
The tip of a one-link robot is located at
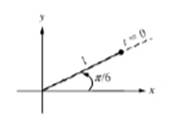
FIGURE P6.2 Rotating one-link robot starting at
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 6 Solutions
Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applications
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Probability And Statistical Inference (10th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- What is the volume of a sphere with a radius of pie cm?arrow_forwardOnly human experts solved it. No ai solutions need okkarrow_forward3. Let sin (22) + cos (T2) f(z) = z(22 + 1)(z+1) Compute f(z)dz over each of the contours/closed curves C1, C2, C3 and C4 shown below. L 10 -C x Don't use any Al tool show ur answer pe n and paper then takearrow_forward
- 1. Evaluate (2,5) (3x+y)dx+(2y-x)dy (0,1) (i) along the straight lines from (0, 1) to (2, 1) and then from (2, 1) to (2,5), and (ii) along the parabola y = x² + 1. Don't use any Al tool show ur answer in pe n and paper then takearrow_forwardDon't use any Al tool show ur answer in pe n and paper then take 20. Solve the given system of differential equations: x' = x+y, x(0) = 0 y' = 2x, y(0) = 1arrow_forward4. Verify the Cauchy-Goursat theorem for the function f(z) =225z around the closed curve C defined by a half circle || = 1 from the point (1,0) to (-1, 0) in the counterclockwise direction and then the straight line from (-1,0) to (1,0). Don't use any Al tool show ur answer in pe n and paper then takearrow_forward
- 2. Evaluate the following integral using cauchy integral theorem: ||=3 sin (22)+cos (22) (2-1)(2-2) -dz Don't use any Al tool show ur answer in pe n and paper then takearrow_forward18. Solve the given differential equation: y' + y = f(t), y(0) = 5, where f(t) = 0arrow_forward16. Solve the given differential equation: y" + 4y Given, = sin (t)u(t2), y(0) = 1, y'(0) = 0 1 = (x² + 1)(x²+4) 1/3 -1/3 + x²+1 x²+4 Don't use any Al tool show ur answer in pe n and paper then takearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward^^ QUESTION 1. Two photos in total, I wrote the questionOnly 100% sure experts solve it correct complete solutions need to get full marks it's my quiz okkkk.take your time but solve full accurate okkk Geometry maths expert solve itarrow_forwardAll 6 questions in the image. Thank youarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning  Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning





