
(a) Interpretation:
The amino acid in Fischer projection and interpret it as D- or L- enantiomer.
Concept introduction:
Fischer projections are the representation of bonds by using horizontal and vertical lines in the 3D state. The horizontal lines represent the bonds that are out of paper towards the vision and the vertical lines represent the bonds pointing out the back of the paper away from vision. The intersection between the two lines represents the carbon atom.
A carbon which has all the four different atoms or group of atoms has tetrahedral geometry and such carbon molecule is referred to as the chiral carbon. The two different forms in which a single chiral center can exist is referred to as enantiomers. Simply, the substances which show optical isomerism exist as two isomers known as enantiomers. Enantiomers are non-super imposable mirror images of each other. The number of enantiomers of a molecule depends on the number of chiral centers.
Pictorial representation:
The Fischer projection of the given amino acidvaline is represented as below:
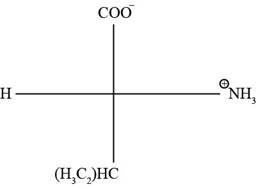
Fig. 1(a): Fischer projection of valine.
(b) Interpretation:
The amino acid in Fischer projection and interpret it as D- or L- enantiomer.
Concept introduction:
Fischer projections are the representation of bonds by using horizontal and vertical lines in the 3D state. The horizontal lines represent the bonds that are out of paper towards the vision and the vertical lines represent the bonds pointing out the back of the paper away from vision. The intersection between the two lines represents the carbon atom.
A carbon which has all the four different atoms or group of atoms has tetrahedral geometry and such carbon molecule is referred to as the chiral carbon. The two different forms in which a single chiral center can exist is referred to as enantiomers. Simply, the substances which show optical isomerism exist as two isomers known as enantiomers. Enantiomers are non-super imposable mirror images of each other. The number of enantiomers of a molecule depends on the number of chiral centers.
Pictorial representation:
The Fischer projection of threonine is represented as below.
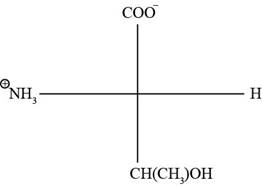
Fig. 2(a): Fischer projection of threonine.
(c) Interpretation:
The amino acid in Fischer projection and interpret it as D- or L- enantiomer.
Concept introduction:
Fischer projections are the representation of bonds by using horizontal and vertical lines in the 3D state. The horizontal lines represent the bonds that are out of paper towards the vision and the vertical lines represent the bonds pointing out the back of the paper away from vision. The intersection between the two lines represents the carbon atom.
A carbon which has all the four different atoms or group of atoms has tetrahedral geometry and such carbon molecule is referred to as the chiral carbon. The two different forms in which a single chiral center can exist is referred to as enantiomers. Simply, the substances which show optical isomerism exist as two isomers known as enantiomers. Enantiomers are non-super imposable mirror images of each other. The number of enantiomers of a molecule depends on the number of chiral centers.
Pictorial representation:
The Fischer projection of glutamine is represented as below:
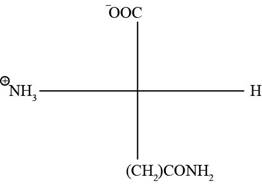
Fig. 3(a): Fischer projection of glutamine.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
- Draw the reaction between sphingosine and arachidonic acid. Draw out the full structures.arrow_forwardDraw both cis and trans oleic acid. Explain why cis-oleic acid has a melting point of 13.4°C and trans-oleic acid has a melting point of 44.5°C.arrow_forwardDraw the full structure of the mixed triacylglycerol formed by the reaction of glycerol and the fatty acids arachidic, lauric and trans-palmitoleic. Draw the line structure.arrow_forward
- Draw out the structure for lycopene and label each isoprene unit. "Where is lycopene found in nature and what health benefits does it provide?arrow_forwardWhat does it mean to be an essential fatty acid? What are the essential fatty acids?arrow_forwardCompare and contrast primary and secondary active transport mechanisms in terms of energy utilisation and efficiency. Provide examples of each and discuss their physiological significance in maintaining ionic balance and nutrient uptake. Rubric Understanding the key concepts (clearly and accurately explains primary and secondary active transport mechanisms, showing a deep understanding of their roles) Energy utilisation analysis ( thoroughly compares energy utilisation in primary and secondary transport with specific and relevant examples Efficiency discussion Use of examples (provides relevant and accurate examples (e.g sodium potassium pump, SGLT1) with clear links to physiological significance. Clarity and structure (presents ideas logically and cohesively with clear organisation and smooth transition between sections)arrow_forward
- 9. Which one of the compounds below is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction sequence, starting with ethyl acetoacetate? 요요. 1. NaOCH2CH3 CH3CH2OH 1. NaOH, H₂O 2. H3O+ 3. A OCH2CH3 2. ethyl acetoacetate ii A 3. H3O+ OH B C D Earrow_forward7. Only one of the following ketones cannot be made via an acetoacetic ester synthesis. Which one is it? Ph کہ A B C D Earrow_forward2. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction sequence? HO A OH 1. NaOEt, EtOH 1. LiAlH4 EtO OEt 2. H3O+ 2. H3O+ OH B OH OH C -OH HO -OH OH D E .CO₂Etarrow_forward
- what is a protein that contains a b-sheet and how does the secondary structure contributes to the overall function of the protein.arrow_forwarddraw and annotate a b-sheet and lable the hydrogen bonding. what is an example that contains the b-sheet and how the secondary structure contributes to the overall function of your example protein.arrow_forwardFour distinct classes of interactions (inter and intramolecular forces) contribute to a protein's tertiary and quaternary structures. Name the interaction then describe the amino acids that can form this type of interaction. Draw and annotate a diagram of the interaction between two amino acids.arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON





