
(a)
Interpretation:
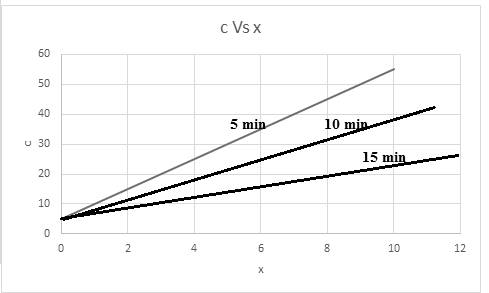
A graph of concentration (c) with x in centimeter at a time for
Concept introduction:
Fick's Law of diffusion: This law states that molar flux is directly proportional to concentration gradient. The law is stated as:
Where,
J is the molar flux defined as the number of atoms passing per unit area per unit time.
D is the diffusion coefficient in
Factors affection diffusion are as follows:
- Temperature
- Diffusion coefficient
The following equation is stated as:
Where,
Q is the activation energy in calorie/ mole.
R is universal gas constant in
T is the absolute temperature in kelvin.
Answer to Problem 5.71P
The required graph for concentration versus x is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The equation used is given as,
Where,
Q is the initial surface concentration having unit of
Temperature for water is
Diffusion coefficient of phosphorous in silicon at a temperature of
t is the time in seconds.
Given equation for finding out the plot between of concentration (c) with x,
Based on given data calculation of
Substituting the values,
The relationship of concentration at a time of 5 min is,
Given equation for finding out the plot between of concentration (c) with x,
Based on given data calculation of
Substituting the values,
The relationship of concentration at a time of 10 min is,
Given equation for finding out the plot between of concentration (c) with x,
Based on given data calculation of
Substituting the values,
The relationship of concentration at a time of 15 min is,
Thus, based on given relation the concentration is dependent on x and t. The graph for the same considering time into consideration,
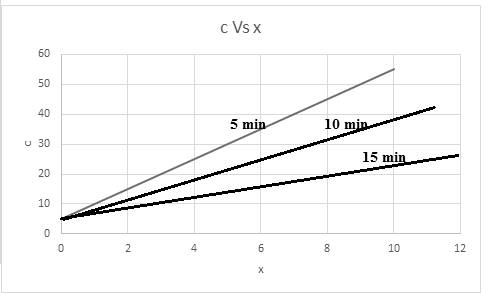
The graph is representing the linear slope of concentration versus x with respect to given time.
(b)
Interpretation:
Time required by the phosphorous concentration to make it equal to the concentration of boron at a depth of
Concept introduction:
Fick's Law of diffusion: This law states that molar flux is directly proportional to concentration gradient. The law is stated as:
Where,
J is the molar flux defined as the number of atoms passing per unit area per unit time.
D is the diffusion coefficient in
Factors affection diffusion are as follows:
- Temperature
- Diffusion coefficient
The following equation is stated as:
Where,
Q is the activation energy in calorie/ mole.
R is universal gas constant in
T is the absolute temperature in kelvin.
Answer to Problem 5.71P
Thus, the value of Time required by the phosphorous concentration to make it equal to the concentration of boron at a depth of
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The equation used is given as,
Where,
Q is the initial surface concentration having unit of
Temperature for water is
Diffusion coefficient of phosphorous in silicon at a temperature of
t is the time in seconds.
Given equation for finding out the value of time (t) in seconds
Based on given data calculation of
Substituting the values,
On solving the equation,
t = 49758906
Conversion of seconds to hours,
Thus, the value of Time required by the phosphorous concentration to make it equal to the concentration of boron at a depth of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Essentials Of Materials Science And Engineering
- I need help on this question. step by step calculations and answers.arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardjan G(f) f Sketch the spectrum of g(t), which has a maximum frequency of 5 kHz, if it is sampled at the following sampling frequencies: 7 kHz, 10 kHz and 15 kHz. Indicate if and how the signal can be recovered at each sampling frequency.arrow_forward
- Don't use ai to answer i will report your answerarrow_forwardA single tone is modulated using FM transmitter. The SNR, at the input of the demodulator 20 dB. If the maximum frequency of the modulating signal is 4 kHz, and the maximum equency deviation is 12 kHz, find the SNR, and the bandwidth (using Carson rule) at the ollowing conditions: . For the given values of fm and Af. !. If the amplitude of the modulating signal is increased by 80%. 3. If the amplitude of the modulating signal is decreased by 50%, and frequency of modulating signal is increased by 50%.arrow_forwardThe circuit shown below on the left has the following parameters: V₁ = 5 V. R₁ = 40, R₂ = 40, α = 0.1. This circuit can be replaced by an equivalent circuit shown below on the right such that the voltage and current received by an arbitrary load resistor RL, are identical when connected to either circuits. Determine the value of the resistor R (in ) in the equivalent circuit. R₁ Rx R2 R₁ Vx R₁ Vi απ. barrow_forward
- Lab 07: Java Graphics (Bonus lab) In this lab, we'll be practicing what we learned about GUIs, and Mouse events. You will need to implement the following: ➤ A GUI with a drawing panel. We can click in this panel, and you will capture those clicks as a Point (see java.awt.Point) in a PointCollection class (you need to build this). о The points need to be represented by circles. Below the drawing panel, you will need 5 buttons: о An input button to register your mouse to the drawing panel. ○ о о A show button to paint the points in your collection on the drawing panel. A button to shift all the points to the left by 50 pixels. The x position of the points is not allowed to go below zero. Another button to shift all the points to the right 50 pixels. The x position of the points cannot go further than the You can implement this GUI in any way you choose. I suggest using the BorderLayout for a panel containing the buttons, and a GridLayout to hold the drawing panel and button panels.…arrow_forwardK/S 46. (O المهمات الجديدة 0 المنتهية 12 المغـ ۱۱:۰۹ search ليس لديك اي مهمات ☐ ○ ☑arrow_forwardthe answer should be: V2= -(P0-PL/2μL)(dx-x^)+Ux/darrow_forward
- For some viscoelastic polymers that are subjected to stress relaxation tests, the stress decays with time according to a(t) = a(0) exp(-4) (15.10) where σ(t) and o(0) represent the time-dependent and initial (i.e., time = 0) stresses, respectively, and t and T denote elapsed time and the relaxation time, respectively; T is a time-independent constant characteristic of the material. A specimen of a viscoelastic polymer whose stress relaxation obeys Equation 15.10 was suddenly pulled in tension to a measured strain of 0.5; the stress necessary to maintain this constant strain was measured as a function of time. Determine E (10) for this material if the initial stress level was 3.5 MPa (500 psi), which dropped to 0.5 MPa (70 psi) after 30 s.arrow_forward1. Consider the following a unity feedback control system. R(s) + E(s) 500(s+2)(s+5)(s+6) s(s+8)(s+10)(s+12) -Y(s) Find the followings: a) Type of the system b) Static position error constant Kp, Static velocity error constant Ry and Static acceleration error constant Ka c) Find the steady-state error of the system for (i) step input 1(t), (ii) ramp input t 1(t), (iii) parabolic input t² 1(t). 2. Repeat the above problem for the following system. R(s) + E(s) 500(s + 2)(s + 5) (s+8)(s+ 10)(s+12) Y(s) 3. Repeat the above problem for the following system. R(s) + E(s) 500(s+2)(s+4)(s+5)(s+6)(s+7) s²(s+8)(s+10)(s+12) Y(s)arrow_forwardFor the flows in Examples 11.1 and 11.2, calculate the magnitudes of the Δ V2 / 2 terms omitted in B.E., and compare these with the magnitude of the ℱ terms.arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage,
Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage, Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY





