
-1 through 5.10-6 A wide-flange beam (see figure) is subjected to a shear force V. Using the dimensions of the cross section, calculate the moment of inertia and then determine the following quantities:
- The maximum shear stress tinixin the web.
Note: Disregard the fillets at the junctions of the web and flanges and determine all quantities, including the moment of inertia, by considering the cross section to consist of three rectangles.
5.10-2 Dimensions of cross section: b = 180 mm, v = 12 mm, h = 420 mm,
i = 380 mm, and V = 125 kN.
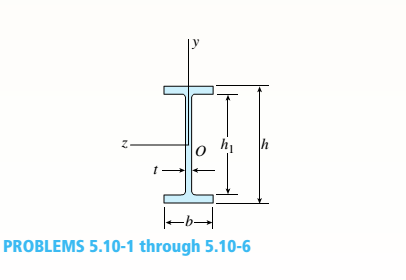
(a).
To Find:
The moment of inertia and the maximum shear stress in the web.
Answer to Problem 5.10.2P
The maximum shear stress in the web is =
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Shear Force
Dimensions:
Concept Used:
Following formula will be used:
Maximum shear stress,
Moment of inertia of rectangle,
Calculation:
Area of upper and lower flanges/rectangles:
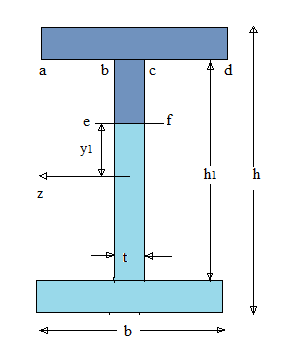
Second rectangle is
In which
The first moment of areas of
By putting the values of
The moment of inertia for the I section is given by following formula:
The maximum value of shear stress will be at neutral axis when
Conclusion:
The maximum shear stress in the web is
(b).
To Find:
The minimum shear stress in web.
Answer to Problem 5.10.2P
The minimum shear stress in the web is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Shear Force
Dimensions,
Concept Used:
Following formula will be used:
Minimum shear stress,
Calculation:
Area of upper and lower flanges:
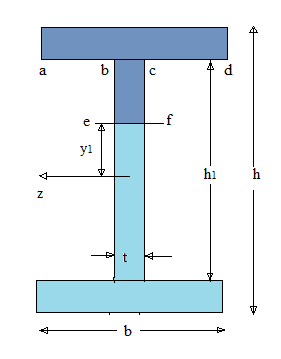
Second rectangle is
In which
The first moment of areas of
By putting the values of
The moment of inertia for the I section is given by following formula:
The minimum value of shear stress will be at
Conclusion:
The minimum shear stress in the web is
(c).
To Find:
The average shear stress in the web.
Answer to Problem 5.10.2P
The average shear stress in the web is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Shear Force
Dimensions:
Concept Used:
Following formula will be used:
Average shear stress,
Calculation:
The average shear stress in the web is:
Conclusion:
The average shear stress in the web is
(d).
To Find:
Shear force
Answer to Problem 5.10.2P
Shear force in the web is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Shear Force
Dimensions,
Concept Used:
Following formula will be used
Shear stress in the web,
Calculation:
Shear stress in the web:
Conclusion:
Shear force in the web is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
- A steel alloy contains 95.7 wt% Fe, 4.0 wt% W, and 0.3 wt% C.arrow_forwardb. A horizontal cantilever of effective length 3a, carries two concentrated loads W at a distance a from the fixed end and W' at a distance a from the free end. Obtain a formula for the maximum deflection due to this loading using Mohr's method. If the cantilever is 250 mm by 150mm steel I beam, 3 m long having a second moment of area I as 8500 cm4, determine W and W'to give a maximum deflection of 6 mm when the maximum stress due to bending is 90 Mpa. Take Young's modulus of material E as 185 Gpa.arrow_forwardWhich of the following sequences converge and which diverge? 1/n 1) a₁ = 2+(0.1)" 3 16) a = n 1-2n 2) a = In n 1+2n 17) an = 1/n n 1-5n4 3) an = n² +8n³ 18) an = √4" n n! n² -2n+1 20) a = 4) an = 106 5) n-1 a₁ =1+(-1)" n+1 a-(+) (1-4) 6) = 7) a = 2n (-1)"+1 2n-1 21) an = n -A" 1/(Inn) 3n+1 22) a = 3n-1 1/n x" 23) a = , x>0 2n+1 3" x 6" 24) a = 2™" xn! 2n 8) a = n+1 πT 1 9) a„ = sin +- 2 n sin n 10) an = n 25) a = tanh(n) 26) a = 2n-1 27) a = tan(n) 1 -sin n n 11) a = 2" 28) an == " 1 + 2" In(n+1) 12) a = n (In n) 200 29) a = n 13) a = 8/n 14) a 1+ =(1+²)" 15) an 7 n = 10n 30) an-√√n²-n 1"1 31) adx nixarrow_forward
- Calculate the angle of incidence of beam radiation on a collector located at (Latitude 17.40S) on June 15 at 1030hrs solar time. The collector is tilted at an angle of 200, with a surface azimuth angle of 150.arrow_forwardMechanical engineering, please don't use chatgpt. Strict warningarrow_forwardCompute the mass fraction of eutectoid cementite in an iron-carbon alloy that contains 1.00 wt% C.arrow_forward
- Compute the mass fraction of eutectoid cementite in an iron-carbon alloy that contains 1.00 wt% C.arrow_forward! Required information Mechanical engineering, don't use chatgpt. Thanks A 60-kip-in. torque T is applied to each of the cylinders shown. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. 3 in. 4 in. (a) (b) Determine the inner diameter of the 4-in. diameter hollow cylinder shown, for which the maximum stress is the same as in part a. The inner diameter is in.arrow_forwardMechanical engineering, Don't use chatgpt. Strict warning.arrow_forward
- 10:38 PM P 4136 54 A man Homework was due west for and 4km. He then changes directies walks on a bearing south-wes IS How far Point? of 1970 until he of his Starting Port Is he then from his stating What do you think about ... ||| Մ כarrow_forwardA simply supported T-shaped beam of 6m in length has to be designed to carry an inclined central point load W. Find the max- imum value of this load such that the maximum tensile and com- pression stresses on the beam do not exceed 30 and 60 respectively. N mm² N mm², 90 mm 80 mm Y W 60 mm 30° 10 mm 10 mm Xarrow_forwardProblem 9.5 9.5 A 1080-kg car is parked on a sloped street. The figure shows its wheels and the position of its center of mass. The street is icy, and as a result the coefficient of static friction between the car's tires and the street surface is μs = 0.2. Determine the steepest slope (in degrees relative to the horizontal) at which the car could remain in equilibrium if a. the brakes are applied to both its front and rear wheels; b. the brakes are applied to the front (lower) wheels only. Problem 9.5 1380 mm 532 mm 2370 mmarrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
