
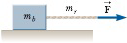
A rope with mass mr is attached to a block with mass mb as in Figure P5.42. The block rests on a frictionless, horizontal surface. The rope does not stretch. The free end of the rope is pulled to the right with a horizontal force
Figure P5.42
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 5 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
- The faster a molecule is moving in the upper atmosphere, the more likely it is to escape Earth's gravity. Given this fact, and your knowledge of rms speed, which of the following molecules can escape most easily from Earth's atmosphere if they are all at the same temperature?arrow_forwardThe temperature in one part of a flame is 2,100 K. What is the rms velocity of the carbon dioxide molecules at this temperature? Give your answer as the number of meters per second. mass of 1 mole of CO2 = 44.0 grams 1 mole contains 6.02 x 1023 molecules the Boltzmann constant k = 1.38 x 10-23 J/Karrow_forwardThe specific heat of a certain substance is 375 J/(kg°C). How much heat energy would you have to add to increase the temperature of 22 kg of this substance from 33°C up to 44°C in a number of Joules?arrow_forward
- 3.9 moles of an ideal gas are sealed in a container with volume 0.22 m3, at a pressure of 146,000 N/m2. What is the temperature of the gas in degrees Celsius?arrow_forwardwhen a cannon is launched at a 65 degree angle, will it have the same horizontal velocity as when it is launched from a 25 degree angle as long as the initial speed is the same?arrow_forwardPlease solve the problem step by step and provide explanations along each step stating what's being done. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- Figure 8.14 shows a cube at rest and a small object heading toward it. (a) Describe the directions (angle 1) at which the small object can emerge after colliding elastically with the cube. How does 1 depend on b, the so-called impact parameter? Ignore any effects that might be due to rotation after the collision, and assume that the cube is much more massive than the small object. (b) Answer the same questions if the small object instead collides with a massive sphere.arrow_forward2. A projectile is shot from a launcher at an angle 0,, with an initial velocity magnitude vo, from a point even with a tabletop. The projectile hits an apple atop a child's noggin (see Figure 1). The apple is a height y above the tabletop, and a horizontal distance x from the launcher. Set this up as a formal problem, and solve for x. That is, determine an expression for x in terms of only v₁, 0, y and g. Actually, this is quite a long expression. So, if you want, you can determine an expression for x in terms of v., 0., and time t, and determine another expression for timet (in terms of v., 0.,y and g) that you will solve and then substitute the value of t into the expression for x. Your final equation(s) will be called Equation 3 (and Equation 4).arrow_forwardDraw a phase portrait for an oscillating, damped spring.arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





