of the region (see figure) in two...Ch. 6.2 - Express the area of the shaded region in Exercise...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 8ECh. 6.2 - Finding area Determine the area of the shaded...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 10ECh. 6.2 - Finding area Determine the area of the shaded...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 12ECh. 6.2 - Finding area Determine the area of the shaded...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 14ECh. 6.2 - Finding area Determine the area of the shaded...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 16ECh. 6.2 - Finding area Determine the area of the shaded...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 18ECh. 6.2 - Finding area Determine the area of the shaded...Ch. 6.2 - Finding area Determine the area of the shaded...Ch. 6.2 - Finding area Determine the area of the shaded...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 22ECh. 6.2 - Finding area Determine the area of the shaded...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 24ECh. 6.2 - Finding area Determine the area of the shaded...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 26ECh. 6.2 - Finding area Determine the area of the shaded...Ch. 6.2 - Finding area Determine the area of the shaded...Ch. 6.2 - Finding area Determine the area of the shaded...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 30ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 31ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 32ECh. 6.2 - Area between velocity curves Two runners, starting...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 34ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 35ECh. 6.2 - Calculus and geometry For the given regions R1 and...Ch. 6.2 - Regions between curves Find the area of the region...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 38ECh. 6.2 - Regions between curves Find the area of the region...Ch. 6.2 - Regions between curves Find the area of the region...Ch. 6.2 - Regions between curves Find the area of the region...Ch. 6.2 - Regions between curves Find the area of the region...Ch. 6.2 - Regions between curves Find the area of the region...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 44ECh. 6.2 - Regions between curves Find the area of the region...Ch. 6.2 - Regions between curves Find the area of the region...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 47ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 48ECh. 6.2 - Any method Use any method (including geometry) to...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 50ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 51ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 52ECh. 6.2 - Regions between curves Find the area of the region...Ch. 6.2 - Regions between curves Find the area of the region...Ch. 6.2 - Regions between curves Find the area of the region...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 56ECh. 6.2 - Regions between curves Find the area of the region...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 58ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 59ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 60ECh. 6.2 - Regions between curves Find the area of the region...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 62ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 63ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 64ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 65ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 66ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 67ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 68ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 69ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 70ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 71ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 72ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 73ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 74ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 75ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 76ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 77ECh. 6.2 - Prob. 78ECh. 6.3 - Why is the volume as given by the general slicing...Ch. 6.3 - In Example 2 what is the cross-sectional area...Ch. 6.3 - What solid results when the region R is revolved...