
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether the following Neman Projection is a representation of the molecule in the previous question should be determined.
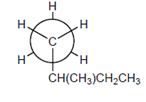
Concept Introduction:
A diagram which is used to denote the specific conformation of a molecule is known as Newman projection. It is classified as: Staggered conformation and Eclipsed conformation.
(b)
Interpretation:
The carbons 1-5 should be labeled on the following Newman projection.
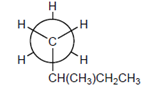
Concept Introduction:
A diagram which is used to denote the specific conformation of a molecule is known as Newman projection. It is classified as: Staggered conformation and Eclipsed conformation.
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of the given Newman projection should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
A diagram which is used to denote the specific conformation of a molecule is known as Newman projection. It is classified as: Staggered conformation and Eclipsed conformation.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
- can someone answer this pleasearrow_forwardcan someone do the reaction mechanism for this reaction and draw the molecules for Q2 and q3arrow_forwardIn this question, the product of the aldol condensation is shown. What would be the reactants for this product? Please provide a detailed explanation, as well as a drawing showing how the reactants will react to produce the product.arrow_forward
- 7. Propene undergoes a hydration reaction with water in the presence of an acid. a. There are two possible products for this reaction, both with the formula C,H,O. Show their structural formulas and names. (A1, B2) SCH4UR Name: (answer for part a. here!) VER 3 2021-2022 b. Which of the two products do you predict will form. Explain your choice using details from your learning. (B3)arrow_forwardWhat are the major products of the following organic reaction? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing as to how the reaction proceeds.arrow_forwardWhat are the major products of the following reaction? Please provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the reaction proceeds.arrow_forward
- What are the major products of the following organic reaction? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing as to how the reaction proceeds.arrow_forwardPredict the organic product that forms in the reaction below: H + гон OH H+ H+ ☑ O Note: You may assume you have an excess of either reactant if the reaction requires more than one of those molecules to form the product. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the missing organic product X. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centearrow_forwardIn the analysis of Mg content in a 25 mL sample, a titration volume of 5 mL was obtained using 0.01 M EDTA. Calculate the Mg content in the sample if the Ca content is 20 ppmarrow_forward
- Predict the organic products that form in the reaction below: H. H+ + OH H+ Y Note: You may assume you have an excess of either reactant if the reaction requires more than one of those molecules to form the products. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. G X C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Access +arrow_forward111 Carbonyl Chem Choosing reagants for a Wittig reaction What would be the best choices for the missing reagents 1 and 3 in this synthesis? 1. PPh3 3 1 2 2. n-BuLi • Draw the missing reagents in the drawing area below. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. Do not draw the missing reagent 2. If you draw 1 correctly, we'll know what it is. • Note: if one of your reagents needs to contain a halogen, use bromine. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. × ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Usearrow_forwardA student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more reactants missing from the left-hand side, but there are no products missing from the right-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow. • Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area. . If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing reactants to the left-hand side, and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow. • You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown. + T X O O лет-ле HO OH HO OH This transformation can't be done in one step.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
