
(a) Interpretation:
The amino acid in Fischer projection and interpret it as D- or L- enantiomer.
Concept introduction:
Fischer projections are the representation of bonds by using horizontal and vertical lines in the 3D state. The horizontal lines represent the bonds that are out of paper towards the vision and the vertical lines represent the bonds pointing out the back of the paper away from vision. The intersection between the two lines represents the carbon atom.
A carbon which has all the four different atoms or group of atoms has tetrahedral geometry and such carbon molecule is referred to as the chiral carbon. The two different forms in which a single chiral center can exist is referred to as enantiomers. Simply, the substances which show optical isomerism exist as two isomers known as enantiomers. Enantiomers are non-super imposable mirror images of each other. The number of enantiomers of a molecule depends on the number of chiral centers.
Pictorial representation:
The Fischer projection of the given amino acidvaline is represented as below:
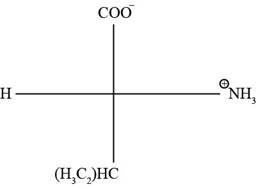
Fig. 1(a): Fischer projection of valine.
(b) Interpretation:
The amino acid in Fischer projection and interpret it as D- or L- enantiomer.
Concept introduction:
Fischer projections are the representation of bonds by using horizontal and vertical lines in the 3D state. The horizontal lines represent the bonds that are out of paper towards the vision and the vertical lines represent the bonds pointing out the back of the paper away from vision. The intersection between the two lines represents the carbon atom.
A carbon which has all the four different atoms or group of atoms has tetrahedral geometry and such carbon molecule is referred to as the chiral carbon. The two different forms in which a single chiral center can exist is referred to as enantiomers. Simply, the substances which show optical isomerism exist as two isomers known as enantiomers. Enantiomers are non-super imposable mirror images of each other. The number of enantiomers of a molecule depends on the number of chiral centers.
Pictorial representation:
The Fischer projection of threonine is represented as below.
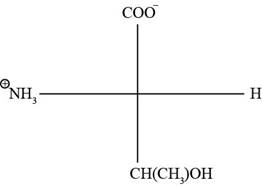
Fig. 2(a): Fischer projection of threonine.
(c) Interpretation:
The amino acid in Fischer projection and interpret it as D- or L- enantiomer.
Concept introduction:
Fischer projections are the representation of bonds by using horizontal and vertical lines in the 3D state. The horizontal lines represent the bonds that are out of paper towards the vision and the vertical lines represent the bonds pointing out the back of the paper away from vision. The intersection between the two lines represents the carbon atom.
A carbon which has all the four different atoms or group of atoms has tetrahedral geometry and such carbon molecule is referred to as the chiral carbon. The two different forms in which a single chiral center can exist is referred to as enantiomers. Simply, the substances which show optical isomerism exist as two isomers known as enantiomers. Enantiomers are non-super imposable mirror images of each other. The number of enantiomers of a molecule depends on the number of chiral centers.
Pictorial representation:
The Fischer projection of glutamine is represented as below:
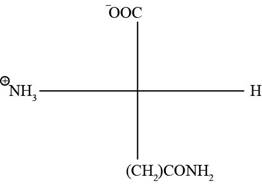
Fig. 3(a): Fischer projection of glutamine.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections
- 9. Which one of the compounds below is a major final product of the reaction sequence shown at the right? A) para-bromonitrobenzene C) meta-bromoaniline B) meta-bromonitrobenzene D) para-bromoaniline 1. HNO3, H2SO4 2. Br₂, FeBr3 3. H₂/Ni (3 atm) E) ortho-bromoanilinearrow_forward10. This reaction sequence includes an intramolecular Friedel-Crafts reaction. Which of the compounds below is expected to be the major product? PhCH2CH2CH2COOH 4-phenylbutanoic acid SOCI₂ AICI 3 A B C D Earrow_forward5. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction sequence? A B C OH i 1. NaBH4 CI 2. H₂O, H+ AICI 3 D OH Earrow_forward
- 1. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the reaction of toluene and cyclopentanol in the presence of H3PO4, as shown here? CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 H3PO4 A B с D E OHarrow_forwardAscorbic acid is a diprotic, with ionizations of: pKa1 = 4.10; pKa2 =11.80. You need to make 350 mL of an ascorbate buffer that is pH 5.05, andyou have 1.5 mM stock solutions of :ascorbic acidmonosodium ascorbatedipotassium ascorbateHow much 1.5 mM monosodium ascorbate do you use to make yoursolution? Answer in mL and report your value to three signicant gures.Please type only the number.arrow_forward1. What is the abbreviated form of the name for the molecule below. Punctuate it correctly ( image attached) 2. How much ATP is formed by the complete oxidation of lignocerate? Show stepsarrow_forward
- fill in the blank and circle the active site for each molecule. urgent!arrow_forwardfill in the table and circle the active sitearrow_forwardThe two half reactions for beginning and end of the electron transport chain are given below in standard form. Calculate & for the overall process. Using the Nernst equation (AG° = -n Fo, F= 96.485 kJ/volt mol), calculate AG°. Explain the need for a stepwise process in the electron transport chain. NAD* + H+ + 2 e- = NADH ½ 0г + 2H+ + 2е- = H20 = -0.32v E = +0.82Varrow_forward
- answer the questions and the example steps should be from carbohydrates glycolysis and citric acid cycle. Please put down reactions and structuresarrow_forwardidentify the general type of reaction catalyzed and an example step from glycolisis structure for each of the following enzymes/ co factor Kinase, isomerase, mutase, dehydrogenase, NAD+ , FADarrow_forwardfill in the blanks with the missing structures and give namesarrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON





