
Concept explainers
All molecules undergo vibrational motions.
Where n is a quantum number
Interpretation:
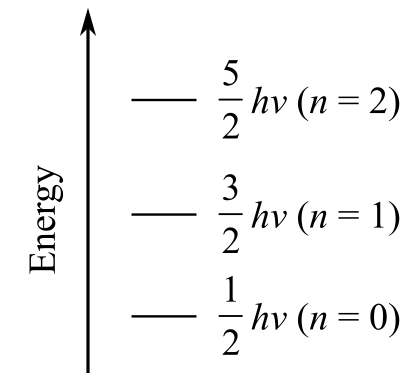
The first three vibrational energy levels for
l is to be drawn. The energy required for the transition of molecule from ground state to first excited state is to be determined, and “the reason for lowest vibrational energy in ground state is not zero, but it is equivalent to
” is to be justified by using Heisenberg Principle.
Concept introduction:
The energy of a photon can be expressed as follows:
Here, E is the energy of photon,
Heisenberg uncertainty principle explains that the product of uncertainty in position and momentum of particle cannot be less than
Here,
denotes uncertainty in position,
denotes uncertainty in momentum, and
denotes Planck’s constant
Answer to Problem 112AP
Solution:
a)
(b)
(c) Consider the diatomic molecule
This is disallowed by the Heisenberg uncertainty principle.
Explanation of Solution
a) Plot the first three vibrational energy levels for HCl
The vibrational energy of diatomic molecules is given as
The first three vibrational energy levels n are
For
For
For
The vibrational energy for the first three energy levels is

b) The vibrational energy required to excite HCl molecule from ground state to first exited state.
The vibrational energy for the ground state and first excited state are as follows:
For the transition from ground state
Now, substitute the value
and
in the above equation
c) Justify the prediction “that the lowest vibrational energy in the ground state is not zero, but it is equivalent to
Consider the diatomic molecule
As the two atoms are bonded to each other, the uncertainty in position, that is,
Thus,
So, this is disallowed by the Heisenberg uncertainty principle.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Physical Science
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Organic Chemistry
Loose Leaf For Integrated Principles Of Zoology
- true or false, given that a 20.00 mL sample of NaOH took 24.15 mL of 0.141 M HCI to reach the endpoint in a titration, the concentration of the NaOH is 1.17 M.arrow_forwardin the bromothymol blue experiment, pKa was measured. A closely related compound has a Ka of 2.10 x 10-5. What is the pKa?a) 7.1b) 4.7c) 2.0arrow_forwardcalculate the equilibrium concentration of H2 given that K= 0.017 at a constant temperature for this reaction. The inital concentration of HBr is 0.050 M.2HBr(g) ↔ H2(g) + Br2(g)a) 4.48 x 10-2 M b) 5.17 x 10-3 Mc) 1.03 x 10-2 Md) 1.70 x 10-2 Marrow_forward
- true or falsegiven these two equilibria with their equilibrium constants:H2(g) + CI2(l) ↔ 2HCI(g) K= 0.006 CI2(l) ↔ CI2(g) K= 0.30The equilibrium contstant for the following reaction is 1.8H2(g) + CI2 ↔ 2HCI(g)arrow_forwardI2(g) + CI2(g) ↔ 2ICIK for this reaction is 81.9. Find the equilibrium concentration of I2 if the inital concentration of I2 and CI2 are 0.010 Marrow_forwardtrue or false,the equilibrium constant for this reaction is 0.50.PCI5(g) ↔ PCI3(g) + CI2(g)Based on the above, the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 0.25.2PCI5(g) ↔. 2PCI3(g) + 2CI2(g)arrow_forward
- true or false, using the following equilibrium, if carbon dioxide is added the equilibrium will shift toward the productsC(s) + CO2(g) ↔ 2CO(g)arrow_forward2S2O2/3- (aq) + I2 (aq) ---> S4O2/6- (aq) +2I- (aq) Experiment I2 (M) S2O3- (M) Initital Rate (M/s) 1 0.01 0.01 0.0004 2 0.01 0.02 0.0004 3 0.02 0.01 0.0008 Calculate the overall order for this reaction using the table data a) 3b) 0c) 2d) 1arrow_forwardthe decomposition of N2O5 is the first order with a half-life of 1.98 minutes. If the inital concentration of N2O5 is 0.200 M, what is the concentration after 6 minutes?a) 0.612 Mb) 0.035 Mc) 0.024 Md) 0.100 Marrow_forward
- 20.00 mL of 0.150 M HCI is titrated with 0.075 M NaOH. What volume of NaOH is needed?a) 50 mLb) 20 mLc) 40 mLd) 26.66 mLarrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCI. What is the molarity of the HCI?a) 0.150 Mb) 0.079 Mc) 0.025 Md) 0.050 Marrow_forwardin the following reaction, the OH- acts as which of these?NO2- (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ OH- (aq) + HNO2 (aq)a) not a weak acidb) basec) acidarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning



