
Concept explainers
The magnitude of the tension in the string which connects two blocks, one of which hangs vertically down and the other resting on an inclined plane.
Answer to Problem 79QAP
The tension in the string is found to be 3.92 N.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Mass of the block placed on the incline
Mass of the hanging block
Angle made by the plane with horizontal
Coefficient of static friction
Coefficient of kinetic friction
Formula used:
Free body diagrams are drawn for the two blocks and the tension in the string is determined using the force equations for both the blocks.
The free body diagram for the block of mass
The weight of the block is
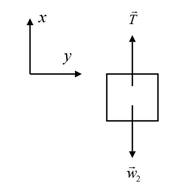
The total force acting along the +x direction is given by,
Draw the free body diagram for the block of mass
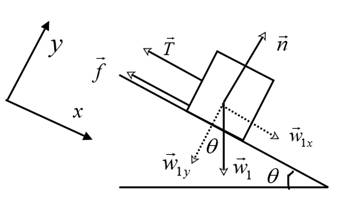
The weight
Resolve the weight
The force equation along the +x direction is given by,
The force equation along the +y direction is given by,
Since the block is in equilibrium in the y direction,
Hence,
The force of friction and the normal force are related as follows:
The value of the coefficient of friction
Calculation:
The system would be at rest, if the following conditions are satisfied:
and
If
Since
Substitute the values of the variables in the above equation,
To check whether the system is at rest, use the expression
Therefore,
Calculate the value of
The component
Therefore,
Use the values of the variables in the equation.
If the system is at rest, assume the maximum force of static friction to act on the block.
Then,
From equation (4),
The component
Calculate the maximum force of static friction acting on the block.
It can be seen that
Conclusion:
Since the system is at rest, the force of tension in the string is equal to 3.92 N.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS
- Please type out answerarrow_forwardUsing f(x) = log x, what is the x-intercept of g(x) = log (x + 4)? Explain your reasoning. Please type out answerarrow_forwardThe function f(x) = log x is transformed to produce g(x) = log (x) – 3. Identify the type of transformation and describe the change. Please type out answerarrow_forward
- Each graph below is the graph of a system of three linear equations in three unknowns of the form Ax = b. Determine whether each system has a solution and, if it does, the number of free variables. A. O free variables ✓ B. no solution C. no solution D. no solution E. 1 free variable F. 1 free variablearrow_forwardSolve the following systems of equations and show all work.y = x2 + 3y = x + 5 Please type out answerarrow_forwardSolve the following system of equations. Show all work and solutions.y = 2x2 + 6x + 1y = −4x2 + 1 Please type out answerarrow_forward
- Dalia buys 20 collectible gems per month. Grace sells 10 gems from her collection of 120 each month. When will Dalia have more gems than Grace? Show your work. Dear Student If You Face any issue let me know i will solve your all doubt. I will provide solution again in more detail systematic and organized way. I would also like my last 3 questions credited to mearrow_forwardDalia buys 20 collectible gems per month. Grace sells 10 gems from her collection of 120 each month. When will Dalia have more gems than Grace? Show your work.arrow_forwardSolve the following system of equations. Show all work and solutions.y = 2x2 + 6x + 1y = −4x2 + 1arrow_forward
- Solve the following systems of equations and show all work.y = x2 + 3y = x + 5arrow_forwardWrite an equation for the function shown. You may assume all intercepts and asymptotes are on integers. The blue dashed lines are the asymptotes. 10 9- 8- 7 6 5 4- 3- 2 4 5 15-14-13-12-11-10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 1 1 2 3 -1 -2 -3 -4 1 -5 -6- -7 -8- -9 -10+ 60 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15arrow_forwardUse the graph of the polynomial function of degree 5 to identify zeros and multiplicity. Order your zeros from least to greatest. -6 3 6+ 5 4 3 2 1 2 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 3 4 6 Zero at with multiplicity Zero at with multiplicity Zero at with multiplicityarrow_forward
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning


