
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780100257061
Author: BEER
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 94RP
Knowing that a given vertical shear V causes a maximum shearing stress of 75 MPa in the hat-shaped extrusion shown, determine the corresponding shearing stress at (a) point a, (b) point b.
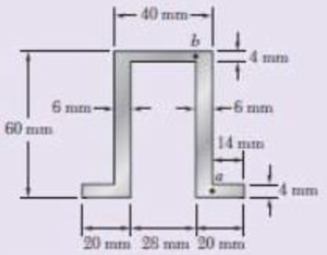
Fig. p6.94
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Need help, please show all work, steps, units and please box out and round answers to 3 significant figures. Thank you!...
FL
y
b
C
Z
Determine the moment about O due to the force F shown,
the magnitude of the force F = 76.0 lbs. Note: Pay attention
to the axis.
Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following
table. Note the figure may not be to scale.
Variable Value
a
1.90 ft
b
2.80 ft
с
2.60 ft
d
2.30 ft
Mo
144
ft-lb
=
-212
× 1 +
xk)
☑+212
20 in.
PROBLEM 15.206
Rod AB is connected by ball-and-socket joints to collar A and to the
16-in.-diameter disk C. Knowing that disk C rotates counterclockwise at
the constant rate ₁ =3 rad/s in the zx plane, determine the velocity of
collar A for the position shown.
25 in.
B
8 in.
Answer: -30 in/s
=
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
Ch. 6.2 - Three full-size 50 100-mm boards are nailed...Ch. 6.2 - For the built-up beam of Prob. 6.1, determine the...Ch. 6.2 - Three boards, each 2 in. thick, are nailed...Ch. 6.2 - A square box beam is made of two 20 80-mm planks...Ch. 6.2 - The American Standard rolled-steel beam shown has...Ch. 6.2 - The beam shown is fabricated by connecting two...Ch. 6.2 - A column is fabricated by connecting the...Ch. 6.2 - The composite beam shown is fabricated by...Ch. 6.2 - 6.9 through 6.12 For beam and loading shown,...Ch. 6.2 - 6.9 through 6.12 For beam and loading shown,...
Ch. 6.2 - 6.9 through 6.12 For beam and loading shown,...Ch. 6.2 - 6.9 through 6.12 For beam and loading shown,...Ch. 6.2 - 6.13 and 6.14 For a beam having the cross section...Ch. 6.2 - 6.13 and 6.14 For a beam having the cross section...Ch. 6.2 - For a timber beam having the cross section shown,...Ch. 6.2 - Two steel plates of 12 220-mm rectangular cross...Ch. 6.2 - Two W8 31 rolled sections may be welded at A and...Ch. 6.2 - For the beam and. loading shown, determine the...Ch. 6.2 - Fig. P6.19 6.19 A timber beam AB of length L and...Ch. 6.2 - A timber beam AB of Length L and rectangular cross...Ch. 6.2 - 6.21 and 6.22 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 6.2 - 6.21 and 6.22 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 6.2 - 6.23 and 6.24 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 6.2 - 6.23 and 6.24 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 6.2 - 6.25 through 6.28 A beam having the cross section...Ch. 6.2 - 6.25 through 6.28 A beam having the cross section...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 27PCh. 6.2 - 6.25 through 6.28 A beam having the cross section...Ch. 6.5 - The built-up timber beam shown is subjected to a...Ch. 6.5 - The built-up beam shown is made by gluing together...Ch. 6.5 - The built-up beam was made by gluing together...Ch. 6.5 - Several wooden planks are glued together to form...Ch. 6.5 - The built-up wooden beam shown is subjected to a...Ch. 6.5 - Knowing that a W360 122 rolled-steel beam is...Ch. 6.5 - 6.35 and 6.36 An extruded aluminum beam has the...Ch. 6.5 - 6.35 and 6.36 An extruded aluminum beam has the...Ch. 6.5 - Knowing that a given vertical shear V causes a...Ch. 6.5 - The vertical shear is 1200 lb in a beam having the...Ch. 6.5 - The vertical shear is 1200 lb in a beam having the...Ch. 6.5 - 6.40 and 6.47 The extruded aluminum beam has a...Ch. 6.5 - Prob. 41PCh. 6.5 - Prob. 42PCh. 6.5 - Three planks are connected as shown by bolts of...Ch. 6.5 - A beam consists of three planks connected as shown...Ch. 6.5 - A beam consists of five planks of 1.5 6-in. cross...Ch. 6.5 - Four L102 102 9.5 steel angle shapes and a 12 ...Ch. 6.5 - A plate of 14-in. thickness is corrugated as shown...Ch. 6.5 - Prob. 48PCh. 6.5 - An extruded beam has the cross section shown and a...Ch. 6.5 - Prob. 50PCh. 6.5 - The design of a beam calls for connecting two...Ch. 6.5 - The cross section of an extruded beam is a hollow...Ch. 6.5 - Prob. 53PCh. 6.5 - Prob. 54PCh. 6.5 - Prob. 55PCh. 6.5 - 6.56 and 6.57 A composite beam is made by...Ch. 6.5 - 6.56 and 6.57 A composite beam is made by...Ch. 6.5 - Prob. 58PCh. 6.5 - Prob. 59PCh. 6.5 - Prob. 60PCh. 6.6 - 6.61 through 6.64 Determine the location of the...Ch. 6.6 - 6.61 through 6.64 Determine the location of the...Ch. 6.6 - 6.61 through 6.64 Determine the location of the...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 64PCh. 6.6 - 6.65 through 6.68 An extruded beam has the cross...Ch. 6.6 - 6.65 through 6.68 An extruded beam has the cross...Ch. 6.6 - 6.65 through 6.68 An extruded beam has the cross...Ch. 6.6 - 6.65 through 6.68 An extruded beam has the cross...Ch. 6.6 - 6.69 through 6.74 Determine the location of the...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 70PCh. 6.6 - Prob. 71PCh. 6.6 - Prob. 72PCh. 6.6 - Prob. 73PCh. 6.6 - Prob. 74PCh. 6.6 - Prob. 75PCh. 6.6 - 6.75 and 6.76 A thin-walled beam has the cross...Ch. 6.6 - 6.77 and 6.78 A thin-walled beam of uniform...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 78PCh. 6.6 - Prob. 79PCh. 6.6 - Prob. 80PCh. 6.6 - Prob. 81PCh. 6.6 - Prob. 82PCh. 6.6 - Prob. 83PCh. 6.6 - Prob. 84PCh. 6.6 - Prob. 85PCh. 6.6 - Solve Prob. 6.85, assuming that the thickness of...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 87PCh. 6.6 - Prob. 88PCh. 6 - Three boards are nailed together to form the beam...Ch. 6 - For the beam and loading shown, consider section...Ch. 6 - For the wide-flange beam with the loading shown,...Ch. 6 - For the beam and loading shown, consider section...Ch. 6 - The built-up timber beam is subjected to a 1500-lb...Ch. 6 - Knowing that a given vertical shear V causes a...Ch. 6 - Three planks are connected as shown by bolts of...Ch. 6 - Three 1 18-in. steel plates are bolted to four L6...Ch. 6 - The composite beam shown is made by welding C200 ...Ch. 6 - Prob. 98RPCh. 6 - A thin-walled beam of uniform thickness has the...Ch. 6 - Determine the location of the shear center O of a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- B Z 001 2.5 ft PROBLEM 15.236 The arm AB of length 16 ft is used to provide an elevated platform for construction workers. In the position shown, arm AB is being raised at the constant rate de/dt = 0.25 rad/s; simultaneously, the unit is being rotated about the Y axis at the constant rate ₁ =0.15 rad/s. Knowing that 20°, determine the velocity and acceleration of Point B. Answers: 1.371 +3.76)+1.88k ft/s a=1.22 -0.342)-0.410k ft/s² Xarrow_forwardF1 3 5 4 P F2 F2 Ꮎ Ꮎ b P 3 4 5 F1 The electric pole is subject to the forces shown. Force F1 245 N and force F2 = 310 N with an angle = 20.2°. Determine the moment about point P of all forces. Take counterclockwise moments to be positive. = Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 2.50 m b 11.3 m C 13.0 m The moment about point P is 3,414 m. × N- If the moment about point P sums up to be zero. Determine the distance c while all other values remained the same. 1.26 m.arrow_forwardZ 0.2 m B PROBLEM 15.224 Rod AB is welded to the 0.3-m-radius plate, which rotates at the constant rate ₁ = 6 rad/s. Knowing that collar D moves toward end B of the rod at a constant speed u = 1.3 m, determine, for the position shown, (a) the velocity of D, (b) the acceleration of D. Answers: 1.2 +0.5-1.2k m/s a=-7.21-14.4k m/s² A 0.25 m 0.3 marrow_forward
- I am trying to code in MATLAB the equations of motion for malankovich orbitlal elements. But, I am having a problem with the B matrix. Since f matrix is 7x1 and a_d matrix has to be 3x1, the B matrix has to be 7x3. I don't know how that is possible. Can you break down the B matrix for me and let me know what size it is?arrow_forwardI am trying to code the solution to the problem in the image in MATLAB. I wanted to know what is the milankovich constraint equation that is talked about in part b.arrow_forwardmylabmastering.pearson.com Chapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Scoresarrow_forwardAir modeled as an ideal gas enters an insulated compressor at a temperature of 300 K and 100 kPa, and leaves at 600 kPa. The mass flowrate of air entering the compressor is 50 kg/hr, and the power consumed by the compressor is 3 kW. (Rair = 0.287 kJ/kg-K, k = 1.4, cp = 1.0045 kJ/kg-K, cv = 0.718 kJ/kg-K) Determine the isentropic exit temperature (Te,s) of the air in [K]. Determine the actual exit temperature (Te) of the air in [K]. Determine the isentropic efficiency of the compressor. (Answer: ηc,s = 93.3%) Determine the rate of entropy generated through the compressor in [kW/K]. (Answer: Ṡgen = 0.000397 kW/K)arrow_forwardmylabmastering.pearson.com Chapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Scoresarrow_forwardA metal plate of thickness 200 mm with thermal diffusivity 5.6 x10-6 m²/s and thermal conductivity 20 W/mK is initially at a uniform temperature of 325°C. Suddenly, the 2 sides of the plate are exposed to a coolant at 15°C for which the convection heat transfer coefficient is 100 W/m²K. Determine temperatures at the surface of the plate after 3 min using (a) Lumped system analysis (b) Analytical one term approximation (c) One dimensional Semi infinite solid Analyze and discuss the resultsarrow_forwardProblem 3 This problem maps back to learning objectives 1-4 & 8. Consider the particle attached to a spring shown below. The particle has a mass m and the spring has a spring constant k. The mass-spring system makes an angle of 0 with respect to the vertical and the distance between point 0 and the particle can be defined as r. The spring is unstretched when r = l. Ꮎ g m a) How many degrees of freedom is this system and what are they? b) Derive the equation(s) of motion that govern the movement of this system.arrow_forwardChapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... Scores ■Review Determine the maximum constant speed at which the pilot can travel, so that he experiences a maximum acceleration an = 8g = 78.5 m/s². Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. μΑ v = Value Units Submit Request Answer Part B ? Determine the normal force he exerts on the seat of the airplane when the plane is traveling at this speed and is at its lowest point. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. о HÅ N = Value Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? Units Next >arrow_forwardI want to know the Milankovich orbital element constraint equation. Is it e*cos(i) = cos(argp), where e is eccentricity, i is inclination, and argp is arguement of periapsisarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Understanding Stress Transformation and Mohr's Circle; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_DH3546mSCM;License: Standard youtube license