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 4QCCh. 6.3 - Prob. 5QCCh. 6.3 - Prob. 6QCCh. 6.3 - Suppose a cut is made through a solid object...Ch. 6.3 - A solid has a circular base and cross sections...Ch. 6.3 - Consider a solid whose base is the region in the...Ch. 6.3 - Why is the disk method a special case of the...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 5ECh. 6.3 - Prob. 6ECh. 6.3 - Use the region R that is bounded by the graphs of...Ch. 6.3 - Use the region R that is bounded by the graphs of...Ch. 6.3 - Use the region R that is bounded by the graphs of...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 10ECh. 6.3 - General slicing method Use the general slicing...Ch. 6.3 - General slicing method Use the general slicing...Ch. 6.3 - General slicing method Use the general slicing...Ch. 6.3 - General slicing method Use the general slicing...Ch. 6.3 - General slicing method Use the general slicing...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 16ECh. 6.3 - Disk method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.3 - Disk method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.3 - Disk method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.3 - Solids of revolution Let R be the region bounded...Ch. 6.3 - Solids of revolution Let R be the region bounded...Ch. 6.3 - Disks/washers about the y-axis Let R be the region...Ch. 6.3 - Washer method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.3 - Washer method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.3 - Washer method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.3 - Washer method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.3 - Solids of revolution Let R be the region bounded...Ch. 6.3 - Disks/washers about the y-axis Let R be the region...Ch. 6.3 - Disk method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 30ECh. 6.3 - Disk method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.3 - Solids of revolution Let R be the region bounded...Ch. 6.3 - Solids of revolution Let R be the region bounded...Ch. 6.3 - Washer method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.3 - Washer method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.3 - Washer method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.3 - Disks/washers about the y-axis Let R be the region...Ch. 6.3 - Solids of revolution Let R be the region bounded...Ch. 6.3 - Solids of revolution Let R be the region bounded...Ch. 6.3 - Solids of revolution Let R be the region bounded...Ch. 6.3 - Solids of revolution Let R be the region bounded...Ch. 6.3 - Solids of revolution Let R be the region bounded...Ch. 6.3 - Solids of revolution Let R be the region bounded...Ch. 6.3 - Solids of revolution Let R be the region bounded...Ch. 6.3 - Which is greater? For the following regions R,...Ch. 6.3 - Which is greater? For the following regions R,...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 47ECh. 6.3 - Prob. 48ECh. 6.3 - Revolution about other axes Let R be the region...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 50ECh. 6.3 - Revolution about other axes Let R be the region...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 52ECh. 6.3 - Prob. 53ECh. 6.3 - Prob. 54ECh. 6.3 - Revolution about other axes Find the volume of the...Ch. 6.3 - Revolution about other axes Find the volume of the...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 57ECh. 6.3 - Prob. 58ECh. 6.3 - Prob. 59ECh. 6.3 - Prob. 60ECh. 6.3 - Prob. 61ECh. 6.3 - Prob. 62ECh. 6.3 - Prob. 63ECh. 6.3 - Prob. 64ECh. 6.3 - Prob. 65ECh. 6.3 - Prob. 66ECh. 6.3 - Prob. 67ECh. 6.3 - Volume of a wooden object A solid wooden object...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 69ECh. 6.3 - Water in a bowl A hemispherical bowl of radius 8...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 71ECh. 6.3 - Prob. 72ECh. 6.3 - Cavalieris principle Cavalieris principle states...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 74ECh. 6.4 - The triangle bounded by the x-axis, the line y =...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 2QCCh. 6.4 - Prob. 3QCCh. 6.4 - Assume f and g are continuous with f(x) g(x) on...Ch. 6.4 - Fill in the blanks: A region R is revolved about...Ch. 6.4 - Fill in the blanks: A region R is revolved about...Ch. 6.4 - Look again at the region R in Figure 6.38 (p 439)....Ch. 6.4 - Let R be the region in the first quadrant bounded...Ch. 6.4 - Let R be the region bounded by the curves...