
Concepts of Genetics (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780321948915
Author: William S. Klug, Michael R. Cummings, Charlotte A. Spencer, Michael A. Palladino
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 17PDQ
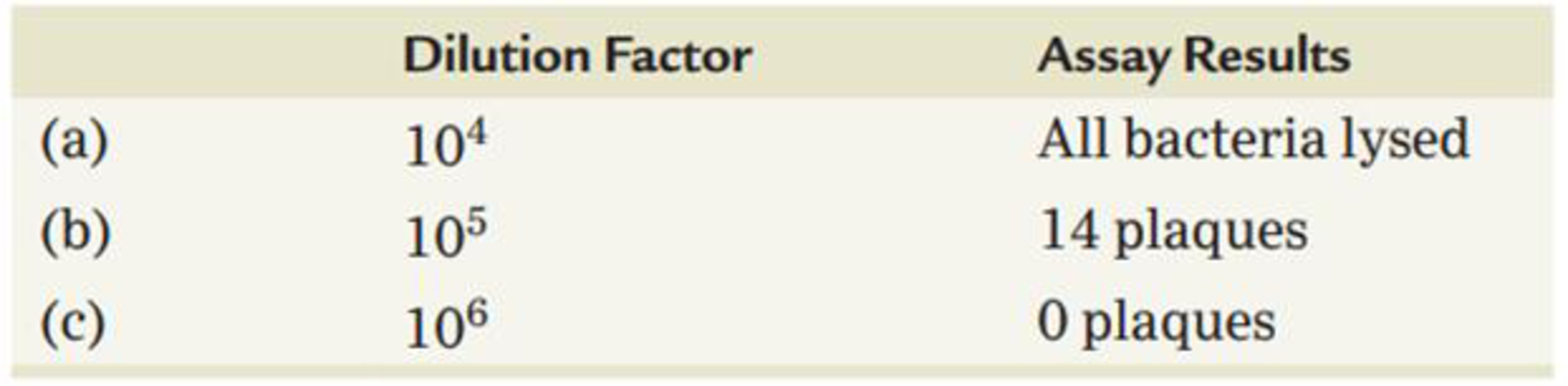
A phage-infected bacterial culture was subjected to a series of dilutions, and a plaque assay was performed in each case, with the results shown in the following table. What conclusion can be drawn in the case of each dilution, assuming that 0.1 mL was used in each plaque assay?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
State the five functions of Globular Proteins, and give an example of a protein for each function.
Diagram of check cell under low power and high power
a couple in which the father has the a blood type and the mother has the o blood type produce an offspring with the o blood type, how does this happen? how could two functionally O parents produce an offspring that has the a blood type?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Concepts of Genetics (11th Edition)
Ch. 6 - When the interrupted mating technique was used...Ch. 6 - In a transformation experiment involving a...Ch. 6 - In complementation studies of the rII locus of...Ch. 6 - Prob. 1CSCh. 6 - Prob. 2CSCh. 6 - Prob. 3CSCh. 6 - Prob. 4CSCh. 6 - HOW DO WE KNOW? In this chapter, we have focused...Ch. 6 - Review the Chapter Concepts list on p. 123. Many...Ch. 6 - With respect to F+ and F bacterial matings, answer...
Ch. 6 - List all major differences between (a) the F+ F...Ch. 6 - Describe the basis for chromosome mapping in the...Ch. 6 - In general, when recombination experiments are...Ch. 6 - Why are the recombinants produced from an Hfr F...Ch. 6 - Describe the origin of F bacteria and merozygotes.Ch. 6 - In a transformation experiment, donor DNA was...Ch. 6 - Describe the role of heteroduplex formation during...Ch. 6 - Explain the observations that led Zinder and...Ch. 6 - Prob. 12PDQCh. 6 - Prob. 13PDQCh. 6 - Two theoretical genetic strains of a virus (abc...Ch. 6 - The bacteriophage genome consists of many genes...Ch. 6 - If a single bacteriophage infects one E. coli cell...Ch. 6 - A phage-infected bacterial culture was subjected...Ch. 6 - In recombination studies of the rII locus in phage...Ch. 6 - In an analysis of rII mutants, complementation...Ch. 6 - If further testing of the mutations in Problem 18...Ch. 6 - Using mutants 2 and 3 from Problem 19, following...Ch. 6 - During the analysis of seven rII mutations in...Ch. 6 - In studies of recombination between mutants 1 and...Ch. 6 - Prob. 24ESPCh. 6 - An Hfr strain is used to map three genes in an...Ch. 6 - A plaque assay is performed beginning with 1 mL of...Ch. 6 - In a cotransformation experiment, using various...Ch. 6 - For the experiment in Problem 26, another gene, g,...Ch. 6 - Bacterial conjugation, mediated mainly by...Ch. 6 - A study was conducted in an attempt to determine...Ch. 6 - Prob. 31ESP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the opening indicated by the pointer? (leaf x.s.) stomate guard cell lenticel intercellular space none of thesearrow_forwardIdentify the indicated tissue? (stem x.s.) parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma ○ xylem ○ phloem none of thesearrow_forwardWhere did this structure originate from? (Salix branch root) epidermis cortex endodermis pericycle vascular cylinderarrow_forward
- Identify the indicated tissue. (Tilia stem x.s.) parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma xylem phloem none of thesearrow_forwardIdentify the indicated structure. (Cucurbita stem l.s.) pit lenticel stomate tendril none of thesearrow_forwardIdentify the specific cell? (Zebrina leaf peel) vessel element sieve element companion cell tracheid guard cell subsidiary cell none of thesearrow_forward
- What type of cells flank the opening on either side? (leaf x.s.) vessel elements sieve elements companion cells tracheids guard cells none of thesearrow_forwardWhat specific cell is indicated. (Cucurbita stem I.s.) vessel element sieve element O companion cell tracheid guard cell none of thesearrow_forwardWhat specific cell is indicated? (Aristolochia stem x.s.) vessel element sieve element ○ companion cell O O O O O tracheid O guard cell none of thesearrow_forward
- Identify the tissue. parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma ○ xylem O phloem O none of thesearrow_forwardPlease answer q3arrow_forwardRespond to the following in a minimum of 175 words: How might CRISPR-Cas 9 be used in research or, eventually, therapeutically in patients? What are some potential ethical issues associated with using this technology? Do the advantages of using this technology outweigh the disadvantages (or vice versa)? Explain your position.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage LearningSurgical Tech For Surgical Tech Pos CareHealth & NutritionISBN:9781337648868Author:AssociationPublisher:CengageEssentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:Cengage
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage LearningSurgical Tech For Surgical Tech Pos CareHealth & NutritionISBN:9781337648868Author:AssociationPublisher:CengageEssentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:Cengage



Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:9781337711067
Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna Balac
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Surgical Tech For Surgical Tech Pos Care
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:9781337648868
Author:Association
Publisher:Cengage

Essentials of Pharmacology for Health Professions
Nursing
ISBN:9781305441620
Author:WOODROW
Publisher:Cengage
genetic recombination strategies of bacteria CONJUGATION, TRANSDUCTION AND TRANSFORMATION; Author: Scientist Cindy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_Va8FZJEl9A;License: Standard youtube license