
Concept explainers
For the problem specified in the table, build upon the results of the original problem to determine the minimum factor of safety for fatigue based on infinite life, using the modified Goodman criterion. The shaft rotates at a constant speed, has a constant diameter, and is made from cold-drawn AISI 1018 steel.

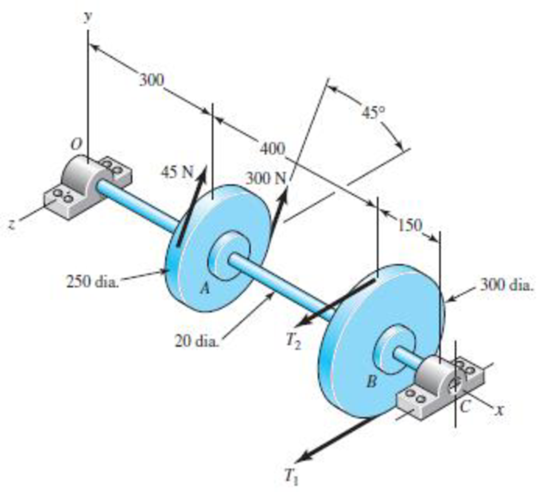
The minimum factor of safety for fatigue on infinite life, using the modified Goodman criterion.
Answer to Problem 40P
The minimum factor of safety for fatigue on infinite life is
Explanation of Solution
Write the relationship between tensions on the loose side with respect to tension on the tight side.
Here, the tension on the tight side is
Write the expression to balance the tension on the counter shaft.
Here, the tension on the tight side of pulley
Substitute
Write the expression for the magnitude of bearing reaction force at
Here, the magnitude of the bearing force at
Write the expression for the magnitude of bearing reaction force at
Here, the magnitude of bearing reaction force at
Write the expression for the magnitude of bearing reaction force at
Here, the magnitude of bearing force at
Write the expression for the magnitude of bearing force at
Here, the magnitude of bearing reaction force at
Write the expression for the bearing reaction force at
Here, the bearing reaction force at
Write the expression for the bearing reaction force at
Here, the bearing reaction force at
Write the expression for the moment at
Here, the moment at
Write the expression for the moment at
Here, the moment at
It is clear from the bending moment diagram, that the critical location is at
Write the expression for the net moment at point
Here, the net moment at
Write expression for the torque transmitted by shaft from
Here, the torque transmitted by shaft from
Write the expression for the bending stress.
Here, the bending stress is
Write the expression for the shear stress.
Here, the shear stress is
Write the expression for von Misses stress for alternating
Here, alternating stress due to completely reversed is
Write the expression for von Misses stress for mid-range.
Here, mean stress due to completely reversed is
Write the expression for von Mises for maximum stress.
Write the expression for yielding by using distortion energy theory.
Here the
Write the expression for endurance limit of rotary test specimen.
Write the expression for surface condition modification factor.
Write the expression for size modification factor.
Write the expression for modified endurance limit.
Write the expression to find out factor of safety by using modified Goodman.
Here modified endurance limit is
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Convert diameter of shaft from millimeter to meter.
