
Concept explainers
The triangular waveform in Fig. 6.91(a) is applied to the input of the op amp differentiator in Fig. 6.91(b). Plot the output.
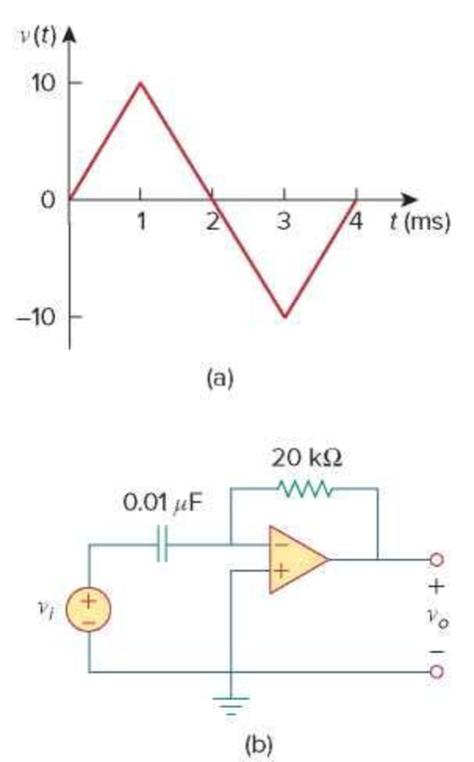
Figure 6.91
For Prob. 6.74.
Sketch the output voltage waveform of an op amp differentiator.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Figure 6.91 in the textbook.
Formula used:
Write the expression to calculate the straight line equation for two points
Refer to Figure 6.91(a) in the textbook.
From the given voltage graph, substitute
Write the expression to calculate the output voltage of an op amp differentiator.
Here,
Calculation:
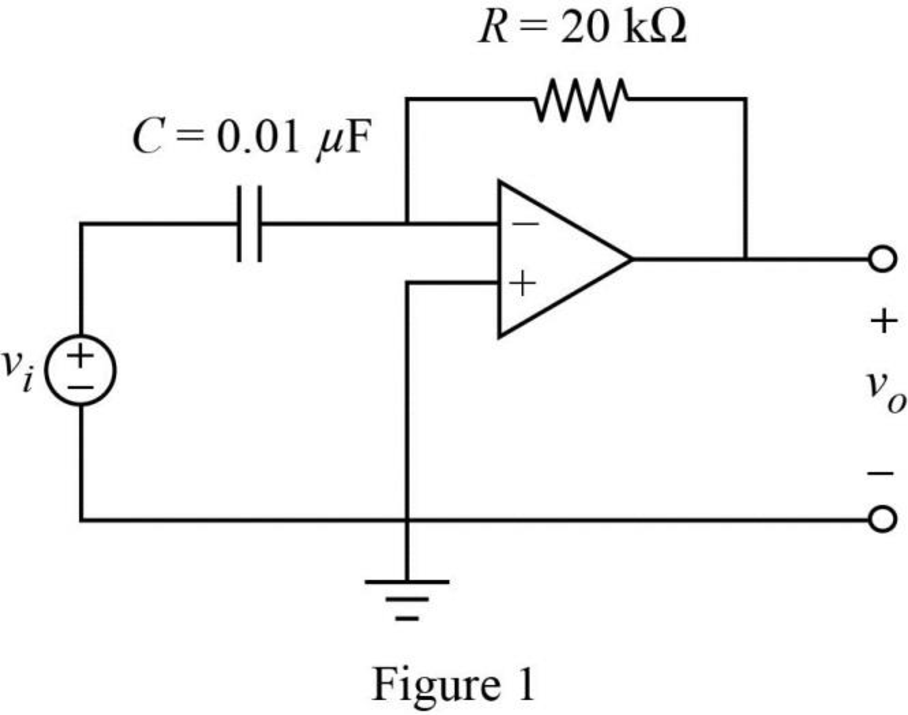
The given circuit is redrawn as Figure 1.
Substitute
The given input voltage waveform is redrawn as Figure 2.
