
(a)
The skydiver acceleration when her speed is
(a)
Answer to Problem 28P
The skydiver acceleration when her speed is
Explanation of Solution
When an object passes through the air it experiences drag force due to the air. The drag force is directly proportional to the square of the velocity of the object.
Write the expression for resistive force by the air on the skydiver as.
Here,
The forces act on the skydiver as shown below.
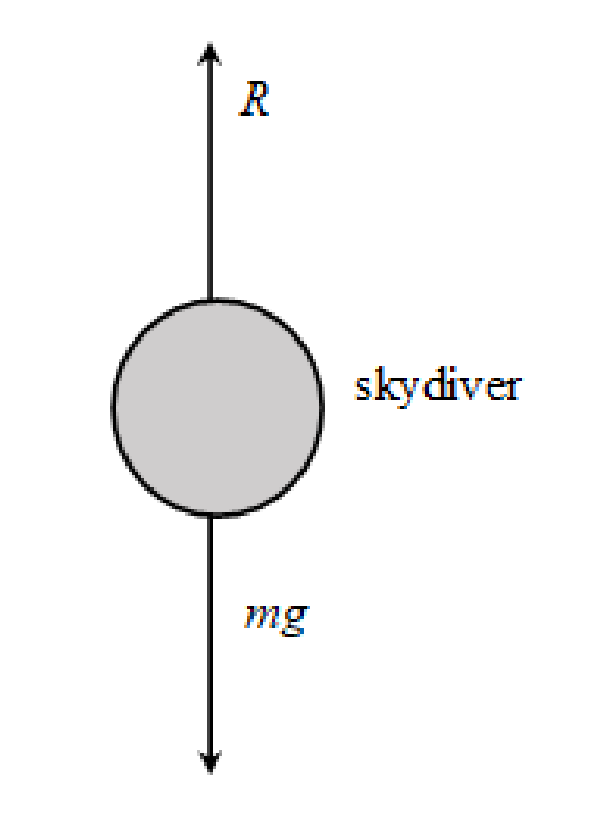
Write the expression corresponding to Newton’s second law of motion in
Here,
Substitute
Simplify the equation (II) for
At the terminal speed of the skydiver, the acceleration becomes zero. If the acceleration is zero then the velocity becomes terminal velocity.
Substitute
Simplify the above expression for
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
The positive direction of the acceleration indicates downward direction.
Thus, the skydiver acceleration when her speed is
(b)
The drag force on the skydiver when her speed is
(b)
Answer to Problem 28P
The drag force on the skydiver when her speed is
Explanation of Solution
At the terminal speed, the weight of the skydiver becomes equal to the drag force.
Write the expression corresponding to the condition of equilibrium in
Conclusion:
Substitute
The positive sign indicates an upward direction of the force.
Thus, the drag force on the skydiver when her speed is
(c)
The drag force on the skydiver when her speed is
(c)
Answer to Problem 28P
The drag force on the skydiver at a speed of
Explanation of Solution
Conclusion:
Substitute
The positive sign of the resistive force indicates an upward direction of the force.
Thus, the drag force on the skydiver at a speed of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Technology Update
- Is it possible for average velocity to be negative?a. Yes, in cases when the net displacement is negative.b. Yes, if the body keeps changing its direction during motion.c. No, average velocity describes only magnitude and not the direction of motion.d. No, average velocity describes only the magnitude in the positive direction of motion.arrow_forwardTutorial Exercise An air-filled spherical capacitor is constructed with an inner-shell radius of 6.95 cm and an outer-shell radius of 14.5 cm. (a) Calculate the capacitance of the device. (b) What potential difference between the spheres results in a 4.00-μC charge on the capacitor? Part 1 of 4 - Conceptualize Since the separation between the inner and outer shells is much larger than a typical electronic capacitor with separation on the order of 0.1 mm and capacitance in the microfarad range, we expect the capacitance of this spherical configuration to be on the order of picofarads. The potential difference should be sufficiently low to avoid sparking through the air that separates the shells. Part 2 of 4 - Categorize We will calculate the capacitance from the equation for a spherical shell capacitor. We will then calculate the voltage found from Q = CAV.arrow_forwardI need help figuring out how to do part 2 with the information given in part 1 and putting it in to the simulation. ( trying to match the velocity graph from the paper onto the simulation to find the applied force graph) Using this simulation https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/cheerpj/forces-1d/latest/forces-1d.html?simulation=forces-1d.arrow_forward
- A Geiger-Mueller tube is a radiation detector that consists of a closed, hollow, metal cylinder (the cathode) of inner radius ra and a coaxial cylindrical wire (the anode) of radius г (see figure below) with a gas filling the space between the electrodes. Assume that the internal diameter of a Geiger-Mueller tube is 3.00 cm and that the wire along the axis has a diameter of 0.190 mm. The dielectric strength of the gas between the central wire and the cylinder is 1.15 × 106 V/m. Use the equation 2πrlE = 9in to calculate the maximum potential difference that can be applied between the wire and the cylinder before breakdown occurs in the gas. V Anode Cathodearrow_forward3.77 is not the correct answer!arrow_forwardA I squar frame has sides that measure 2.45m when it is at rest. What is the area of the frame when it moves parellel to one of its diagonal with a m² speed of 0.86.c as indicated in the figure? >V.arrow_forward
- An astronent travels to a distant star with a speed of 0.44C relative to Earth. From the austronaut's point of view, the star is 420 ly from Earth. On the return trip, the astronent travels speed of 0.76c relative to Earth. What is the distance covered on the return trip, as measured by the astronant? your answer in light-years. with a Give ly.arrow_forwardstar by spaceship Sixus is about 9.00 ly from Earth. To preach the star in 15.04 (ship time), how fast must you travel? C.arrow_forwardIf light-bulb A is unscrewed, how will the brightness of bulbs B and C change, if at all? How does the current drawn by from the battery change?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





