
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305116399
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 6.16P
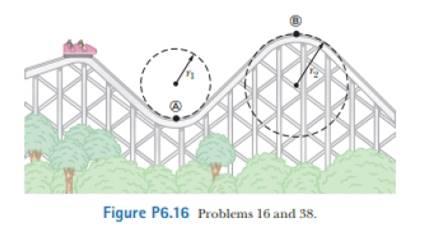
A roller-coaster car (Fig. P6.16) has a mass of 500 kg when fully loaded with passengers. The path of the ca coaster from its initial point shown in the figure to point Ⓑ involves only up-and-down motion (as seen by the riders), with no motion to the left or right, (a) If the vehicle has a speed of 20.0 m/s at point Ⓐ. what is the force exerted by the track on the car at this point? (b) What is the maximum speed the vehicle can have at point Ⓑ and still remain on the track? Assume the roller-coaster tracks at points Ⓐ andl Ⓑ are parts of vertical circles of radius r1 = 10.0 m and i2 = 15.0 m, respectively.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Imagine a planet where gravity mysteriously acts tangent to the equator and in the eastward directioninstead of radially inward. Would this force do work on an object moving on the earth? What is the sign ofthe work, and does it depend on the path taken? Explain by using the work integral and provide a sketch ofthe force and displacement vectors. Provide quantitative examples.
If a force does zero net work on an object over a closed loop, does that guarantee the force is conservative? Explain with an example or counterexample
A futuristic amusement ride spins riders in a horizontal circle of radius 5 m at a constant speed. Thefloor drops away, leaving riders pinned to the wall by friction (coefficient µ = 0.4). What minimum speedensures they don’t slip, given g = 10 m/s²? Draw diagram (or a few) showing all forces, thevelocity of the rider, and their acceleration
Chapter 6 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
Ch. 6 - You are riding on a Ferris wheel that is rotating...Ch. 6 - A bead slides at constant speed along a curved...Ch. 6 - Consider the passenger in the car making a left...Ch. 6 - A basketball and a 2-inch-diameter steel ball,...Ch. 6 - A child is practicing for a BMX race. His speed...Ch. 6 - Consider a skydive r who has stepped from a...Ch. 6 - A door in a hospital has a pneumatic closer that...Ch. 6 - A pendulum consists of a small object called a bob...Ch. 6 - As a raindrop falls through the atmosphere, its...Ch. 6 - An office door is given a sharp push and swings...
Ch. 6 - Before takeoff on an airplane, an inquisitive...Ch. 6 - What forces cause (a) an automobile, (b) a...Ch. 6 - A falling skydiver reaches terminal speed with her...Ch. 6 - An object executes circular motion with constant...Ch. 6 - Describe the path of a moving body in the event...Ch. 6 - The observer in the accelerating elevator of...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.6CQCh. 6 - It has been suggested dial rotating cylinders...Ch. 6 - Consider a small raindrop and a large raindrop...Ch. 6 - Why does a pilot lend to black out when pulling...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.10CQCh. 6 - If the current position and velocity of every...Ch. 6 - A light string can support a stationary hanging...Ch. 6 - Whenever two Apollo astronauts were on the surface...Ch. 6 - In the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, an...Ch. 6 - A curve in a road forms part of a horizontal...Ch. 6 - In a cyclotron (one type of particle accelerator),...Ch. 6 - A car initially traveling eastward turns north by...Ch. 6 - A space station, in the form of a wheel 120 m in...Ch. 6 - Consider a conical pendulum (Fig. P6.8) with a bob...Ch. 6 - A coin placed 30.0 cm from the center of a...Ch. 6 - Why is the following situation impossible? The...Ch. 6 - A crate of eggs is located in the middle of the...Ch. 6 - A pail of water is rotated in a vertical circle of...Ch. 6 - A hawk flies in a horizontal arc of radius 12.0 m...Ch. 6 - A 40.0-kg child swings in a swing supported by two...Ch. 6 - A child of mass m swings in a swing supported by...Ch. 6 - A roller-coaster car (Fig. P6.16) has a mass of...Ch. 6 - A roller coaster at the Six Flags Great America...Ch. 6 - One end of a cord is fixed and a small 0.500-kg...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.19PCh. 6 - An object of mass m = 5.00 kg, attached to a...Ch. 6 - All object of mass m = 500 kg is suspended from...Ch. 6 - A child lying on her back experiences 55.0 N...Ch. 6 - A person stands on a scale in an elevator. As the...Ch. 6 - Review. A student, along with her backpack on the...Ch. 6 - A small container of water is placed on a...Ch. 6 - Review. (a) Estimate the terminal speed of a...Ch. 6 - The mass of a sports car is 1 200 kg. The shape of...Ch. 6 - A skydiver of mass 80.0 kg jumps from a...Ch. 6 - Calculate the force required to pull a copper ball...Ch. 6 - A small piece of Styrofoam packing material is...