
Concept explainers
The cross section of a concrete dam is as shown. For a 1-m-wide dam section determine (a) the resultant of the reaction forces exerted by the ground on the base AB of the dam, (b) the point of application of the resultant of part a, (c) the resultant of the pressure forces exerted by the water on the face BC of the dam.
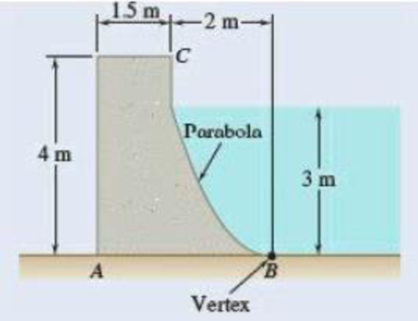
Fig. P5.81
(a)
The reaction forces exerted by the ground on the base of the concrete dam
Answer to Problem 5.81P
The resultant reaction forces acts on the base of the dam is
Explanation of Solution
Given that the width of the dam section
The free-body diagram consists of dam and the triangular section
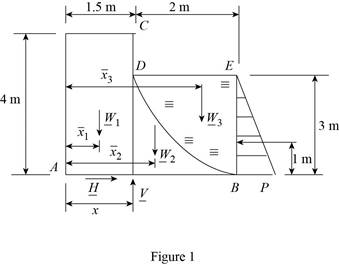
The length
Write the equation for weight force acts on the dam.
Here, the weight of the dam is
Replace
Here, the thickness of the dam section is
Write the equation for the weight of the dam represented by the weights of its components.
Here, the weight of the dam by the components of fist section is
Substitute
Write the equation for the weight of the dam represented in the triangular section.
Here, the weight of the dam by the components of second section is
Substitute
Write the equation for the weight of the dam represented in the parabola section by the weights of its components.
Here, the weight of the dam by the components of third section is
Substitute
Write the equation of the force pressure exerted by the ground on the base of the dam.
Here, the reaction force exerted on the dam is
Replace
Write the equilibrium equation for the section of dam acts along x axis (Refer Fig 1).
Here, the reaction force exerted by the ground on the base
Write the equilibrium equation for the section of beam acts along y axis and then calculate the reaction force (Refer Fig 1).
Here, the reaction force exerted by the ground on the base
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the resultant reaction forces acts on the base of the dam is
(b)
The point of forces acts on the base
Answer to Problem 5.81P
The point in which the forces acts on the base
Explanation of Solution
The distance from the base of the dam to the point
The distance from the base of the dam to the side
The distance from the base of the dam to the point
Write the equilibrium equation for the section on the base
Here, the different section of the dam is represented as
Conclusion:
Substitute
Solve the above equation for
Therefore, the point in which the forces acts on the base
(c)
The resultant pressure force exerted by the water on the face
Answer to Problem 5.81P
The resultant pressure force exerted by the water on the face
Explanation of Solution
The free body diagram of the water section
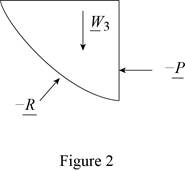
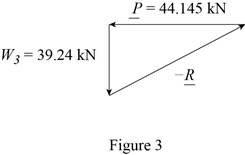
Write the equilibrium equation for the s resultant pressure force exerted by the water on the face
Here, the resultant pressure force exerted by the water on the dam is
Solve for the angle of resultant force exerted by the water on the dam by using trigonometric relation (Refer fig 3).
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the resultant pressure force exerted by the water on the face
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
VECTOR MECH....F/ENGNRS-STATICS -CONNECT
- The horizontal x axis is drawn through the centroid C of the area shown, and it divides the area into two component areas A1 and A2. Determine the first moment of each component area with respect to the x axis, and explain the results obtained. 7.5 in. A1 C A2 4.5 in. 4.5 in. Fig. P5.21arrow_forwardA caisson for closing the entrance to a dry dock is of trapezoidal from 16 m wide at the top and 12 m wide at the bottom and 8 m deep. Find the total force in MN on the caisson if the water on the outside is 1 m below the top level of the caisson and the dock is empty. enclude your free body diagram. a.117.72 b.80.93 c.3.164 d.37.77arrow_forwardAny help is appreciated. Thank you.arrow_forward
- 5.74 Determine (a) the distance a so that the vertical reactions at supports A and B are equal, (b) the corresponding reactions at the supports. Answer Fig. P5.74 and P5.75 1800 N/m A 4 m 600 N/m Barrow_forwardRequired information Problem 02.003 - Addition of planar forces applied to a hook NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Two forces P and Q are applied as shown at point A of a hook support. ट 20°i 35° Problem 02.003.b - Resultant of forces applied to a hook using the triangle rule Knowing that P = 75 N and Q = 195 N, determine graphically the magnitude and direction of their resultant using the triangle rule. The magnitude of the resultant is The direction of the resultant is 245.8 N. 14.5°arrow_forwardFor the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the magnitude and location of the resultant of the distributed load, (b) the reactions at the beam supports.arrow_forward
- Q.2) If two forces are applied to a rigid body, which have the same magnitude (F) anc the same direction, the resultant force is: (a) 2F (b) F (c) 0 (d) - Farrow_forwardH.W: A frame ABC is supported in part by cable DBE that passes through a frictionless ring at B. Knowing that the tension in the cable is 385 N, determine (a)- the resultant (R) of the forces as a vector which exerted by the cables on the support at D and E, (b)- the angles between R and each of the coordinate axes. Answer: 20 mm 10 mn R= Fan + FRE =-(375 N)i +(455 N)j-(460 N)k E 0, =120.1° « 0, = 52.5° 4 510 mm 400 mm 0. =128.0° 4arrow_forwardPage 115 3.41 Ropes AB and BC are two of the ropes used to support a tent. The two ropes are attached to a stake at B. If the tension in rope AB is 540 N, determine (a) the angle between rope AB and the stake, (b) the projection on the stake of the force exerted by rope AB at point B. Fig. P3.41 and P3.42 3 m A 3 m Z B 1.5 m x D 0.38 m 0.08 m. B 0.16 m Detail of the stake at Barrow_forward
- Please don't provide handwritten solution .....arrow_forwardQ6. 1) For the sectional area shown in the image below, if the dimensions are a = 14 mm, b = 52 mm, and c = 27 mm, determine the coordinate y (in mm) for its centroid location. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. %3D al x' C a. Your Answer:arrow_forwardQ6. 1) For the sectional area shown in the image below, if the dimensions are a = 14 mm, b = 52 mm, and c = 27 mm, determine the coordinate y (in mm) for its centroid location. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. %3D r'arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





