
University Physics with Modern Physics Plus Mastering Physics with eText -- Access Card Package (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780321982582
Author: Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 5.65P
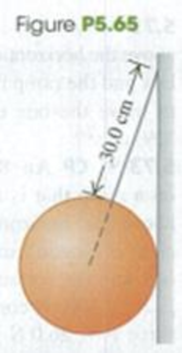
A solid uniform 45.0-kg ball of diameter 32.0 cm is supported against a vertical, frictionless wall by a thin 30.0-cm wire of negligible mass (Fig. P5.65). (a) Draw a free-body diagram for the ball, and use the diagram to find the tension in the wire. (b) How hard does the ball push against the wall?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The distance between two telephone poles is d = 54.0 m. When a 1.20 kg bird lands on the telephone wire midway between the poles, the wire sags h = 0.206 m.
(a) Draw a free-body diagram of the midpoint of the wire (where the bird is perched).
mg
O X*
(b) How much tension (in N) does the bird produce in the wire? Ignore the weight of the wire.
3.15
Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step carefully. N
Need Help?
Read It
A 60.0 cm, uniform, 50.0 N shelf is supported horizontally by two vertical wires attached to the sloping ceiling (Fig. ). A very small 25.0 N tool is placed on the shelf midway between the points where the wires are attached to it. Find the tension in each wire. Begin by making a free-body diagram of the shelf.
A 4.00 kg block sits on a table top with a coefficient of static friction of 0.470 and a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.320. A weight is attached by a string to the block so as to just overcome the force of static friction acting on the block. What is the acceleration of the block?Please give a step by step for the solution and a final answer.Thanks!!
Chapter 5 Solutions
University Physics with Modern Physics Plus Mastering Physics with eText -- Access Card Package (14th Edition)
Ch. 5.1 - A traffic light of weight w hangs from two...Ch. 5.2 - Suppose you hold the glider in Example 5.12 so...Ch. 5.3 - Consider a box that is placed on different...Ch. 5.4 - Satellites are held in orbit by the force of our...Ch. 5 - A man sits in a seat that is hanging from a rope....Ch. 5 - In general, the normal force is not equal to the...Ch. 5 - A clothesline hangs between two poles. No matter...Ch. 5 - You drive a car up a steep hill at constant speed....Ch. 5 - For medical reasons, astronauts in outer space...Ch. 5 - To push a box up a ramp, which requires less...
Ch. 5 - A woman in an elevator lets go of her briefcase,...Ch. 5 - A block rests on an inclined plane with enough...Ch. 5 - A crate slides up an inclined ramp and then slides...Ch. 5 - A crate of books rests on a level floor. To move...Ch. 5 - In a world without friction, which of the...Ch. 5 - When you stand with bare feet in a wet bathtub,...Ch. 5 - You are pushing a large crate from the back of a...Ch. 5 - It is often said that friction always opposes...Ch. 5 - If there is a net force on a particle in uniform...Ch. 5 - A curve in a road has a bank angle calculated and...Ch. 5 - You swing a ball on the end of a lightweight...Ch. 5 - The centrifugal force is not included in the...Ch. 5 - A professor swings a rubber stopper in a...Ch. 5 - To keep the forces on the riders within allowable...Ch. 5 - A tennis ball drops from rest at the top of a tall...Ch. 5 - You throw a baseball straight upward with speed 0....Ch. 5 - You throw a baseball straight upward. If you do...Ch. 5 - You have two identical tennis balls and fill one...Ch. 5 - A ball is dropped from rest and feels air...Ch. 5 - A ball is dropped from rest and feels air...Ch. 5 - When a balled baseball moves with air drag, when...Ch. 5 - A ball is thrown from the edge of a high cliff....Ch. 5 - Two 25.0-N weights are suspended at opposite ends...Ch. 5 - In Fig. E5.2 each of the suspended blocks has...Ch. 5 - A 75.0-kg wrecking ball hangs from a uniform,...Ch. 5 - BIO Injuries to the Spinal Column. In the...Ch. 5 - A picture frame hung against a wall is suspended...Ch. 5 - A large wrecking ball is held in place by two...Ch. 5 - Find the tension in each cord in Fig. E5.7 if the...Ch. 5 - A 1130-kg car is held in place by a light cable on...Ch. 5 - A man pushes on a piano with mass 180 kg; it...Ch. 5 - In Fig. E5.10 the weight w is 60.0 N. (a) What is...Ch. 5 - BIO Stay Awake! An astronaut is inside a 2.25 106...Ch. 5 - A rocket of initial mass 125 kg (including all the...Ch. 5 - CP Genesis Crash. On September 8, 2004, the...Ch. 5 - Three sleds are being pulled horizontally on...Ch. 5 - Atwoods Machine. A 15.0-kg load of bricks hangs...Ch. 5 - CP An 8.00-Kg block of ice, released from rest at...Ch. 5 - A light rope is attached to a block with mass 4.00...Ch. 5 - CP Runway Design. A transport plane lakes off from...Ch. 5 - CP A 750.0-kg boulder is raised from a quarry 125...Ch. 5 - Apparent Weight. A 550-N physics student stands on...Ch. 5 - CP BIO Force During a Jump. When jumping straight...Ch. 5 - CP CALC A 2540-kg test rocket is launched...Ch. 5 - CP CALC A 2.00-kg box is moving to the right with...Ch. 5 - CP CALC A 5.00-kg crate is suspended from the end...Ch. 5 - BIO The Trendelenburg Position. After emergencies...Ch. 5 - In a laboratory experiment on friction, a 135-N...Ch. 5 - CP A stockroom worker pushes a box with mass 16.8...Ch. 5 - A box of bananas weighing 40.0 N rests on a...Ch. 5 - A 45.0-kg crate of tools rests on a horizontal...Ch. 5 - Some sliding rocks approach the base of a hill...Ch. 5 - A box with mass 10.0 kg moves on a ramp that is...Ch. 5 - A pickup truck is carrying a toolbox, but the rear...Ch. 5 - You are lowering two boxes, one on top of the...Ch. 5 - Consider the system shown in Fig. E5.34. Block A...Ch. 5 - CP Stopping Distance. (a) If the coefficient of...Ch. 5 - CP A 25.0-kg box of textbooks rests on a loading...Ch. 5 - Two crates connected by a rope lie on a horizontal...Ch. 5 - A box with mass m is dragged across a level floor...Ch. 5 - CP As shown in Fig. E5.34, block A (mass 2.25 kg)...Ch. 5 - You throw a baseball straight upward. The drag...Ch. 5 - A large crate with mass m rests on a horizontal...Ch. 5 - (a) In Example 5.18 (Section 5.3), what value of D...Ch. 5 - A stone with mass 0.80 kg is attached to one end...Ch. 5 - BIO Force on a Skaters Wrist. A 52-kg ice skater...Ch. 5 - A small remote-controlled car with mass 1.60 kg...Ch. 5 - 5.46A small car with mass 0.800 kg travels at...Ch. 5 - A small model car with mass m travels at constant...Ch. 5 - A flat (unbanked) curve on a highway has a radius...Ch. 5 - A 1125-kg car and a 2250-kg pickup truck approach...Ch. 5 - The Giant Swing at a county fair consists of a...Ch. 5 - In another version of the Giant Swing (see...Ch. 5 - A small button placed on a horizontal rotating...Ch. 5 - Rotating Space Stations. One problem for humans...Ch. 5 - The Cosmo Clock 21 Ferris wheel in Yokohama,...Ch. 5 - An airplane flies in a loop (a circular path in a...Ch. 5 - A 50.0-kg stunt pilot who has been diving her...Ch. 5 - Stay Dry! You tie a cord to a pail of water and...Ch. 5 - A bowling ball weighing 71.2 N (16.0 lb) is...Ch. 5 - BIO Effect on Blood of Walking. While a person is...Ch. 5 - An adventurous archaeologist crosses between two...Ch. 5 - Two ropes are connected to a steel cable that...Ch. 5 - In Fig. P5.62 a worker lifts a weight w by pulling...Ch. 5 - In a repair shop a truck engine that has mass 409...Ch. 5 - A horizontal wire holds a solid uniform ball of...Ch. 5 - A solid uniform 45.0-kg ball of diameter 32.0 cm...Ch. 5 - CP A box is sliding with a constant speed of 4.00...Ch. 5 - CP BIO Forces During Chin-ups. When you do a...Ch. 5 - CP CALC A 2.00-kg box is suspended from the end of...Ch. 5 - CALC A 3.00-kg box that is several hundred meters...Ch. 5 - CP A 5.00-kg box sits at rest at the bottom of a...Ch. 5 - Two boxes connected by a light horizontal rope are...Ch. 5 - A 6.00-kg box sits on a ramp that is inclined at...Ch. 5 - CP An 8.00-kg box sits on a ramp that is inclined...Ch. 5 - CP In Fig. P5.74, m1 = 20.0 kg and = 53.1. The...Ch. 5 - CP You place a book of mass 5.00 kg against a...Ch. 5 - Block A in Fig. P5.76 weighs 60.0 N. The...Ch. 5 - A block with mass m1 is placed on an inclined...Ch. 5 - BIO The Flying Leap of a Flea. High-speed motion...Ch. 5 - Block A in Fig. P5.79 weighs 1.20 N, and block B...Ch. 5 - CP Elevator Design. You are designing an elevator...Ch. 5 - CP CALC You are standing on a bathroom scale in an...Ch. 5 - A hammer is hanging by a light rope from the...Ch. 5 - A 40.0-kg packing case is initially at rest on the...Ch. 5 - If the coefficient of static friction between a...Ch. 5 - Two identical 15.0-kg balls, each 25.0 cm in...Ch. 5 - CP Traffic Court. You are called as an expert...Ch. 5 - Block A in Fig. P5.87 weighs 1.90 N, and block B...Ch. 5 - CP Losing Cargo. A 12.0-kg box rests on the level...Ch. 5 - Block A in Fig. P5.89 has mass 4.00 kg, and block...Ch. 5 - Two blocks connected by a cord passing over a...Ch. 5 - In terms of m1, m2, and g, find the acceleration...Ch. 5 - Block B, with mass 5.00 kg, rests on block A, with...Ch. 5 - Two objects, with masses 5.00 kg and 2.00 kg, hang...Ch. 5 - Friction in an Elevator. You are riding in an...Ch. 5 - A block is placed against the vertical front of a...Ch. 5 - Two blocks, with masses 4.00 kg and 8.00 kg, are...Ch. 5 - Block A, with weight 3w, slides down an inclined...Ch. 5 - Jack sits in the chair of a Ferris wheel that is...Ch. 5 - Bunked Curve I. A curve with a 120-m radius on a...Ch. 5 - Banked Curve II. Consider a wet roadway banked as...Ch. 5 - Blocks A, B, and C are placed as in Fig. P5.101...Ch. 5 - You are riding in a school bus. As the bus rounds...Ch. 5 - CALC You throw a rock downward into water with a...Ch. 5 - A 4.00-kg block is attached to a vertical rod by...Ch. 5 - On the ride Spindletop at the amusement park Six...Ch. 5 - A 70-kg person rides in a 30-kg cart moving at 12...Ch. 5 - A small bead can slide without friction on a...Ch. 5 - A physics major is working to pay her college...Ch. 5 - DATA In your physics lab, a block of mass m is at...Ch. 5 - DATA A road heading due cast passes over a small...Ch. 5 - DATA You are an engineer working for a...Ch. 5 - Moving Wedge. A wedge with mass M rests on a...Ch. 5 - Figure P5.112 5.113A wedge with mass M rests on a...Ch. 5 - Double Atwoods Machine. In Fig. P5.114 masses m1...Ch. 5 - A ball is held at rest at position A in Fig....Ch. 5 - FRICTION AND CLIMBING SHOES. Shoes made for the...Ch. 5 - FRICTION AND CLIMBING SHOES. Shoes made for the...Ch. 5 - FRICTION AND CLIMBING SHOES. Shoes made for the...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The pV-diagram of the Carnot cycle.
Sears And Zemansky's University Physics With Modern Physics
(a) Show that .
[Hint: Use integration by parts.]
(b) Let be the step function: . (1.95)
Show that .
Introduction to Electrodynamics
3. How does evaporation of perspiration from your skin cool your body?
College Physics (10th Edition)
A mole is approximately the number of protons in a gram of protons. The mass of a neutron is about the same as ...
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
The value of CA for a Ford Escape Hybrid is 1.08m2. Which answer below is closest to the drag force on this car...
College Physics
3. What is free-fall, and why does it make you weightless? Briefly describe why astronauts are weightless in th...
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I need (b) onlyarrow_forwardAnswer must be according the correct signifcant numbers.arrow_forwardA 2.00-kg block is at rest on a horizontal plank that is 1.50 m long. When one end of the plane is raised to 0.50 m, the block starts sliding down. What is the coefficient of static/starting friction between the block and the plank? O 0.43 O 0.35 0.33 O 0.53arrow_forward
- e weight of the block in the drawing is 97.0 N. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the vertical wall is 0.430. (a) What minimum magnitude of the force is required to prevent the block from sliding down the wall? (Hint: The static frictional force erted by the block is directed upward, paraliel to the wall.) (b) What minimum force is required to start the block moving up the wall? (Hint: The static frictional force is now directed down the wall.) Block wall ) Number Units p) Number Unitsarrow_forwardHopeful for greater opportunities, Juan applies for an international scholarship. Fortunately, he gotaccepted and is now at the airport to travel to New Zealand. Waiting on queue at the entrance, Juanis holding his 30kg luggage up on a ramp that is inclined at an angle of 10° from the horizontal.He is holding on to his luggage at an angle of 65° from the ramp. Compute for the tension theluggage exerts on his hand and the normal force.arrow_forwardIn an old-fashioned amusement park ride, passengers stand inside a 3.90 m diameter hollow steel cylinder with the backs against the wall. The cylinder begins to rotate about a vertical axis. Then the floor on which the passengers are standing drops away! If all goes well, the passengers will "stick" to the wall and not slide. Clothing has a coefficient of static coefficient of friction against steel in the range of 0.690 to 1.0 and a kinetic coefficient in the range 0.480 to 0.70. A sign next to the entrance says "No children under 30 kg allowed." What is the minimum angular speed in rpm (do not enter units) for which the ride is safe? Assume that the local acceleration due to gravity is -9.80 m/s². Submit Answer Tries 0/10arrow_forward
- The distance between two telephone poles is d = 52.0 m. When a 0.850-kg bird lands on the telephone wire midway between the poles, the wire sags h = 0.205 m. (a) Draw a free-body diagram of the bird. (b) How much tension does the bird produce in the wire? Ignore the weight of the wire.arrow_forwardRoss and Rachel are fighting if they were on a break. Ross is trying to get his stuff weighing 150. N placed on an inclined plane by pulling it upwards parallel to the inclined plane with 150. N force. However, Rachel is trying to stop Ross by exerting 50.0 N perpendicular to the inclined plane. The coefficients of friction between the box and the incline are us = 0.450 and uk = 0.350. Rachel was able to stop Ross. The object is in static equilibrium. Rachel wins. The object is impending to move up. Nobody wins; the object slides down to the plane. Ross was able to get the object. The object slides up along the incline. 50 N F·R·I·E·N·D·S 30° Was Ross able to get the object or was Rachel able to stop him? (Ctrl)- 150 Narrow_forwardAll questions on this assessment use the same scenario as the lab immediately preceding it: A team of sled dogs pull a 50.00 kg dogsled via the tension (magnitude 85.0 N) in a horizontal cord that connects the dogs to the sled. The force of friction between the waxed wood of the sled's skis and the wet snow acts in the direction opposite to the sled's displacement, which has a magnitude of 15.00 m. The FBD for the sled is given for you below, so we're all understanding the scenario the same way. 1) Calculate the work done on the sled by the tension during this displacement of the sled. A) OJ B) 735.75 J C) -735.75 J D) 1030.05 J E) -1030.05 J F) 1275 J G) -1275 J H) 7357.5 J I) -7357.5 J 1 14 10arrow_forward
- In an old-fashioned amusement park ride, passengers stand inside a 4.50 m diameter hollow steel cylinder with the backs against the wall. The cylinder begins to rotate about a vertical axis. Then the floor on which the passengers are standing drops away! If all goes well, the passengers will "stick" to the wall and not slide. Clothing has a coefficient of static coefficient of friction against steel in the range of 0.540 to 1.0 and a kinetic coefficient in the range 0.380 to 0.70. A sign next to the entrance says "No children under 30 kg allowed." What is the minimum angular speed in rpm (do not enter units) for which the ride is safe? Assume that the local acceleration due to gravity is -9.80 m/s2.arrow_forwardSuppose a horse leans against a wall as in Figure 5.35. Calculate the force exerted on the wall assuming that force is horizontal and using the data in the schematic representation of the situation. Note that the force exerted on the wall is equal and opposite to the force exerted on the horse, keeping it in equilibrium. The total mass of the horse and rider is 350 kg. Take the data to be accurate to three digits.Narrow_forwardTwo identical 15.0 kg balls, each 25.0 cm in diameter, are suspended by two 35.0 cm wires . The entire apparatus is supported by a single 18.0 cm wire, and the surfaces of the balls are perfectly smooth. (a) Find the tension in each of the three wires. (b) How hard does each ball push on the other one?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON
Newton's Third Law of Motion: Action and Reaction; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y61_VPKH2B4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY