
Concept explainers
Determine the reactions at ball-and-socket joints D, E, and F of the space truss shown. Express the answers in
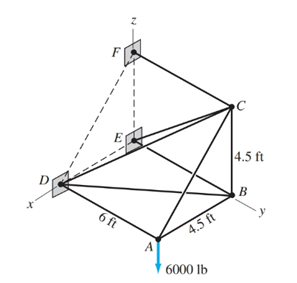
Reaction at D, E and F.
Answer to Problem 5.49P
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The follwing truss with ball and socket joint at D, E and F is given,

Calculation:
Draw free body diagram of as shown in following figure,
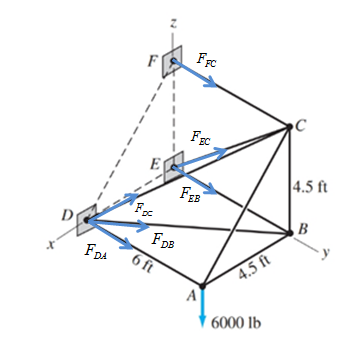
Forces and corresponding position vectors are listed in the following table,
| Force | Position vector |
| | |
| | |
| | |
Take equilibrium of moments about origin as,
Above vector equations gives following scalars equations,
Take equilibrium of forces as,
Above vector equations gives following scalars equations,
Solve equations (1-6) to get
Calculate reaction at D as,
Calculate reaction at E as,
Calculate reaction at F as,
Conclusion:
Therefore,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
- From thermodynamics please fill in the table show all work step by steparrow_forwardThe 150-lb skater passes point A with a speed of 6 ft/s. (Figure 1) Determine his speed when he reaches point B. Neglect friction. Determine the normal force exerted on him by the track at this point. 25 ft B = 4x A 20 ft xarrow_forwardA virtual experiment is designed to determine the effect of friction on the timing and speed of packages being delivered to a conveyor belt and the normal force applied to the tube. A package is held and then let go at the edge of a circular shaped tube of radius R = 5m. The particle at the bottom will transfer to the conveyor belt, as shown below. Run the simulations for μ = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6 and determine the time and speed at which the package is delivered to the conveyor belt. In addition, determine the maximum normal force and its location along the path as measured by angle 0. Submit in hardcopy form: (0) Free Body Diagram, equations underneath, derivations (a) Your MATLAB mfile (b) A table listing the values in 5 columns: μ, T (time of transfer), V (speed of transfer), 0 (angle of max N), Nmax (max N) (c) Based on your results, explain in one sentence what you think will happen to the package if the friction is increased even further, e.g. μ = 0.8. NOTE: The ODE is…arrow_forward
- Patm = 1 bar Piston m = 50 kg 5 g of Air T₁ = 600 K P₁ = 3 bar Stops A 9.75 x 10-3 m² FIGURE P3.88arrow_forwardAssume a Space Launch System (Figure 1(a)) that is approximated as a cantilever undamped single degree of freedom (SDOF) system with a mass at its free end (Figure 1(b)). The cantilever is assumed to be massless. Assume a wind load that is approximated with a concentrated harmonic forcing function p(t) = posin(ωt) acting on the mass. The known properties of the SDOF and the applied forcing function are given below. • Mass of SDOF: m =120 kip/g • Acceleration of gravity: g = 386 in/sec2 • Bending sectional stiffness of SDOF: EI = 1015 lbf×in2 • Height of SDOF: h = 2000 inches • Amplitude of forcing function: po = 6 kip • Forcing frequency: f = 8 Harrow_forwardAssume a Space Launch System (Figure 1(a)) that is approximated as a cantilever undamped single degree of freedom (SDOF) system with a mass at its free end (Figure 1(b)). The cantilever is assumed to be massless. Assume a wind load that is approximated with a concentrated harmonic forcing function p(t) = posin(ωt) acting on the mass. The known properties of the SDOF and the applied forcing function are given below. • Mass of SDOF: m =120 kip/g • Acceleration of gravity: g = 386 in/sec2 • Bending sectional stiffness of SDOF: EI = 1015 lbf×in2 • Height of SDOF: h = 2000 inches • Amplitude of forcing function: po = 6 kip • Forcing frequency: f = 8 Hz Figure 1: Single-degree-of-freedom system in Problem 1. Please compute the following considering the steady-state response of the SDOF system. Do not consider the transient response unless it is explicitly stated in the question. (a) The natural circular frequency and the natural period of the SDOF. (10 points) (b) The maximum displacement of…arrow_forward
- Assume a Space Launch System (Figure 1(a)) that is approximated as a cantilever undamped single degree of freedom (SDOF) system with a mass at its free end (Figure 1(b)). The cantilever is assumed to be massless. Assume a wind load that is approximated with a concentrated harmonic forcing function p(t) = posin(ωt) acting on the mass. The known properties of the SDOF and the applied forcing function are given below. • Mass of SDOF: m =120 kip/g • Acceleration of gravity: g = 386 in/sec2 • Bending sectional stiffness of SDOF: EI = 1015 lbf×in2 • Height of SDOF: h = 2000 inches • Amplitude of forcing function: po = 6 kip • Forcing frequency: f = 8 Hz Figure 1: Single-degree-of-freedom system in Problem 1. Please compute the following considering the steady-state response of the SDOF system. Do not consider the transient response unless it is explicitly stated in the question. (a) The natural circular frequency and the natural period of the SDOF. (10 points) (b) The maximum displacement of…arrow_forwardPlease solve 13 * √(2675.16)² + (63.72 + 2255,03)² = 175x106 can you explain the process for getting d seperate thank youarrow_forwardIf the 300-kg drum has a center of mass at point G, determine the horizontal and vertical components of force acting at pin A and the reactions on the smooth pads C and D. The grip at B on member DAB resists both horizontal and vertical components of force at the rim of the drum. P 60 mm; 60 mm: 600 mm A E 30° B C 390 mm 100 mm D Garrow_forward
- The design of the gear-and-shaft system shown requires that steel shafts of the same diameter be used for both AB and CD. It is further required that the angle D through which end D of shaft CD rotates not exceed 1.5°. Knowing that G = 77.2 GPa, determine the required diameter of the shafts. 40 mm 400 mm 100 mm 600 mm T-1000 N-m Darrow_forwardAssume a Space Launch System (Figure 1(a)) that is approximated as a cantilever undamped single degree of freedom (SDOF) system with a mass at its free end (Figure 1(b)). The cantilever is assumed to be massless. Assume a wind load that is approximated with a concentrated harmonic forcing function p(t) = posin(ωt) acting on the mass. The known properties of the SDOF and the applied forcing function are given below. • Mass of SDOF: m =120 kip/g • Acceleration of gravity: g = 386 in/sec2 • Bending sectional stiffness of SDOF: EI = 1015 lbf×in2 • Height of SDOF: h = 2000 inches • Amplitude of forcing function: po = 6 kip • Forcing frequency: f = 8 Hzarrow_forward13.44 The end of a cylindrical liquid cryogenic propellant tank in free space is to be protected from external (solar) radiation by placing a thin metallic shield in front of the tank. Assume the view factor Fts between the tank and the shield is unity; all surfaces are diffuse and gray, and the surroundings are at 0 K. Tank T₁ Shield, T T₁ = 100 K E1 Solar irradiation Gs ε₁ = ε₂ = 0.05 ε₁ = 0.10 Gs = 1250 W/m² E2 Find the temperature of the shield T, and the heat flux (W/m²) to the end of the tank.arrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