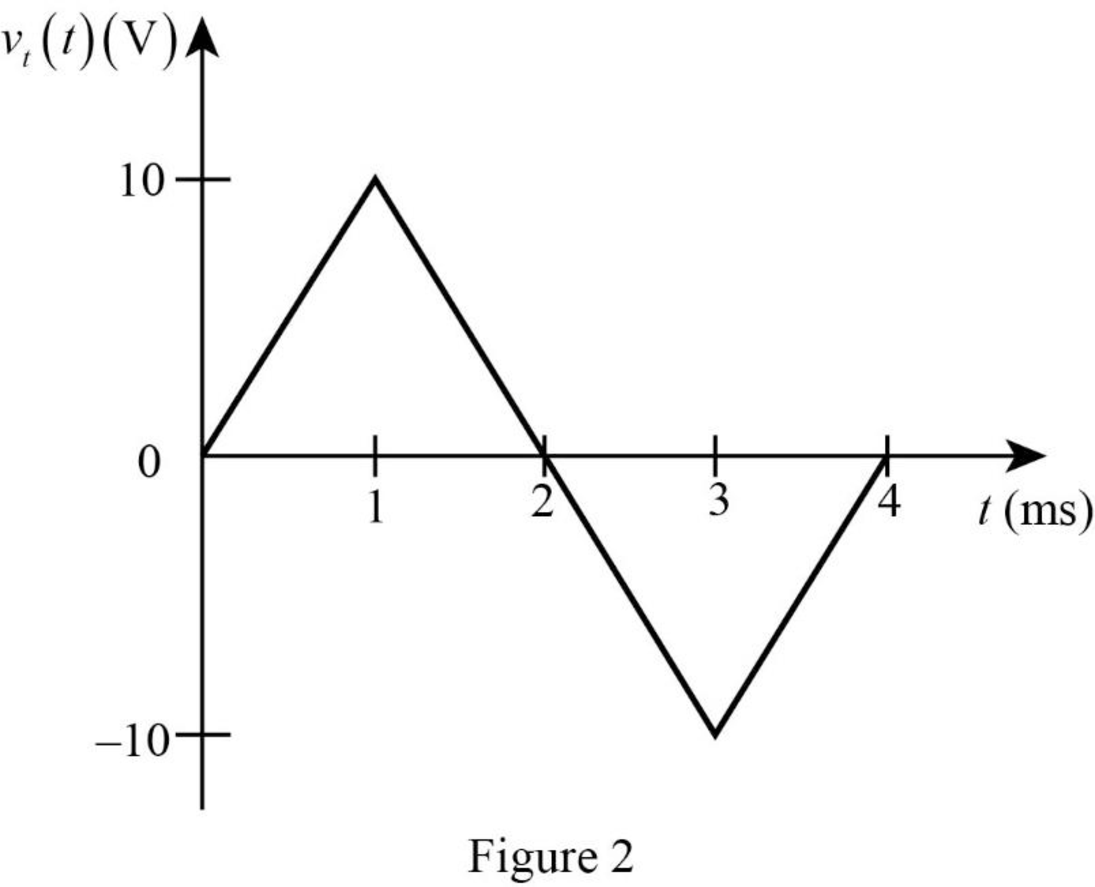
Refer to Figure 2, split up the time period as three divisions such as
Case (i):
The two points
Substitute
Simplify the equation to find
Case (ii):
The two points
Substitute
Simplify the equation to find
Case (iii):
The two points
Substitute
Simplify the equation to find
Therefore, the input voltage function
For
Substitute
Simplify the equation to find
For
Substitute
Simplify the equation to find
For
Substitute
Simplify the equation to find
Therefore, the output voltage function
The output voltage waveform is drawn as Figure 3.
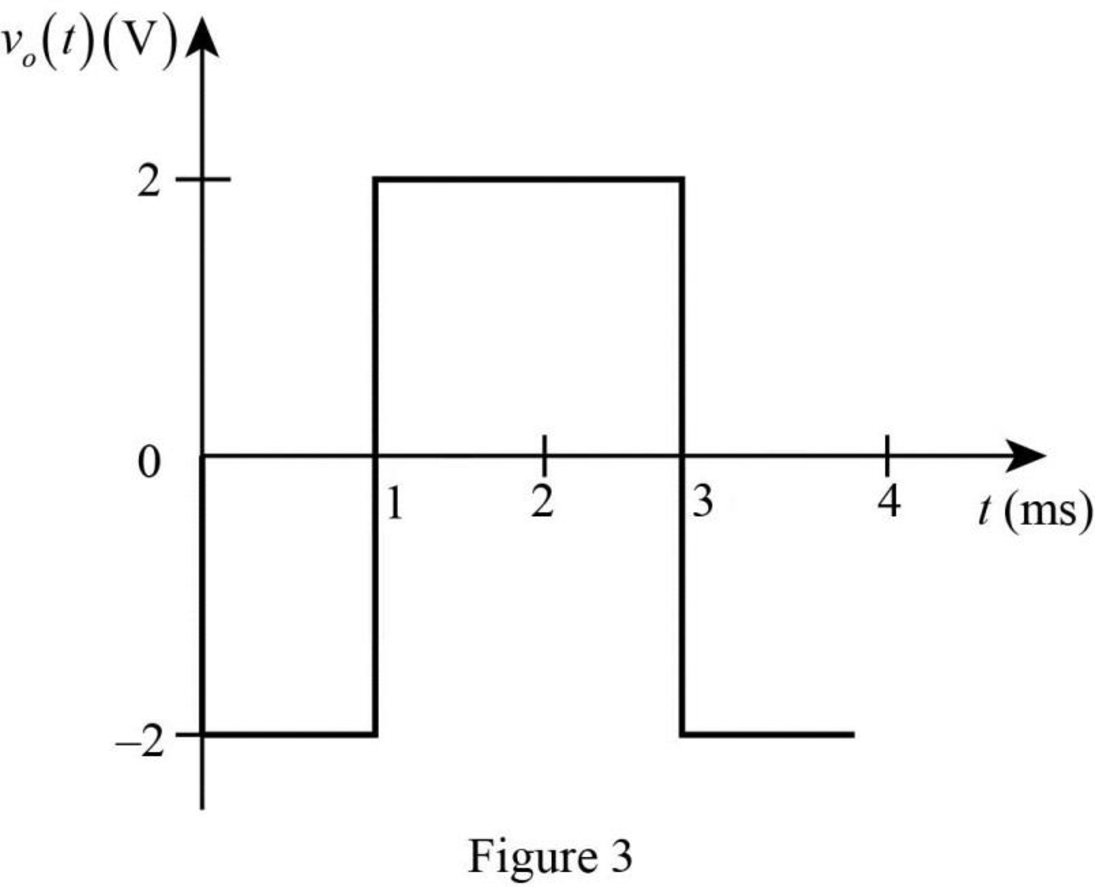
Conclusion:
Thus, the output voltage waveform of an op amp differentiator
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
- : Write VHDL code to implement the finite-state machine/described by the state Diagram in Fig. 4. X=1 X=0 solo X=1 X=0 $1/1 X=0 X=1 X=1 52/2 $3/3 X=1 Fig. 4 X=1 X=1 56/6 $5/5 X=1 54/4 X=0 X-O X=O 5=0 57/7arrow_forwardQuestions: Q1: Verify that the average power generated equals the average power absorbed using the simulated values in Table 7-2. Q2: Verify that the reactive power generated equals the reactive power absorbed using the simulated values in Table 7-2. Q3: Why it is important to correct the power factor of a load? Q4: Find the ideal value of the capacitor theoretically that will result in unity power factor. Vs pp (V) VRIPP (V) VRLC PP (V) AT (μs) T (us) 8° pf Simulated 14 8.523 7.84 84.850 1000 29.88 0.866 Measured 14 8.523 7.854 82.94 1000 29.85 0.86733 Table 7-2 Power Calculations Pvs (mW) Qvs (mVAR) PRI (MW) Pay (mW) Qt (mVAR) Qc (mYAR) Simulated -12.93 -7.428 9.081 3.855 12.27 -4.84 Calculated -12.936 -7.434 9.083 3.856 12.32 -4.85 Part II: Power Factor Correction Table 7-3 Power Factor Correction AT (us) 0° pf Simulated 0 0 1 Measured 0 0 1arrow_forwardQuestions: Q1: Verify that the average power generated equals the average power absorbed using the simulated values in Table 7-2. Q2: Verify that the reactive power generated equals the reactive power absorbed using the simulated values in Table 7-2. Q3: Why it is important to correct the power factor of a load? Q4: Find the ideal value of the capacitor theoretically that will result in unity power factor. Vs pp (V) VRIPP (V) VRLC PP (V) AT (μs) T (us) 8° pf Simulated 14 8.523 7.84 84.850 1000 29.88 0.866 Measured 14 8.523 7.854 82.94 1000 29.85 0.86733 Table 7-2 Power Calculations Pvs (mW) Qvs (mVAR) PRI (MW) Pay (mW) Qt (mVAR) Qc (mYAR) Simulated -12.93 -7.428 9.081 3.855 12.27 -4.84 Calculated -12.936 -7.434 9.083 3.856 12.32 -4.85 Part II: Power Factor Correction Table 7-3 Power Factor Correction AT (us) 0° pf Simulated 0 0 1 Measured 0 0 1arrow_forward
- electric plants. Prepare the load schedulearrow_forwardelectric plants Draw the column diagram. Calculate the voltage drop. by hand writingarrow_forwardelectric plants. Draw the lighting, socket, telephone, TV, and doorbell installations on the given single-story project with an architectural plan by hand writingarrow_forward
- A circularly polarized wave, traveling in the +z-direction, is received by an elliptically polarized antenna whose reception characteristics near the main lobe are given approx- imately by E„ = [2â, + jâ‚]ƒ(r. 8, 4) Find the polarization loss factor PLF (dimensionless and in dB) when the incident wave is (a) right-hand (CW) An elliptically polarized wave traveling in the negative z-direction is received by a circularly polarized antenna. The vector describing the polarization of the incident wave is given by Ei= 2ax + jay.Find the polarization loss factor PLF (dimensionless and in dB) when the wave that would be transmitted by the antenna is (a) right-hand CParrow_forwardjX(1)=j0.2p.u. jXa(2)=j0.15p.u. jxa(0)=0.15 p.u. V₁=1/0°p.u. V₂=1/0° p.u. 1 jXr(1) = j0.15 p.11. jXT(2) = j0.15 p.u. jXr(0) = j0.15 p.u. V3=1/0° p.u. А V4=1/0° p.u. 2 jX1(1)=j0.12 p.u. 3 jX2(1)=j0.15 p.u. 4 jX1(2)=0.12 p.11. JX1(0)=0.3 p.u. jX/2(2)=j0.15 p.11. X2(0)=/0.25 p.1. Figure 1. Circuit for Q3 b).arrow_forwardcan you show me full workings for this problem. the solution is - v0 = 10i2 = 2.941 volts, i0 = i1 – i2 = (5/3)i2 = 490.2mA.arrow_forward
- Q4. a) Consider a transmission line modelled as a four-terminal network with an unknown configuration. You are provided with the following measured parameters at the operating frequency: Open-circuit voltage ratio: 0.9521° • Short-circuit impedance: 40+j80 • Open-circuit admittance: -j2 × 10-4 S Use the four terminal equations and the provided measurements to mathematically derive the A, B, C, and D parameters of the network and explain their physical significance. Show your work and formulas used in the derivation.arrow_forwardQ1. Consider a single-phase step-down transformer with primary and secondary turns of 600 and 100 respectively and a primary voltage of 11 kV. (i) An open circuit test was conducted on the transformer and the primary current was measured as: I₁ = 2.20 A Use these results to calculate the magnetising reactance in the equivalent circuit (X) given that Rm, representing the core loss, has a value of 21 km. (ii) The remaining equivalent circuit parameters are as follows: R₁ = 40, X₁ = 25 N, R₂ = 0.4 N, X₂ = 0.3 N Draw the complete simplified equivalent circuit, by referring series components on the primary side to the secondary, giving all component values. (iii) The transformer is connected, on its secondary side, to a load of 10 at a power factor of 1. Calculate the voltage across the load. (iv) Calculate the efficiency of the transformer when operating at the load given in part (iii).arrow_forwardb) A 132 kV supply feeds a line of reactance 15 which is connected to a 100 MVA, 132/33 kV transformer of 0.08 p.u. reactance as shown in the Figure 2. The transformer feeds a 33 kV line of reactance 8 Q, which, in turn, is connected to a 75 MVA, 33/11 KV transformer of 0.12 p.u. reactance. The transformer supplies an 11 KV substation from which a local 11 kV feeder of 4 Q reactance is supplied. T1 T2 132 kV 33 kV 11 kV Fault X CB Relay Figure 2. Network for Q4 b). (i) Given the system base of 100 MVA, compute the total equivalent reactance of the radial circuit in per unit (p.u.). (ii) Determine the three-phase fault current at the load end of the 11 kV feeder, assuming a fault impedance of 0.05 Q. Calculate the fault current in Amperes. (iii) The 11 kV feeder connects to a protective overcurrent relay via 200/5 A current transformers. This relay has a standard normally inverse IDMT characteristic, with a setting current of 3 A and a time multiplier setting of 0.4. Calculate the…arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