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 7ECh. 6.4 - Let R be the region bounded by the curves...Ch. 6.4 - Shell method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 10ECh. 6.4 - Shell method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 12ECh. 6.4 - Shell method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 14ECh. 6.4 - Shell method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 16ECh. 6.4 - Shell method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 18ECh. 6.4 - Shell method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 20ECh. 6.4 - Shell method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.4 - Shell method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.4 - Shell method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.4 - Shell method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 25ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 26ECh. 6.4 - Shell method Let R be the region bounded by the...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 28ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 29ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 30ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 31ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 32ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 33ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 34ECh. 6.4 - Washers vs. shells Let R be the region bounded by...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 36ECh. 6.4 - Washers vs. shells Let R be the region bounded by...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 38ECh. 6.4 - Shell method about other lines Let R be the region...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 40ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 41ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 42ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 43ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 44ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 45ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 46ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 47ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 48ECh. 6.4 - Volume of a sphere Let R be the region bounded by...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 50ECh. 6.4 - A torus (doughnut) A torus is formed when a circle...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 52ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 53ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 54ECh. 6.4 - Choose your method Find the volume of the...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 56ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 57ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 58ECh. 6.4 - Choose your method Let R be the region bounded by...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 60ECh. 6.4 - Choose your method Let R be the region bounded by...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 62ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 63ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 64ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 65ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 66ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 67ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 68ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 69ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 70ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 71ECh. 6.4 - Equal integrals Without evaluating integrals,...Ch. 6.4 - Volumes without calculus Solve the following...