
Concept explainers
One Tough Bug The genus Ferroplasma consists of a few species of acid-loving archaea. One species, Ferroplasma acidarmanus, was discovered in one of the most contaminated sites in the United States: Iron Mountain Mine in California. F. acidarmamus is the main constituent of .slime streamers (a type of biofilm) growing in water draining from this abandoned copper mine (right). The water is hot (about 40°C, or 104°F), heavily laden with arsenic and other toxic metals, and has a pH of zero.
F. acidarmanus cells have an ancient energy-harvesting pathway that uses electrons pulled from iron-sulfur compounds in minerals such as pyrite. Removing electrons from these compounds dissolves the minerals, so groundwater in the mine ends up with extremely high concentrations of solutes, including metal ions such as copper, zinc, cadmium, and arsenic. The pathway also produces .sulfuric acid, which lowers the pH of the water around the cell to zero.
F. acidarmanus cells keep their internal pH at a cozy 5.0 despite Living in an environment similar to hot battery acid. However, most of the cell’s enzymes function best al much lower pH (FIGURE 5.13). Thus, researchers think F. acidarmanus may have an unknown type of internal compartment that keeps their enzymes in a highly acidic environmental.

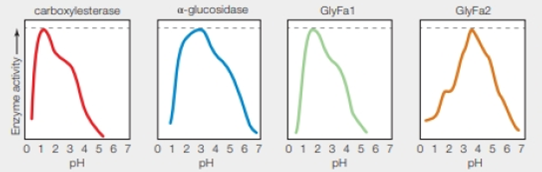
FIGURE 5.13 pH anomaly of Ferroplasma acidarmanus.
Left graphs showing pH activity profile of four enzymes isolated from Ferraplasma acidarmanus Researchers had expected all of these enzymes to function best at the calls’ cytoplasmic pH (5.0).
Of the four enzymes profiled in the graphs, how many function optimally at a pH lower than 5? How many retain significant function at pH 5?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biological Science (6th Edition)
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
SEELEY'S ANATOMY+PHYSIOLOGY
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
HUMAN ANATOMY
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
- when we collect fish or mussels we record a variety of biological information, including but not limited their sex, length, weight or a scale or finray or other tissue sample. Why do we do this, and what information are we hoping to obtain from these measurements and taking these samples?arrow_forwardDraw a rough sketch of the control and experimental data using a normal dose/response curve plot: i.e. % of total bound ligand vs. concentration. Indicate Kd and Bmax on this sketch. You don’t need to use exact numbers, but the relative proportions should be closearrow_forwardName something that could be happening to glutamate transporters that could have this effect on glutamate transport (i.e. the difference in glutamate transporters between control and experimental conditions). (Bonus: if you can also guess what the experimental condition is).arrow_forward
- a. For the control condition, calculate Kd. Include units and show your work. b. For the control condition, calculate Bmax. Include units and show your work. c. For the experimental condition, calculate Kd. Include units and show your work. For the experimental condition, calculate Bmax. Include units and show your work.arrow_forwardNow draw a rough sketch of what the control data might look like if in addition to the specific binding, there was also a considerable amount of nonspecific binding (again using a normal dose/response curve)arrow_forwarda. Which drug is the most potent? a,b,c,d,e b. Which drug has the highest efficacy?arrow_forward
- The shape of radishes may be long (SL/SL), oval (SL/SS), or round (SS/SS), and the color of radishes may be red (CR/CR), purple (CR/CW) or white (CW/CW). If a long, red radish plant is crossed with a round, white plant, what will be the appearance of the F1 and F2 generations?arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardQuestion #3: In the KeyGene paper, the authors state that it would be useful if pollen from an apomict would transmit apomixis-inducing genes to the female in the cross (assuming the pollen is viable). Assuming there was just one gene conferring gametophytic obligate apomixis, and that the two parents are inbreds, what would be the consequences of such a cross if: a) The apomixis was a dominant trait? Indicate the genotypes and phenotypes (apomict or non- apomict) of the parents, F1 and F2 generations. Remember to include the expected genotypic and phenotypic ratios (or percentages) in the F1 and F2 generations, and to position the female first (left side) in the parental cross. b) The apomixis was a recessive trait? Indicate the genotypes and phenotypes (apomict or non- apomict) of the parents, F1 and F2 generations. Remember to include the expected genotypic and phenotypic ratios (or percentages) in the F1 and F2 generations, and to position the female first (left side) in the…arrow_forward
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax