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Refer to Table A-20 “Deterministic ASTM tensile and yield strengths for some hot-rolled (HR) and cold-drawn (CD) steels” to obtain the yield strength for AISI 1018 CD steel as
Substitute
Refer to Table A-20 “Deterministic ASTM tensile and yield strengths for some hot-rolled (HR) and cold-drawn (CD) steels” to obtain the ultimate strength for AISI 1018 CD steel as
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Thus minimum factor of safety by using modified Goodman criterion is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design (McGraw-Hill Series in Mechanical Engineering)
- Only question 1arrow_forwardOnly question 3arrow_forwardI have Euler parameters that describe the orientation of N relative to Q, e = -0.7071*n3, e4 = 0.7071. I have Euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to N, e = -1/sqrt(3)*n1, e4 = sqrt(2/3). After using euler parameter rule of successive rotations, I get euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q, e = -0.4082*n1 - 0.4082*n2 - 0.5774*n3. I need euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q in vector basis of q instead of n. How do I get that?arrow_forward
- Describe at least 4 processes in engineering where control charts are (or should be) appliedarrow_forwardDescribe at least two (2) processes where control charts are (or should be) applied.arrow_forwardProblem 3: A cube-shaped spacecraft is in a circular Earth orbit. Let N (n,) be inertial and the spacecraft is denoted S (ŝ₁). The spacecraft is described such that ¯½º = J ŝ₁ŝ₁ + J ŝ₂§₂ + J §¸Ŝ3 Location of the spacecraft in the orbit is determined by the orbit-fixed unit vectors ê, that are oriented by the angle (Qt), where is a constant angular rate. 52 €3 3> 2t 55 Λ Из At the instant when Qt = 90°, the spacecraft S is oriented relative to the orbit such that 8₁ = 0° Space-three 1-2-3 angles 0₂ = 60° and ES = $₂ rad/s 0₁ = 135° (a) At this instant, determine the direction cosine matrix that describes the orientation of the spacecraft with respect to the inertial frame N.arrow_forward
- This problem illustrates that the factor of safety for a machine element depends on the particular point selected for analysis. Here you are to compute factors of safety, based upon the distortion-energy theory, for stress elements at A and B of the member shown in the figure. This bar is made of AISI 1006 cold-drawn steel and is loaded by the forces F = 1.100 kN, P = 8.00 kN, and T = 50.00 N-m. Given: Sy = 280 MPa. B -100 mm- 15-mm D. a) Determine the value of the axial stress at point B. b) Determine the value of the shear stress at point B. c) Determine the value of the Von Mises stress at point B. P Farrow_forwardA piston-cylinder device initially contains 0.08 m^3 of nitrogen gas at 130 kPa and 170°C. The nitrogen is expanded to a pressure of 80 kPa via isentropic expansion. Determine the final temperature and the boundary work done by the system during this process.arrow_forwardA Carnot (ideal) heat pump is to be used to heat a house and maintain it at 22°C in winter. On a day when the average outdoor temperature remains at about 0°C, the house is estimated to lose heat at a rate of 65,000 kJ/h. If the heat pump consumes 6 kW of power while operating, determine: (a) how long the heat pump ran on that day (b) the total heating costs, assuming an average price of 11¢/kWh for electricity (c) the heating cost for the same day if an 85% efficient electric furnace is used instead of a heat pump.arrow_forward
- From the information in the image, I needed to find the orientation of U relative to Q in vector basis q_hat. I transformed the euler angle/axis representation to euler parameters. Then I got its conjugate in order to get the euler parameter in N frame relative to Q. The problem gave the euler angle/axis representation in Q frame relative to N, so I needed to find the conjugate. Then I used the euler parameter rule of successive rotation to find the final euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q. However that orientation is in n_hat which is the intermediate frame. How do I get the final result in q_hat?arrow_forwardA proposed method of power generation involves collecting and storing solar energy in large artificial lakes a few meters deep, called solar ponds. Solar energy is absorbed by all parts of the pond, and the water temperature rises everywhere. The top part of the pond, however, loses much of the heat it absorbs to the atmosphere, and as a result, the cool surface water serves as insulation for the bottom part of the pond and helps trap the energy there. Usually, salt is planted at the bottom of the pond to prevent the rise of this hot water to the top. A heat engine that uses an organic fluid, such as alcohol, as the working fluid can be operated between the top and the bottom portions of the pond. If the water temperature is 27°C near the surface and 72°C near the bottom of the pond, determine the maximum thermal efficiency that this power plant can have. Treat the cycle as an ideal heat engine. Would a heat engine operating under these temperature conditions (27°C and 72°C) be…arrow_forwardA standard Carnot heat engine cycle is executed in a closed system between the temperature limits of 320 and 1350 K, with air as the working fluid. The pressures before and after the isothermal compression are 150 and 300 kPa, respectively. Sketch the TS diagram for this cycle. If the net work output per cycle is 0.75 kJ, determine the efficiency of the cycle and the heat transfer to the air (working fluid) per cycle.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