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.31PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.32PCh. 6 - Assume the resistive force acting on a speed...Ch. 6 - Review. A window washer pulls a rubber squeegee...Ch. 6 - A motorboat cuts its engine when its speed is 10.0...Ch. 6 - You can feel a force of air drag on your hand if...Ch. 6 - A car travels clockwise at constant speed around a...Ch. 6 - The mass of a roller-coaster car, including its...Ch. 6 - A string under a tension of 50.0 N is used to...Ch. 6 - Disturbed by speeding cars outside his workplace,...Ch. 6 - A car of mass m passes over a hump in a road that...Ch. 6 - A childs toy consists of a small wedge that has an...Ch. 6 - A seaplane of total mass m lands on a lake with...Ch. 6 - An object of mass m1 = 4.00 kg is tied to an...Ch. 6 - A ball of mass m = 0.275 kg swings in a vertical...Ch. 6 - Why is the following situation impossible? A...Ch. 6 - (a) A luggage carousel at an airport has the form...Ch. 6 - In a home laundry dryer, a cylindrical tub...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.49APCh. 6 - A basin surrounding a drain has the shape of a...Ch. 6 - A truck is moving with constant acceleration a up...Ch. 6 - The pilot of an airplane executes a loop-the-loop...Ch. 6 - Review. While learning to drive, you arc in a 1...Ch. 6 - A puck of mass m1 is tied to a string and allowed...Ch. 6 - Because the Earth rotates about its axis, a point...Ch. 6 - Galileo thought about whether acceleration should...Ch. 6 - Figure P6.57 shows a photo of a swing a ride at an...Ch. 6 - Review. A piece of putty is initially located at...Ch. 6 - An amusement park ride consists of a large...Ch. 6 - Members of a skydiving club were given the...Ch. 6 - A car rounds a banked curve as discussed in...Ch. 6 - In Example 6.5, we investigated the forces a child...Ch. 6 - A model airplane of mass 0.750 kg flies with a...Ch. 6 - A student builds and calibrates an accelerometer...Ch. 6 - A 9.00-kg object starting from rest falls through...Ch. 6 - For t 0, an object of mass m experiences no force...Ch. 6 - A golfer tees off from a location precisely at i =...Ch. 6 - A single bead can slide with negligible friction...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.69CPCh. 6 - Because of the Earths rotation, a plumb bob does...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Your RL circuit has a characteristic time constant of 19.5 ns, and a resistance of 4.60 MQ. (a) What is the inductance (in H) of the circuit? 0.00897 × H (b) What resistance (in MQ) should you use (instead of the 4.60 MQ resistor) to obtain a 1.00 ns time constant, perhaps needed for quick response in an oscilloscope? 8.97 * ΜΩarrow_forwardYour RL circuit has a characteristic time constant of 19.5 ns, and a resistance of 4.60 MQ. (a) What is the inductance (in H) of the circuit? H (b) What resistance (in MQ) should you use (instead of the 4.60 MQ resistor) to obtain a 1.00 ns time constant, perhaps needed for quick response in an oscilloscope? ΜΩarrow_forwardAt a distance of 0.212 cm from the center of a charged conducting sphere with radius 0.100cm, the electric field is 485 N/C . What is the electric field 0.598 cm from the center of the sphere? At a distance of 0.196 cmcm from the axis of a very long charged conducting cylinder with radius 0.100cm, the electric field is 485 N/C . What is the electric field 0.620 cm from the axis of the cylinder? At a distance of 0.202 cm from a large uniform sheet of charge, the electric field is 485 N/C . What is the electric field 1.21 cm from the sheet?arrow_forward
- A hollow, conducting sphere with an outer radius of 0.260 m and an inner radius of 0.200 m has a uniform surface charge density of +6.67 × 10−6 C/m2. A charge of -0.800 μC is now introduced into the cavity inside the sphere. What is the new charge density on the outside of the sphere? Calculate the strength of the electric field just outside the sphere. What is the electric flux through a spherical surface just inside the inner surface of the sphere?arrow_forwardA point charge of -3.00 μC is located in the center of a spherical cavity of radius 6.60 cm inside an insulating spherical charged solid. The charge density in the solid is 7.35 × 10−4 C/m3. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field inside the solid at a distance of 9.10 cm from the center of the cavity. Find the direction of this electric field.arrow_forwardAn infinitely long conducting cylindrical rod with a positive charge λ per unit length is surrounded by a conducting cylindrical shell (which is also infinitely long) with a charge per unit length of −2λ and radius r1, as shown in the figure. What is E(r), the radial component of the electric field between the rod and cylindrical shell as a function of the distance r from the axis of the cylindrical rod? Express your answer in terms of λ, r, and ϵ0, the permittivity of free space. What is σinner, the surface charge density (charge per unit area) on the inner surface of the conducting shell? What is σouterσouter, the surface charge density on the outside of the conducting shell? (Recall from the problem statement that the conducting shell has a total charge per unit length given by −2λ.) What is the radial component of the electric field, E(r), outside the shell?arrow_forward
- A very long conducting tube (hollow cylinder) has inner radius aa and outer radius b. It carries charge per unit length +α, where αα is a positive constant with units of C/m. A line of charge lies along the axis of the tube. The line of charge has charge per unit length +α. Calculate the electric field in terms of α and the distance r from the axis of the tube for r<a. Calculate the electric field in terms of α and the distance rr from the axis of the tube for a<r<b. Calculate the electric field in terms of αα and the distance r from the axis of the tube for r>b. What is the charge per unit length on the inner surface of the tube? What is the charge per unit length on the outer surface of the tube?arrow_forwardTwo small insulating spheres with radius 9.00×10−2 m are separated by a large center-to-center distance of 0.545 m . One sphere is negatively charged, with net charge -1.75 μC , and the other sphere is positively charged, with net charge 3.70 μC . The charge is uniformly distributed within the volume of each sphere. What is the magnitude E of the electric field midway between the spheres? Take the permittivity of free space to be ϵ0 = 8.85×10−12 C2/(N⋅m2) . What is the direction of the electric field midway between the spheres?arrow_forwardA conducting spherical shell with inner radius aa and outer radius bb has a positive point charge Q located at its center. The total charge on the shell is -3Q, and it is insulated from its surroundings. Derive the expression for the electric field magnitude in terms of the distance r from the center for the region r<a. Express your answer in terms of some or all of the variables Q, a, b, and appropriate constants. Derive the expression for the electric field magnitude in terms of the distance rr from the center for the region a<r<b. Derive the expression for the electric field magnitude in terms of the distance rr from the center for the region r>b. What is the surface charge density on the inner surface of the conducting shell? What is the surface charge density on the outer surface of the conducting shell?arrow_forward
- A small sphere with a mass of 3.00×10−3 g and carrying a charge of 4.80×10−8 C hangs from a thread near a very large, charged insulating sheet, as shown in the figure (Figure 1). The charge density on the sheet is −2.20×10−9 C/m2 . Find the angle of the thread.arrow_forwardA small conducting spherical shell with inner radius aa and outer radius bb is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius c and outer radius d (Figure 1). The inner shell has total charge +2q, and the outer shell has charge −2q. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field in terms of q and the distance rr from the common center of the two shells for r<a. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field for a<r<b. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field for b<r<c.arrow_forwardA cube has sides of length L = 0.800 m . It is placed with one corner at the origin as shown in the figure. The electric field is not uniform but is given by E→=αxi^+βzk^, where α=−3.90 and β= 7.10. What is the sum of the flux through the surface S5 and S6? What is the sum of the flux through the surface S2 and S4? Find the total electric charge inside the cube.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
8.01x - Lect 11 - Work, Kinetic & Potential Energy, Gravitation, Conservative Forces; Author: Lectures by Walter Lewin. They will make you ♥ Physics.;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9gUdDM6LZGo;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY