
5.50.19 In chemical vapor deposition (CVD), a semiconducting or insulating solid material is formed in a reaction between a gaseous species and a species adsorbed on the surface of silicon wafers (disks about 10 cm in diameter and l mm thick). The coated wafers are subjected to further processing to produce the microelectronic chips in computers and most other electronic devices in use today.
In one such process, silicon dioxide (MW = 60.06, SG = 2.67) is formed in the reaction between gaseous dichlorosilane (DCS) and adsorbed nitrous oxide:
A mixture of DCS and N2O ?ows through a “boat reactor"—a horizontal pipe in which 50 to 100 silicon wafers about 12 cm in diameter and 1 mm thick are set upright along the reactor length, with about 20 mm separation between each wafer. A side view of the reactor is shown below:
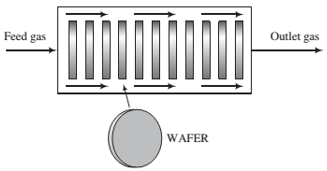
The feed gas enters the reactor at a rate of 3.74 SCMM (standard cubic meters per minute) and contains 22.0 mole% DCS and the balance N2O. In the reactor, the gas ?ows around the wafers, DCS and N2O diffuse into the spaces between the wafers, N2O is adsorbed on the wafer surfaces, and the adsorbed N2O reacts with gaseous DCS. The silicon dioxide formed remains on the surface, and the nitrogen and hydrogen chloride go into the gas phase and eventually leave the reactor with the unconsumed reactants. The temperature and absolute pressure in the reactor are constant at 900°C and 604 millitorr.
(a) The percentage conversion of DCS at a certain axial position (distance along the length of the reactor) is 60%. Calculate the volumetric ?ow rate (m3/min) of gas at this axial position.
(b) The rate of deposition of silicon dioxide per unit area of wafer surface is given by the formula
where
(c) Consider a wafer located at the axial position determined in Part (b). How thick is the silicon dioxide layer on that wafer after two hours of reactor operation, assuming that gas diffusion is rapid enough at the low reactor pressure for the composition of the gas (and hence the component partial pressures) to be uniform over the wafer surface? Express your answer in angstroms, where
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Elementary Principles Of Chemical Processes
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Modern Database Management
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- 9.3. An ideal PD controller has the transfer function P Ke (TDs + 1) E An actual PD controller had the transfer function P = Ke E TDS +1 (TDIẞ)s +1 where ẞis a large constant in an industrial controller. If a unit-step change in error is introduced into a controller having the second transfer function, show that P(1) = Kc (1 + Ae˜¯BD) where A is a function of ẞwhich you are to determine. For ẞ=5 and K = 0.5, plot P(t) versus tl tp. As ẞ, show that the unit-step response approaches that for the ideal controller.arrow_forward9.1. A pneumatic PI temperature controller has an output pressure of 10 psig when the set point and process temperature coincide. The set point is suddenly increased by 10°F (i.e., a step change in error is introduced), and the following data are obtained: Time, s psig 0- 10 0+ 8 20 7 60 90 5 3.5 Determine the actual gain (psig per degree Fahrenheit) and the integral time.arrow_forward2. A unit-step change in error is introduced into a PID controller. If Ke TD = 0.5, plot the response of the controller P(t). = =10, 1, andarrow_forward
- A distribution of values is normal with a mean of 211 and a standard deviation of 50.4. Find the probability that a randomly selected value is between 59.8 and 155.6. P(59.8 X 155.6) = Enter your answer as a number accurate to 4 decimal places. Answers obtained using exact z-scores or z- scores rounded to 3 decimal places are accepted.arrow_forwardTopic: Production of propylene glycol from glycerol derived from palm oil. QUESTION:Estimate capital items, operating costs and economics of the plant. Finally, report the estimatedreturn.The Detailed Factorial Method with approximately 25% accuracy must be used for detailedeconomic evaluation.Plant lifetime is fixed at 15 years.1) Depreciation and TaxesCalculate the depreciation using a suitable method (e.g., straight-line, declining balance) andincorporate tax implications based on current tax laws applicable to chemical plants. Use following attached Process Flow Diagram as reference for this question.arrow_forwardTopic: Production of propylene glycol from glycerol derived from palm oil. QUESTION:Estimate capital items, operating costs and economics of the plant. Finally, report the estimatedreturn.The Detailed Factorial Method with approximately 25% accuracy must be used for detailedeconomic evaluation.Plant lifetime is fixed at 15 years.1) Revenue EstimationEstimate the annual revenue based on the production capacity, product selling price, and marketdemand. Groups should also consider potential market fluctuations. Use following attached Process Flow Diagram as reference for this question.arrow_forward
- Topic: Production of propylene glycol from glycerol derived from palm oil. QUESTION:Estimate capital items, operating costs and economics of the plant. Finally, report the estimatedreturn.The Detailed Factorial Method with approximately 25% accuracy must be used for detailedeconomic evaluation.Plant lifetime is fixed at 15 years.TASKS:1) Capital Cost EstimationProvide a detailed breakdown of the initial capital investment, including land, building,equipment, and installation costs. Include any assumptions made in the estimation. Use following attached Process Flow Diagram as reference for this question.arrow_forwardTopic: Production of propylene glycol from glycerol derived from palm oil. QUESTION:Estimate capital items, operating costs and economics of the plant. Finally, report the estimatedreturn.The Detailed Factorial Method with approximately 25% accuracy must be used for detailedeconomic evaluation.Plant lifetime is fixed at 15 years.1) Breakeven Year CalculationUsing the cash flow analysis, calculate the breakeven year when the cumulative cash inflowequals the initial investment. Groups should graphically represent the breakeven point. Use following attached Process Flow Diagram as reference for this question.arrow_forwardTopic: Production of propylene glycol from glycerol derived from palm oil. QUESTION:Estimate capital items, operating costs and economics of the plant. Finally, report the estimatedreturn.The Detailed Factorial Method with approximately 25% accuracy must be used for detailedeconomic evaluation.Plant lifetime is fixed at 15 years.1) Cash Flow AnalysisDevelop a projected cash flow statement for the first 10 years of plant operation, consideringall the costs and revenues. Include working capital, loans, and interest payments if applicable. Use following attached Process Flow Diagram as reference for this question.arrow_forward
- Topic: Production of propylene glycol from glycerol derived from palm oil.QUESTION:Estimate capital items, operating costs and economics of the plant. Finally, report the estimatedreturn.The Detailed Factorial Method with approximately 25% accuracy must be used for detailedeconomic evaluation.Plant lifetime is fixed at 15 years.1) Operational Cost AnalysisCalculate the yearly operational costs, including raw materials, labor, utilities, maintenance,and other recurring expenses. Provide a clear explanation of how these costs are derived. Use following attached Process Flow Diagram as reference for this question.arrow_forwardChemical Engineering Questionarrow_forwardA steam boiler or steam generator is a device used to produce steam by transferring heat to water. In our case, the combustion chamber is fueled with propane (C3H8) at a flowrate of 50.0 mol/h in an excess air of 50%. Assume that both propane and air are fed at 25ºC and the combustion gases leave the chamber at 200ºC. Pressure can be assumed to be atmospheric.* Determine: 1. The heat obtained assuming complete combustion. Compare the results using elements or compounds 2. The steam flowrate that could be generated if the heat is directed to obtain superheated steam at 2 bar and 160ºC from saturated liquid water at this pressure solvearrow_forward
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The





