
Concept explainers
Interpretation:Stereocenters in the indicated chiral molecules should be marked and any one of the stereoisomers should be drawn along with absolute stereochemistry as R or S.
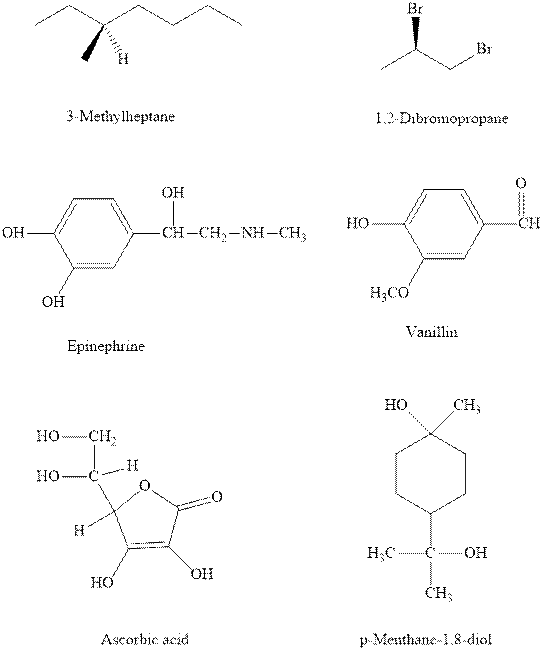
Concept introduction:Chiral carbon is any stereocenter attached to four different alkyl substituents. It is also known as stereocenter. If any two of the substituent happen to be similar the center is regarded as achiral. However, the most essential criteria that help to distinguish a chiral or non-chiral system is presence of any symmetry element. If any plane center or axis of symmetry is identified it makes molecule achiral and optically inactive.
In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of
If the groups read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
The Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Calculate the pH and the pOH of each of the following solutions at 25 °C for which the substances ionize completely: (a) 0.000259 M HClO4arrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. NaN₃arrow_forward
- A. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this.arrow_forward
- Determine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,