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 74ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 75ECh. 6.4 - Prob. 76ECh. 6.5 - What does the arc length formula give for the...Ch. 6.5 - Prob. 2QCCh. 6.5 - Prob. 3QCCh. 6.5 - Prob. 1ECh. 6.5 - Prob. 2ECh. 6.5 - Setting up arc length integrals Write and...Ch. 6.5 - Setting up arc length integrals Write and...Ch. 6.5 - Setting up arc length integrals Write and...Ch. 6.5 - Prob. 6ECh. 6.5 - Prob. 7ECh. 6.5 - Prob. 8ECh. 6.5 - Arc lezngth calculations Find the arc length of...Ch. 6.5 - Arc length calculations Find the arc length of the...Ch. 6.5 - Arc length calculations Find the arc length of the...Ch. 6.5 - Arc length calculations Find the arc length of the...Ch. 6.5 - Arc length calculations Find the arc length of the...Ch. 6.5 - Arc length calculations Find the arc length of the...Ch. 6.5 - Arc length calculations Find the arc length of the...Ch. 6.5 - Arc length calculations Find the arc length of the...Ch. 6.5 - Arc length calculations with respect to y Find the...Ch. 6.5 - Arc length calculations with respect to y Find the...Ch. 6.5 - Arc length calculations with respect to y Find the...Ch. 6.5 - Arc length calculations with respect to y Find the...Ch. 6.5 - Arc length by calculator a. Write and simplify the...Ch. 6.5 - Prob. 22ECh. 6.5 - Prob. 23ECh. 6.5 - Prob. 24ECh. 6.5 - Arc length by calculator a. Write and simplify the...Ch. 6.5 - Arc length by calculator a. Write and simplify the...Ch. 6.5 - Arc length by calculator a. Write and simplify the...Ch. 6.5 - Prob. 28ECh. 6.5 - Arc length by calculator a. Write and simplify the...Ch. 6.5 - Arc length by calculator a.Write and simplify the...Ch. 6.5 - Prob. 31ECh. 6.5 - Prob. 32ECh. 6.5 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 6.5 - Prob. 34ECh. 6.5 - Functions from arc length What differentiable...Ch. 6.5 - Function from arc length Find a curve that passes...Ch. 6.5 - Prob. 37ECh. 6.5 - Prob. 38ECh. 6.5 - Prob. 39ECh. 6.5 - Prob. 40ECh. 6.5 - Prob. 41ECh. 6.5 - Bernoullis parabolas Johann Bernoulli (16671748)...Ch. 6.6 - Which is greater the surface area of a cone of...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 2QCCh. 6.6 - Prob. 3QCCh. 6.6 - Prob. 1ECh. 6.6 - Prob. 2ECh. 6.6 - Prob. 3ECh. 6.6 - Prob. 4ECh. 6.6 - Prob. 5ECh. 6.6 - Prob. 6ECh. 6.6 - Prob. 7ECh. 6.6 - Prob. 8ECh. 6.6 - Computing surface areas Find the area of the...Ch. 6.6 - Computing surface areas Find the area of the...Ch. 6.6 - Revolving about the y-axis Find the area of the...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 12ECh. 6.6 - Computing surface areas Find the area of the...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 14ECh. 6.6 - Prob. 15ECh. 6.6 - Prob. 16ECh. 6.6 - Prob. 17ECh. 6.6 - Prob. 18ECh. 6.6 - Prob. 19ECh. 6.6 - Prob. 20ECh. 6.6 - Painting surfaces A 1.5-mm layer of paint is...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 22ECh. 6.6 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 6.6 - T 2629. Surface area using technology Consider the...Ch. 6.6 - T 2629. Surface area using technology Consider the...Ch. 6.6 - Surface area using technology Consider the...Ch. 6.6 - Surface area using technology Consider the...Ch. 6.6 - Surface area using technology Consider the...Ch. 6.6 - Revolving an astroid Consider the upper half of...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 30ECh. 6.6 - Prob. 31ECh. 6.6 - Prob. 32ECh. 6.6 - Prob. 33ECh. 6.6 - Prob. 34ECh. 6.6 - Prob. 35ECh. 6.6 - Prob. 36ECh. 6.6 - Prob. 37ECh. 6.6 - Prob. 38ECh. 6.6 - Surface-area-to-volume ratio (SAV) In the design...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 40ECh. 6.6 - Prob. 41ECh. 6.6 - Surface plus cylinder Suppose f is a nonnegative...Ch. 6.7 - In Figure 6.69, suppose a = 0, b = 3, and the...Ch. 6.7 - Prob. 2QCCh. 6.7 - Prob. 3QCCh. 6.7 - Prob. 4QCCh. 6.7 - In Example 3b, the bucket occupies the interval...Ch. 6.7 - Prob. 6QCCh. 6.7 - Prob. 7QCCh. 6.7 - Suppose a 1-m cylindrical bar has a constant...Ch. 6.7 - Explain how to find the mass of a one-dimensional...Ch. 6.7 - How much work is required to move an object from x...Ch. 6.7 - Why is integration used to find the work done by a...Ch. 6.7 - Why is integration used to find the work required...Ch. 6.7 - Prob. 6ECh. 6.7 - What is the pressure on a horizontal surface with...Ch. 6.7 - Prob. 8ECh. 6.7 - Consider the cylindrical tank in Example 4 that...Ch. 6.7 - Consider the cylindrical tank in Example 4 that...Ch. 6.7 - Consider the cylindrical tank in Example 4 that...Ch. 6.7 - Prob. 12ECh. 6.7 - Mass of one-dimensional objects Find the mass of...Ch. 6.7 - Mass of one-dimensional objects Find the mass of...Ch. 6.7 - Mass of one-dimensional objects Find the mass of...Ch. 6.7 - Prob. 16ECh. 6.7 - Mass of one-dimensional objects Find the mass of...Ch. 6.7 - Mass of one-dimensional objects Find the mass of...Ch. 6.7 - Mass of one-dimensional objects Find the mass of...Ch. 6.7 - Prob. 20ECh. 6.7 - Work from force How much work is required to move...Ch. 6.7 - Prob. 22ECh. 6.7 - Compressing and stretching a spring Suppose a...Ch. 6.7 - Compressing and stretching a spring Suppose a...Ch. 6.7 - Prob. 25ECh. 6.7 - Prob. 26ECh. 6.7 - Prob. 27ECh. 6.7 - Prob. 28ECh. 6.7 - Calculating work for different springs Calculate...Ch. 6.7 - Prob. 30ECh. 6.7 - Winding a chain A 30-m-long chain hangs vertically...Ch. 6.7 - Prob. 32ECh. 6.7 - Winding part of a chain A 20-m-long, 50-kg chain...Ch. 6.7 - Leaky Bucket A 1-kg bucket resting on the ground...Ch. 6.7 - Emptying a swimming pool A swimming pool has the...Ch. 6.7 - Prob. 36ECh. 6.7 - Emptying a half-full cylindrical tank Suppose the...Ch. 6.7 - Prob. 38ECh. 6.7 - Emptying a conical tank A water tank is shaped...Ch. 6.7 - Prob. 40ECh. 6.7 - Filling a spherical tank A spherical water tank...Ch. 6.7 - Emptying a water trough A water trough has a...Ch. 6.7 - Emptying a water trough A cattle trough has a...Ch. 6.7 - Prob. 44ECh. 6.7 - Emptying a conical tank An inverted cone is 2 m...Ch. 6.7 - Force on dams The following figures show the shape...Ch. 6.7 - Force on dams The following figures show the shape...Ch. 6.7 - Force on dams The following figures show the shape...Ch. 6.7 - Force on dams The following figures show the shape...Ch. 6.7 - Prob. 50ECh. 6.7 - Prob. 51ECh. 6.7 - Prob. 52ECh. 6.7 - Prob. 53ECh. 6.7 - Prob. 54ECh. 6.7 - Prob. 55ECh. 6.7 - Prob. 56ECh. 6.7 - Prob. 57ECh. 6.7 - Prob. 58ECh. 6.7 - Prob. 59ECh. 6.7 - Prob. 60ECh. 6.7 - Prob. 61ECh. 6.7 - Prob. 62ECh. 6.7 - Drinking juice A glass has circular cross sections...Ch. 6.7 - Prob. 64ECh. 6.7 - Prob. 65ECh. 6.7 - Prob. 66ECh. 6.7 - Prob. 67ECh. 6.7 - Work by two different integrals A rigid body with...Ch. 6.7 - Work in a gravitational field For large distances...Ch. 6.7 - Prob. 70ECh. 6 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 2RECh. 6 - Prob. 3RECh. 6 - Prob. 4RECh. 6 - Prob. 5RECh. 6 - Prob. 6RECh. 6 - Prob. 7RECh. 6 - Prob. 8RECh. 6 - Prob. 9RECh. 6 - Prob. 10RECh. 6 - Prob. 11RECh. 6 - Prob. 12RECh. 6 - Prob. 13RECh. 6 - Prob. 14RECh. 6 - Prob. 15RECh. 6 - Prob. 16RECh. 6 - Prob. 17RECh. 6 - Prob. 18RECh. 6 - Prob. 19RECh. 6 - Prob. 20RECh. 6 - Prob. 21RECh. 6 - Prob. 22RECh. 6 - Prob. 23RECh. 6 - Prob. 24RECh. 6 - Prob. 25RECh. 6 - Prob. 26RECh. 6 - Prob. 27RECh. 6 - Multiple regions The regions R1, R2, and R3 (see...Ch. 6 - Prob. 29RECh. 6 - Prob. 30RECh. 6 - Prob. 31RECh. 6 - Prob. 32RECh. 6 - Prob. 33RECh. 6 - Prob. 34RECh. 6 - Prob. 35RECh. 6 - Area and volume Let R be the region in the first...Ch. 6 - Prob. 37RECh. 6 - Prob. 38RECh. 6 - Prob. 39RECh. 6 - Prob. 40RECh. 6 - Prob. 41RECh. 6 - Prob. 42RECh. 6 - Prob. 43RECh. 6 - Prob. 44RECh. 6 - Prob. 45RECh. 6 - Prob. 46RECh. 6 - Prob. 47RECh. 6 - Prob. 48RECh. 6 - Prob. 49RECh. 6 - Prob. 50RECh. 6 - Prob. 51RECh. 6 - Prob. 52RECh. 6 - Prob. 53RECh. 6 - Prob. 54RECh. 6 - Prob. 55RECh. 6 - Prob. 56RECh. 6 - Prob. 57RECh. 6 - Prob. 58RECh. 6 - Prob. 59RECh. 6 - Prob. 60RECh. 6 - Prob. 61RECh. 6 - Prob. 62RECh. 6 - Prob. 63RECh. 6 - Prob. 64RECh. 6 - Prob. 65RECh. 6 - Surface area and volume Let f(x)=13x3 and let R be...Ch. 6 - Surface area and volume Let f(x)=3xx2 and let R be...Ch. 6 - Prob. 68RECh. 6 - Surface area and more Let f(x)=x42+116x2 and let R...Ch. 6 - Prob. 70RECh. 6 - Prob. 71RECh. 6 - Prob. 72RECh. 6 - Prob. 73RECh. 6 - Leaky bucket A 1-kg bucket resting on the ground...Ch. 6 - Prob. 75RECh. 6 - Prob. 76RECh. 6 - Pumping water A water tank has the shape of a box...Ch. 6 - Prob. 78RECh. 6 - Prob. 79RECh. 6 - Prob. 80RECh. 6 - Prob. 81RECh. 6 - Prob. 82RECh. 6 - Fluid Forces Suppose the Mowing plates are placed...Ch. 6 - Prob. 84RECh. 6 - Prob. 85RECh. 6 - Prob. 86RE
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. Consider the vector force: F(x, y, z) = 2xye²i + (x²e² + y)j + (x²ye² — z)k. (A) [80%] Show that F satisfies the conditions for a conservative vector field, and find a potential function (x, y, z) for F. Remark: To find o, you must use the method explained in the lecture. (B) [20%] Use the Fundamental Theorem for Line Integrals to compute the work done by F on an object moves along any path from (0,1,2) to (2, 1, -8).arrow_forwardhelp pleasearrow_forwardIn each of Problems 1 through 4, draw a direction field for the given differential equation. Based on the direction field, determine the behavior of y as t → ∞. If this behavior depends on the initial value of y at t = 0, describe the dependency.1. y′ = 3 − 2yarrow_forward
- B 2- The figure gives four points and some corresponding rays in the xy-plane. Which of the following is true? A B Angle COB is in standard position with initial ray OB and terminal ray OC. Angle COB is in standard position with initial ray OC and terminal ray OB. C Angle DOB is in standard position with initial ray OB and terminal ray OD. D Angle DOB is in standard position with initial ray OD and terminal ray OB.arrow_forwardtemperature in degrees Fahrenheit, n hours since midnight. 5. The temperature was recorded at several times during the day. Function T gives the Here is a graph for this function. To 29uis a. Describe the overall trend of temperature throughout the day. temperature (Fahrenheit) 40 50 50 60 60 70 5 10 15 20 25 time of day b. Based on the graph, did the temperature change more quickly between 10:00 a.m. and noon, or between 8:00 p.m. and 10:00 p.m.? Explain how you know. (From Unit 4, Lesson 7.) 6. Explain why this graph does not represent a function. (From Unit 4, Lesson 8.)arrow_forwardFind the area of the shaded region. (a) 5- y 3 2- (1,4) (5,0) 1 3 4 5 6 (b) 3 y 2 Decide whether the problem can be solved using precalculus, or whether calculus is required. If the problem can be solved using precalculus, solve it. If the problem seems to require calculus, use a graphical or numerical approach to estimate the solution. STEP 1: Consider the figure in part (a). Since this region is simply a triangle, you may use precalculus methods to solve this part of the problem. First determine the height of the triangle and the length of the triangle's base. height 4 units units base 5 STEP 2: Compute the area of the triangle by employing a formula from precalculus, thus finding the area of the shaded region in part (a). 10 square units STEP 3: Consider the figure in part (b). Since this region is defined by a complicated curve, the problem seems to require calculus. Find an approximation of the shaded region by using a graphical approach. (Hint: Treat the shaded regi as…arrow_forward
- Solve this differential equation: dy 0.05y(900 - y) dt y(0) = 2 y(t) =arrow_forwardSuppose that you are holding your toy submarine under the water. You release it and it begins to ascend. The graph models the depth of the submarine as a function of time. What is the domain and range of the function in the graph? 1- t (time) 1 2 4/5 6 7 8 -2 -3 456700 -4 -5 -6 -7 d (depth) -8 D: 00 t≤ R:arrow_forward0 5 -1 2 1 N = 1 to x = 3 Based on the graph above, estimate to one decimal place the average rate of change from x =arrow_forwardComplete the description of the piecewise function graphed below. Use interval notation to indicate the intervals. -7 -6 -5 -4 30 6 5 4 3 0 2 1 -1 5 6 + -2 -3 -5 456 -6 - { 1 if x Є f(x) = { 1 if x Є { 3 if x Єarrow_forwardComplete the description of the piecewise function graphed below. 6 5 -7-6-5-4-3-2-1 2 3 5 6 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 { f(x) = { { -6 if -6x-2 if -2< x <1 if 1 < x <6arrow_forwardLet F = V where (x, y, z) x2 1 + sin² 2 +z2 and let A be the line integral of F along the curve x = tcost, y = t sint, z=t, starting on the plane z = 6.14 and ending on the plane z = 4.30. Then sin(3A) is -0.598 -0.649 0.767 0.278 0.502 0.010 -0.548 0.960arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...
Algebra
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL


Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...
Algebra
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:McGraw Hill

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:9780395977224
Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:McDougal Littell

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781337798310
Author:Peterson, John.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Problems on Area and Circumference of Circle| Basics of Circle| Questions on Circle||BrainPanthers; Author: Brain Panthers;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RcNEL9OzcC0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY