
Methanol is synthesized from carbon monoxide and hydrogen in the reaction
A process ?owchart is shown below.
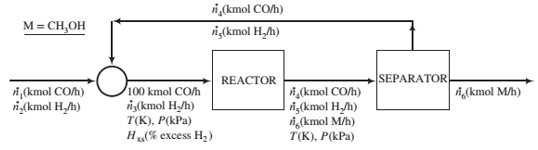
The fresh feed to the system, which contains only CO and H2, is blended with a recycle stream containing the same species. The combined stream is heated and compressed to a temperature T(K) and a pressure P(kPa) and fed to the reactor. The percentage excess hydrogen in this stream is Hxs. The reactor ef?uent—also at T and P—goes to a separation unit where essentially all of the methanol produced in the reactor is condensed and removed as product. The unreacted CO and H2constitute the recycle stream blended with the fresh feed.
Provided that the reaction temperature (and hence the rate of reaction) is high enough and the ideal- gas equation of state is a reasonable approximation at the reactor outlet conditions (a questionable assumption), the ratio
In these equations, piis the partial pressure of species i in kilopascals
Suppose P = 5000 kPa, T = 500 K, and the percentage excess of hydrogen in the feed to the reactor (Hxs) = 5.0%. Calculate
- ) and the ?ow rate (SCMH) of the recycle stream.
Run the program for the following nine conditions (three of which are the same):
(c) You should ?nd that the methanol yield increases with increasing pressure and decreasing temperature. What cost is associated with increasing the pressure?
(d) Why might the yield be much lower than the calculated value if the temperature is too low?
(e) If you actually ran the reaction at the given conditions and analyzed the reactor ef?uent, why might the spreadsheet values in Columns F—M be signi?cantly different from the measured values of these quantities? (Give several reasons, including assumptions made in obtaining the spreadsheet values.)
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Elementary Principles Of Chemical Processes
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Modern Database Management
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
Concepts Of Programming Languages
- (b) Provide the number of peaks in each of the indicated signals ('H NMR) for the compound below. CH3 6 1 H&C. C H₂ H2 3 HA 2 2 4 5 5arrow_forward8. The emission spectrum below for a one-electron (hydrogen-like) species in the gas phase shows all the lines, before they merge together, resulting from transitions to the ground state from higher energy states. Line A has a wavelength of 10.8 nm. BA Increasing wavelength, \ - a) What are the upper and lower principal quantum numbers corresponding to the lines labeled A and B? b) Identify the one-electron species that exhibits the spectrum.arrow_forwardShow work with explanation....don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
- achieve.macmillanlearning.com Canvas EA eac h Hulu YouTube G 3 methyl cyclobutanol - Google Search Ranking Phenol Acidity Course -236 - Organic Chemistry - Mac... ← Assessment Completed 10 of 22 Questions 1 + Netflix paramount plus chem hw Galdehyde reaction with grignard reagent... b My Questions | bartleby M Inbox - chenteislegit@gmail.com - Gmail Due: Fri, Jan 31 Resources Solution Penalized ? Hint Submit Answer Use retrosynthetic analysis to suggest two paths to synthesize 2-methyl-3-hexanol using the Grignard reaction. (Click and drag the appropriate image to the correct position in the reactions.) Route 1 Aldehyde 1 or +98 Aldehyde 2 Route 2 Q6 +100 Solved in 1 attempt Q7 +95 Solved in 2 attempts Q8 +98 Unlimited attempts possible + + Grignard 1 OH H3O+ Grignard 2 Answer Bank Q9 +90 MgBr Unlimited attempts possible CH3CH2CH2MgBr Q10 Unlimited attempts Q11 ? ? +100 in 1 attempt 2-methyl-3-hexanol CH3CH2MgBr H H о H Attempt 3arrow_forward2) (4 pt) After the reaction was completed, the student collected the following data. Crude product data is the data collected after the reaction is finished, but before the product is purified. "Pure" product data is the data collected after attempted purification using recrystallization. Student B's data: Crude product data "Pure" product data after recrystallization Crude mass: 0.93 g grey solid Crude mp: 96-106 °C Crude % yield: Pure mass: 0.39 g white solid Pure mp: 111-113 °C Pure % yield: a) Calculate the crude and pure percent yields for the student's reaction. b) Summarize what is indicated by the crude and pure melting points.arrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





