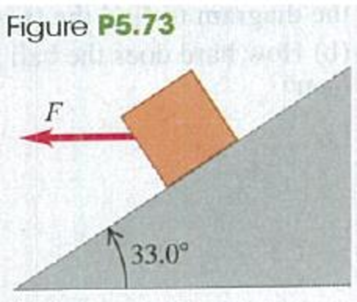
Problem 5.1DQ: A man sits in a seat that is hanging from a rope. The rope passes over a pulley suspended from the... Problem 5.2DQ: In general, the normal force is not equal to the weight. Give an example in which these two forces... Problem 5.3DQ: A clothesline hangs between two poles. No matter how tightly the line is stretched, it sags a little... Problem 5.4DQ: You drive a car up a steep hill at constant speed. Discuss all of the forces that act on the car.... Problem 5.5DQ: For medical reasons, astronauts in outer space must determine their body mass at regular intervals.... Problem 5.6DQ: To push a box up a ramp, which requires less force: pushing horizontally or pushing parallel to the... Problem 5.7DQ: A woman in an elevator lets go of her briefcase, but it does not fall to the floor. How is the... Problem 5.8DQ: A block rests on an inclined plane with enough friction to prevent it from sliding down. To start... Problem 5.9DQ: A crate slides up an inclined ramp and then slides down the ramp after momentarily stopping near the... Problem 5.10DQ: A crate of books rests on a level floor. To move it along the floor at a constant velocity, why do... Problem 5.11DQ: In a world without friction, which of the following activities could you do (or not do)? Explain... Problem 5.12DQ: When you stand with bare feet in a wet bathtub, the grip feels fairly secure, and yet a catastrophic... Problem 5.13DQ: You are pushing a large crate from the back of a freight elevator to the front as the elevator is... Problem 5.14DQ: It is often said that friction always opposes motion. Give at least one example in which (a) static... Problem 5.15DQ: If there is a net force on a particle in uniform circular motion, why doesnt the particles speed... Problem 5.16DQ: A curve in a road has a bank angle calculated and posted for 80 km/h. However, the road is covered... Problem 5.17DQ: You swing a ball on the end of a lightweight string in a horizontal circle at constant speed. Can... Problem 5.18DQ: The centrifugal force is not included in the free-body diagrams of Figs. 5.34b and 5.35. Explain why... Problem 5.19DQ: A professor swings a rubber stopper in a horizontal circle on the end of a string in front of his... Problem 5.20DQ: To keep the forces on the riders within allowable limits, many loop-the-loop roller coaster rides... Problem 5.21DQ: A tennis ball drops from rest at the top of a tall glass cylinderfirst with the air pumped out of... Problem 5.22DQ: You throw a baseball straight upward with speed 0. When the ball returns to the point from where you... Problem 5.23DQ: You throw a baseball straight upward. If you do not ignore air resistance, how does the time... Problem 5.24DQ: You have two identical tennis balls and fill one with water. You release both balls simultaneously... Problem 5.25DQ: A ball is dropped from rest and feels air resistance as it falls. Which of the graphs in Fig. Q5.25... Problem 5.26DQ: A ball is dropped from rest and feels air resistance as it falls. Which of the graphs in Fig. Q5.26... Problem 5.27DQ: When a balled baseball moves with air drag, when does the ball travel a greater horizontal distance?... Problem 5.28DQ: A ball is thrown from the edge of a high cliff. Regardless of the angle at which it is thrown, due... Problem 5.1E: Two 25.0-N weights are suspended at opposite ends of a rope that passes over a light, frictionless... Problem 5.2E: In Fig. E5.2 each of the suspended blocks has weight w. The pulleys are frictionless, and the ropes... Problem 5.3E: A 75.0-kg wrecking ball hangs from a uniform, heavy-duty chain of mass 26.0 kg. (a) Find the maximum... Problem 5.4E: BIO Injuries to the Spinal Column. In the treatment of spine injuries, it is often necessary to... Problem 5.5E: A picture frame hung against a wall is suspended by two wires attached to its upper corners. If the... Problem 5.6E: A large wrecking ball is held in place by two light steel cables (Fig. E5.6). If the mass m of the... Problem 5.7E: Find the tension in each cord in Fig. E5.7 if the weight of the suspended object is w. Problem 5.8E: A 1130-kg car is held in place by a light cable on a very smooth (frictionless) ramp (Fig. E5.8).... Problem 5.9E: A man pushes on a piano with mass 180 kg; it slides at constant velocity down a ramp that is... Problem 5.10E: In Fig. E5.10 the weight w is 60.0 N. (a) What is the tension in the diagonal string? (b) Find the... Problem 5.11E: BIO Stay Awake! An astronaut is inside a 2.25 106 kg rocket that is blasting off vertically from... Problem 5.12E: A rocket of initial mass 125 kg (including all the contents) has an engine that produces a constant... Problem 5.13E: CP Genesis Crash. On September 8, 2004, the Genesis spacecraft crashed in the Utah desert because... Problem 5.14E: Three sleds are being pulled horizontally on frictionless horizontal ice using horizontal ropes... Problem 5.15E: Atwoods Machine. A 15.0-kg load of bricks hangs from one end of a rope that passes over a small,... Problem 5.16E: CP An 8.00-Kg block of ice, released from rest at the top of a 1.50-m-long frictionless ramp, slides... Problem 5.17E: A light rope is attached to a block with mass 4.00 kg that rests on a frictionless, horizontal... Problem 5.18E: CP Runway Design. A transport plane lakes off from a level landing field with two gliders in tow,... Problem 5.19E: CP A 750.0-kg boulder is raised from a quarry 125 m deep by a long uniform chain having a mass of... Problem 5.20E: Apparent Weight. A 550-N physics student stands on a bathroom scale in an elevator that is supported... Problem 5.21E: CP BIO Force During a Jump. When jumping straight up from a crouched position, an average person can... Problem 5.22E: CP CALC A 2540-kg test rocket is launched vertically from the launch pad. Its fuel (of negligible... Problem 5.23E: CP CALC A 2.00-kg box is moving to the right with speed 9.00 m/s on a horizontal, frictionless... Problem 5.24E: CP CALC A 5.00-kg crate is suspended from the end of a short vertical rope of negligible mass. An... Problem 5.25E: BIO The Trendelenburg Position. After emergencies with major blood loss, a patient is placed in the... Problem 5.26E: In a laboratory experiment on friction, a 135-N block resting on a rough horizontal table is pulled... Problem 5.27E: CP A stockroom worker pushes a box with mass 16.8 kg on a horizontal surface with a constant speed... Problem 5.28E: A box of bananas weighing 40.0 N rests on a horizontal surface. The coefficient of static friction... Problem 5.29E: A 45.0-kg crate of tools rests on a horizontal floor. You exert a gradually increasing horizontal... Problem 5.30E: Some sliding rocks approach the base of a hill with a speed of 12 m/s. The hill rises at 36 above... Problem 5.31E: A box with mass 10.0 kg moves on a ramp that is inclined at an angle of 55.0 above the horizontal.... Problem 5.32E: A pickup truck is carrying a toolbox, but the rear gate of the truck is missing. The toolbox will... Problem 5.33E: You are lowering two boxes, one on top of the other, down a ramp by pulling on a rope parallel to... Problem 5.34E: Consider the system shown in Fig. E5.34. Block A weighs 45.0 N, and block B weighs 25.0 N. Once... Problem 5.35E: CP Stopping Distance. (a) If the coefficient of kinetic friction between tires and dry pavement is... Problem 5.36E: CP A 25.0-kg box of textbooks rests on a loading ramp that makes an angle with the horizontal. The... Problem 5.37E: Two crates connected by a rope lie on a horizontal surface (Fig. E5.37). Crate A has mass mA, and... Problem 5.38E: A box with mass m is dragged across a level floor with coefficient of kinetic friction k by a rope... Problem 5.39E: CP As shown in Fig. E5.34, block A (mass 2.25 kg) rests on a tabletop. It is connected by a... Problem 5.40E: You throw a baseball straight upward. The drag force is proportional to 2. In terms of g. what is... Problem 5.41E: A large crate with mass m rests on a horizontal floor. The coefficients of friction between the... Problem 5.42E: (a) In Example 5.18 (Section 5.3), what value of D is required to make t = 42 m/s for the skydiver?... Problem 5.43E: A stone with mass 0.80 kg is attached to one end of a string 0.90 m long. The string will break if... Problem 5.44E: BIO Force on a Skaters Wrist. A 52-kg ice skater spins about a vertical axis through her body with... Problem 5.45E: A small remote-controlled car with mass 1.60 kg moves at a constant speed of = 12.0 m/s in a track... Problem 5.46E: 5.46A small car with mass 0.800 kg travels at constant speed on the inside of a track that is a... Problem 5.47E: A small model car with mass m travels at constant speed on the inside of a track that is a vertical... Problem 5.48E: A flat (unbanked) curve on a highway has a radius of 170.0 m. A car rounds the curve at a speed of... Problem 5.49E: A 1125-kg car and a 2250-kg pickup truck approach a curve on a highway that has a radius of 225 m.... Problem 5.50E: The Giant Swing at a county fair consists of a vertical central shaft with a number of horizontal... Problem 5.51E: In another version of the Giant Swing (see Exercise 5.50), the seat is connected to two cables, one... Problem 5.52E: A small button placed on a horizontal rotating platform with diameter 0.520 m will revolve with the... Problem 5.53E: Rotating Space Stations. One problem for humans living in outer space is that they are apparently... Problem 5.54E: The Cosmo Clock 21 Ferris wheel in Yokohama, Japan, has a diameter of 100 m. Its name comes from its... Problem 5.55E: An airplane flies in a loop (a circular path in a vertical plane) of radius 150 m. The pilots head... Problem 5.56E: A 50.0-kg stunt pilot who has been diving her airplane vertically pulls out or the dive by changing... Problem 5.57E: Stay Dry! You tie a cord to a pail of water and swing the pail in a vertical circle of radius 0.600... Problem 5.58E: A bowling ball weighing 71.2 N (16.0 lb) is attached to the ceiling by a 3.80-m rope. The ball is... Problem 5.59E: BIO Effect on Blood of Walking. While a person is walking, his arms swing through approximately a 45... Problem 5.60P: An adventurous archaeologist crosses between two rock cliffs by slowly going hand over hand along a... Problem 5.61P: Two ropes are connected to a steel cable that supports a hanging weight (Fig. P5.61). (a) Draw a... Problem 5.62P: In Fig. P5.62 a worker lifts a weight w by pulling down on a rope with a force F. The upper pulley... Problem 5.63P: In a repair shop a truck engine that has mass 409 kg is held in place by four light cables (Fig.... Problem 5.64P: A horizontal wire holds a solid uniform ball of mass m in place on a tilted ramp that rises 35.0... Problem 5.65P: A solid uniform 45.0-kg ball of diameter 32.0 cm is supported against a vertical, frictionless wall... Problem 5.66P: CP A box is sliding with a constant speed of 4.00 m/s in the +x-direction on a horizontal,... Problem 5.67P: CP BIO Forces During Chin-ups. When you do a chin-up, you raise your chin just over a bar (the... Problem 5.68P: CP CALC A 2.00-kg box is suspended from the end of a light vertical rope. A time-dependent force is... Problem 5.69P: CALC A 3.00-kg box that is several hundred meters above the earth's surface is suspended from the... Problem 5.70P: CP A 5.00-kg box sits at rest at the bottom of a ramp that is 8.00 m long and is inclined at 30.0... Problem 5.71P: Two boxes connected by a light horizontal rope are on a horizontal surface (Fig. E5.37). The... Problem 5.72P: A 6.00-kg box sits on a ramp that is inclined at 37.0 above the horizontal. The coefficient of... Problem 5.73P: CP An 8.00-kg box sits on a ramp that is inclined at 33.0 above the horizontal. The coefficient of... Problem 5.74P: CP In Fig. P5.74, m1 = 20.0 kg and = 53.1. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block of... Problem 5.75P: CP You place a book of mass 5.00 kg against a vertical wall. You apply a constant force F to the... Problem 5.76P: Block A in Fig. P5.76 weighs 60.0 N. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the... Problem 5.77P: A block with mass m1 is placed on an inclined plane with slope angle and is connected to a hanging... Problem 5.78P: BIO The Flying Leap of a Flea. High-speed motion pictures (3500 frames/second) of a jumping 210-g... Problem 5.79P: Block A in Fig. P5.79 weighs 1.20 N, and block B weighs 3.60 N. The coefficient of kinetic friction... Problem 5.80P: CP Elevator Design. You are designing an elevator for a hospital. The force exerted on a passenger... Problem 5.81P: CP CALC You are standing on a bathroom scale in an elevator in a tall building. Your mass is 64 kg.... Problem 5.82P: A hammer is hanging by a light rope from the ceiling of a bus. The ceiling is parallel to the... Problem 5.83P: A 40.0-kg packing case is initially at rest on the floor of a 1500-kg pickup truck. The coefficient... Problem 5.84P: If the coefficient of static friction between a table and a uniform, massive rope is s, what... Problem 5.85P: Two identical 15.0-kg balls, each 25.0 cm in diameter, are suspended by two 35.0-cm wires (Fig.... Problem 5.86P: CP Traffic Court. You are called as an expert witness in a trial for a traffic violation. The facts... Problem 5.87P: Block A in Fig. P5.87 weighs 1.90 N, and block B weighs 4.20 N. The coefficient of kinetic friction... Problem 5.88P: CP Losing Cargo. A 12.0-kg box rests on the level bed of a truck. The coefficients of friction... Problem 5.89P: Block A in Fig. P5.89 has mass 4.00 kg, and block B has mass 12.0 kg. The coefficient of kinetic... Problem 5.90P: Two blocks connected by a cord passing over a small, friction less pulley rest on frictionless... Problem 5.91P: In terms of m1, m2, and g, find the acceleration of each block in Fig. P5.91. There is no friction... Problem 5.92P: Block B, with mass 5.00 kg, rests on block A, with mass 8.00 kg, which in turn is on a horizontal... Problem 5.93P: Two objects, with masses 5.00 kg and 2.00 kg, hang 0.600 m above the floor from the ends of a cord... Problem 5.94P: Friction in an Elevator. You are riding in an elevator on the way to the 18th floor of your... Problem 5.95P: A block is placed against the vertical front of a cart (Fig. P5.95). What acceleration must the cart... Problem 5.96P: Two blocks, with masses 4.00 kg and 8.00 kg, are connected by a string and slide down a 30.0... Problem 5.97P: Block A, with weight 3w, slides down an inclined plane S of slope angle 36.9 at a constant speed... Problem 5.98P: Jack sits in the chair of a Ferris wheel that is rotating at a constant 0.100 rev/s. As Jack passes... Problem 5.99P: Bunked Curve I. A curve with a 120-m radius on a level road is banked at the correct angle for a... Problem 5.100P: Banked Curve II. Consider a wet roadway banked as in Example 5.22 (Section 5.4), where there is a... Problem 5.101P: Blocks A, B, and C are placed as in Fig. P5.101 and connected by ropes of negligible mass. Both A... Problem 5.102P: You are riding in a school bus. As the bus rounds a flat curve at constant speed, a lunch box with... Problem 5.103P: CALC You throw a rock downward into water with a speed of 3mg/k, where k is the coefficient in Eq.... Problem 5.104P: A 4.00-kg block is attached to a vertical rod by means of two strings. When the system rotates about... Problem 5.105P: On the ride Spindletop at the amusement park Six Flags Over Texas, people stood against the inner... Problem 5.106P: A 70-kg person rides in a 30-kg cart moving at 12 m/s at the top of a hill that is in the shape of... Problem 5.107P: A small bead can slide without friction on a circular hoop that is in a vertical plane and has a... Problem 5.108P: A physics major is working to pay her college tuition by performing in a traveling carnival. She... Problem 5.109P: DATA In your physics lab, a block of mass m is at rest on a horizontal surface. You attach a light... Problem 5.110P: DATA A road heading due cast passes over a small hill. You drive a car of mass m at constant speed ... Problem 5.111P: DATA You are an engineer working for a manufacturing company. You are designing a mechanism that... Problem 5.112CP: Moving Wedge. A wedge with mass M rests on a friction less, horizontal tabletop. A block with mass m... Problem 5.113CP: Figure P5.112 5.113A wedge with mass M rests on a frictionless, horizontal tabletop. A block with... Problem 5.114CP: Double Atwoods Machine. In Fig. P5.114 masses m1 and m2 are connected by a light string A over a... Problem 5.115CP: A ball is held at rest at position A in Fig. P5.115 by two light strings. The horizontal string is... Problem 5.116PP: FRICTION AND CLIMBING SHOES. Shoes made for the sports of bouldering and rock climbing are designed... Problem 5.117PP: FRICTION AND CLIMBING SHOES. Shoes made for the sports of bouldering and rock climbing are designed... Problem 5.118PP: FRICTION AND CLIMBING SHOES. Shoes made for the sports of bouldering and rock climbing are designed... format_list_bulleted


 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning




