
Materials for Civil and Construction Engineers (4th Edition)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780134320533
Author: Michael S. Mamlouk, John P. Zaniewski
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 5.19QP
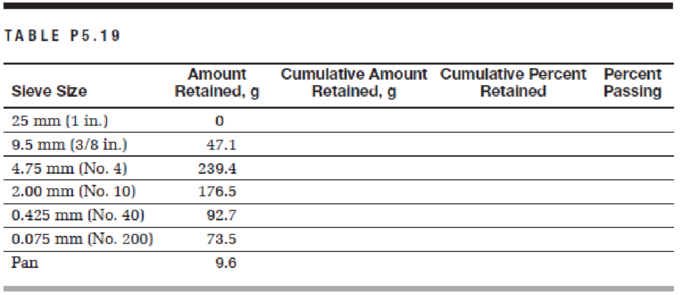
Calculate the sieve analysis shown in Table P5.19 and plot on a semilog gradation paper. What is the maximum size? What is the nominal maximum size?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
help me find solutions for a,b,c,d,and e
A sieve analysis test was performed on a sample of fine aggregate and produced the results in Table below.
Calculate the percent passing through each sieve.
What is the maximum size?
What is the nominal maximum size?
What is the Fineness Modulus?
Plot the percent passing versus sieve size on a semi-log gradation size. (You can use Excel sheets or you can draw on a semi-log attached to page 3 of this assignment)
Sieve size (mm)
Amount retained (g)
Cumulative amount retained (g)
Cumulative percentage retained
Percent passing
12.5
0
9.5
21
4.75
104
2.36
79
1.18
78
0.6
51
0.30
78
0.15
82
0.075
39
pan
5
A sieve analysis test was performed on a sample of coarse aggregate and produced the following results. Referring to ASTM C33, what is the closest size number, and does it meet the gradation for that standard size?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Materials for Civil and Construction Engineers (4th Edition)
Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.1QPCh. 5 - Discuss five different desirable characteristics...Ch. 5 - Discuss five different desirable characteristics...Ch. 5 - The shape and surface texture of aggregate...Ch. 5 - Define the following terms: a. Saturated...Ch. 5 - Three samples of fine aggregate have the...Ch. 5 - A sample of wet aggregate weighed 297.2 N. After...Ch. 5 - 46.5 kg (102.3 lb) of fine aggregate is mixed with...Ch. 5 - Samples of coarse aggregate from a stockpile are...Ch. 5 - Base course aggregate has a target dry density of...
Ch. 5 - Calculate the percent voids between aggregate...Ch. 5 - Calculate the percent voids between aggregate...Ch. 5 - Coarse aggregate is placed in a rigid bucket and...Ch. 5 - The following laboratory tests are performed on...Ch. 5 - Students in the materials lab performed the...Ch. 5 - The specific gravity and absorption test (ASTM...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.18QPCh. 5 - Calculate the sieve analysis shown in Table P5.19...Ch. 5 - Calculate the sieve analysis shown in Table P5.20,...Ch. 5 - A sieve analysis test was performed on a sample of...Ch. 5 - A sieve analysis test was performed on a sample of...Ch. 5 - Draw a graph to show the cumulative percent...Ch. 5 - Referring to Table 5.6, plot the specification...Ch. 5 - Referring to the aggregate gradations A, B, and C...Ch. 5 - Table P5.26 shows the grain size distributions of...Ch. 5 - Table P5.27 shows the grain size distributions of...Ch. 5 - Three aggregates are to be mixed together in the...Ch. 5 - Table P5.29 shows the grain size distribution for...Ch. 5 - Laboratory specific gravity and absorption tests...Ch. 5 - Table P5.31 shows the grain size distribution for...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.32QPCh. 5 - Laboratory specific gravity and absorption tests...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.34QPCh. 5 - Define the fineness modulus of aggregate. What is...Ch. 5 - Calculate the fineness modulus of aggregate A in...Ch. 5 - Calculate the fineness modulus of aggregate B in...Ch. 5 - A portland cement concrete mix requires mixing...Ch. 5 - Discuss the effect of the amount of material...Ch. 5 - Aggregates from three sources having the...Ch. 5 - Aggregates from three sources having the...Ch. 5 - A contractor is considering using three stockpiles...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.43QPCh. 5 - What are the typical deleterious substances in...Ch. 5 - Review ASTM D75 and summarize the following: a....
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
A nozzle at A discharges water with an initial velocity of 36 ft/s at an angle with the horizontal. Determine ...
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Why is the study of database technology important?
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
How are relationships between tables expressed in a relational database?
Modern Database Management
This optional Google account security feature sends you a message with a code that you must enter, in addition ...
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
What types of coolant are used in vehicles?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Given the image below. What is the maximum diameter of aggregate considering the narrowest dimension of the beam in cm if the value of c is 40cm and the value of e is 69cm? slab Oslab=10mm Obeam=25™m beam b earrow_forwardWhat is the maximum diameter of aggregate in cm? 160mm sab 130mm beam 17.25™m 500mm 700mm Slab=10mm @beam=25mm D =?arrow_forwardQuestion # 3: Calculate the fineness mnlulus of aggregate according to the table of the sieve analysis below. Sieve size Mass Cumulative Cumulative Percentage retained according to ASTM retained (g) percentage passing percentage retained 3/8 in 4 8. 32 16 34 30 56 50 104 100 54 <100 24arrow_forward
- With aid of diagram, elaborate on the method to test material hardness using Brinell hardness testarrow_forwardDefine Particle Shape and Texture of Fine Aggregates.arrow_forwardA sieve analysis test was performed on a sample of aggregate and produced the results shown in Table .Calculate the percent passing through each sieve. Plot the percent passingversus sieve size on:a. a semilog gradation chart, andb. a 0.45 gradation chart (Figure A.25).What is the maximum size? What is the nominal maximum size?arrow_forward
- Determine the maximum normal stress developed in the bar when it is subjected to a tension of P� = 6.1 kNkN .arrow_forwardPlease solve with a step by step solution and a clear understanding so I can understandarrow_forwardA sieve analysis test was performed on a sample of coarse aggregate and pro- duced the results in Table P5.22. a. Calculate the percent passing through each sieve. b. What is the maximum size? c. What is the nominal maximum size? d. Plot the percent passing versus sieve size on a semilog gradation chart. e. Plot the percent passing versus sieve size on a 0.45 gradation chart (Figure A.25). f. Referring to Table 5.5 (ASTM C33), what is the closest size number and does it meet the gradation for that standard size? TABLE P5.22 Sieve Size, mm Amount Retained, g 75.0 50.0 37.5 1678 25.0 7212 19.0 5443 12.5 6124 9.5 12111 4.75 4581 Pan 590arrow_forward
- A small amount of resin weighing 4.56g occupies a height of a 10-ml graduated cylinder equivalent to one ml. One mL of water was added and the level was read at 1.7 mL. Estimate the porosity of the resin.arrow_forwardCalculate the fineness modulus of this fine aggregate sample. Report your answer to the nearest 1 decimal place (tens). Sieve Size, Retained Mass, % Retained Cumulative % % Passing mm (US) 12.5 (1/2") 9.5 (3/8") 4.75 (#4) 2.36 (#8) 1.18 (#16) 0.600 (#30) 0.300 (#50) 0.150 (#100) 0.075 (#200) Grams on Sieves retained on seives 3.0 0.36 0.36 99.64 10.0 1.22 1.58 98.42 30.0 3.65 5.22 94.78 55.0 6.68 11.91 88.09 230.0 27.95 39.85 60.15 175.0 21.26 61.12 38.88 140.0 17.01 78.13 21.87 120.0 14.58 92.71 7.29 40.0 4.86 97.57 2.43 Pan 20.0 2.43 100.00 0.00 Total: 823.0arrow_forwardReferring to the aggregate gradations A, B, and C in Figure P5.26, answer the following questions: a. What is the maximum size of each gradation? b. What is the nominal maximum size of each gradation? c. Classify each gradation as dense, open, or gap indicating the reason for each classification. 100 A 80- 60 40 0.075 0.30 1.18 2.36 4.75 9.5 12.5 19.0 25.0 0.15 0.60 Sieve sizes (mm) FIGURE P5.26 Percent passing 20arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
What Is A Construction Takeoff? | Are They Still Necessary In Quantity Surveying?; Author: Metroun Quantity Surveying;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uTWoDPtcOjg;License: Standard Youtube License