
Delsing Canning Company is considering an expansion of its facilities. Its current income statement is as follows:
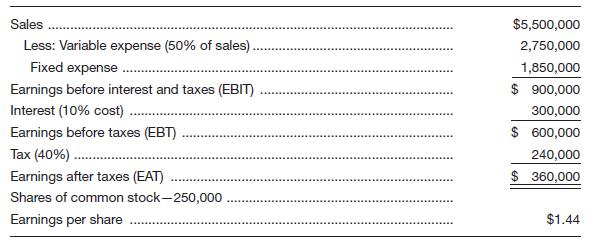
The company is currently financed with 50 percent debt and 50 percent equity (common stock, par value of $10). In order to expand the facilities, Mr. Delsing estimates a need for $2.5 million in additional financing. His investment banker has laid out three plans for him to consider:
Variable costs are expected to stay at 50 percent of sales, while fixed expenses will increase to
Delsing is interested in a thorough analysis of his expansion plans and methods of financing. He would like you to analyze the following:
a. The break-even point for operating expenses before and after expansion (in sales dollars).
b. The degree of operating leverage before and after expansion. Assume sales of
c. The degree of financial leverage before expansion and for all three methods of financing after expansion. Assume sales of
d. Compute EPS under all three methods of financing the expansion at
e. What can we learn from the answer to part d about the advisability of the three methods of financing the expansion?
a.
To calculate: The BEP (in dollars) for the operating expenses of Delsing Canning Company prior to and post expansion.
Introduction:
Break-even point (BEP):
It refers to the production level at which the revenue of the product is equal to the cost of the product. It is calculated by dividing the total fixed cost with the difference between the revenue per unit and variable cost per unit.
Answer to Problem 27P
The BEP of sales prior to the expansion of Delsing Canning Company is $3,700,000 and that post expansion is $4,700,000.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of BEP before expansion:
Calculation of BEP after expansion:
Working Notes:
Calculation of the contribution margin ratio prior to expansion:
Calculation of the contribution margin ratio post expansion:
b.
To calculate: The DOL before and after expansion for Delsing Canning Company.
Introduction:
Degree of Operating Leverage (DOL):
It refers to the ratio that measures the change in the operating income of the company with the change in sales volume.
Answer to Problem 27P
The DOL of Delsing Canning Company before expansion is 3.06 times and that after expansion is 3.61 times.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of DOL before expansion with sales of $5,500,000:
Calculation of DOL after expansion with sales of $6,500,000:
c.
To calculate: The DFL before and after expansion for Delsing Canning Company.
Introduction:
Degree of financial leverage (DFL):
It refers to the leverage ratio that evaluates the EPS of the company with respect to variations in its operating income. This ratio indicates that a higher DFL leads to higher earnings for the firm.
Answer to Problem 27P
The DFL before expansion for Delsing Canning Company is 1.50 times and that after expansion for plan 1 is 3.27 times, that for plan 2 is 1.50 times, and that for plan 3 is 2 times.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of DFL before expansion:
Calculation of DFL after expansion for plan 1:
Calculation of DFL after expansion for plan 2:
Calculation of DFL after expansion for plan 3:
Working Notes:
Calculation of EBIT for plan 1 with 100% debt:
Calculation of EBIT for plan 2 with 100% equity:
Calculation of EBIT for plan 3 with 50% debt and 50% equity:
Calculation of interest for plan 1 with 100% debt:
Calculation of interest for plan 2 with 100% equity:
Calculation of interest for plan 3 with 50% debt and 50% equity:
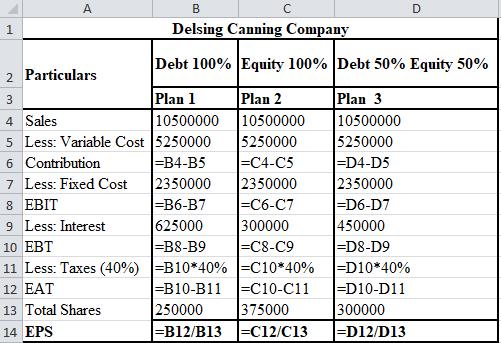
d.
To calculate: The EPS, given that the sales in the first year were $6,500,000 and that in the last year were $10,000,000, using the three methods of financing after the expansion of Delsing Canning Company.
Introduction:
Earnings per share (EPS):
It is the profit per outstanding share of a public company. A higher EPS indicates a higher value of the company because investors are ready to pay a higher price for one share of the company.
Answer to Problem 27P
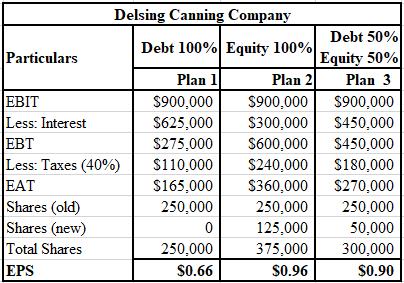
The calculation of EPS with sales of $6,500,000 for Delsing Canning Company is shown below.
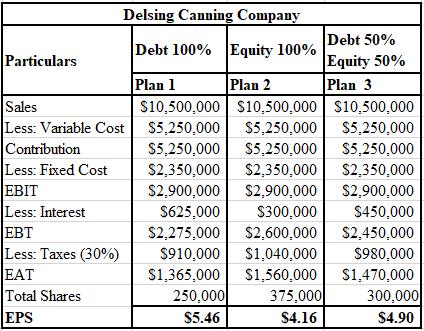
The calculation of EPS with sales of $10,500,000 for Delsing Canning Company is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The formulae used for the calculation of EPS with sales of $6,500,000 are shown below.
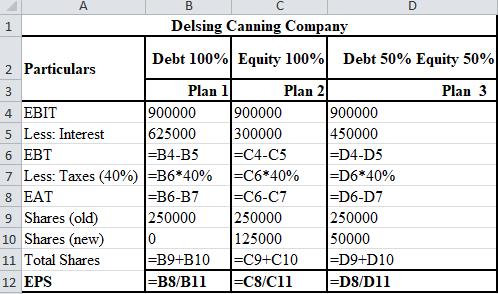
The formulae used for the calculation of EPS with sales of $10,500,000 are shown below.
e.
To determine: The outcome of the calculation of part (d) using the three methods of financing the expansion for the Delsing Canning Company.
Introduction:
Earnings Before Interest and Tax (EBIT):
It is the profit of a firm that includes all operating and non-operating expenses. It is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold and operating expenses from the revenue of the corporation.
Answer to Problem 27P
When sales and profits are comparatively low, plan 2, that is, the plan with 100% equity, seems to be the best alternative in the first year. However, after expansion, when sales and profits are high, plan 1, that is, the one with 100% debt, seems to be the best one on the basis of higher yield.
Explanation of Solution
Plan 2 with 100% equity is comparatively the best alternative for the first year when there are low profits as well as sales. Moreover, with the increase in the level of sales of approximately $10.5 million, it is clear that the financial leverage has started producing results as it increased the EBIT in plan 1, which has 100% debt.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Foundations of Financial Management
- What are AIrbnb's Legal Foundations? What are Airbnb's Business Ethics? What are Airbnb's Corporate Social Responsibility?arrow_forwardDiscuss in detail the differences between the Primary Markets versus the Secondary Markets, The Money Market versus the Capital Market AND the Spot Market versus the Futures Market. Additionally, discuss the various Interest Rate Determinants listed in your textbook (such as default-risk premium.....).arrow_forwardHow can the book value still serve as a useful metric for investors despite the dominance of market value?arrow_forward
- How do you think companies can practically ensure that stakeholder interests are genuinely considered, while still prioritizing the financial goal of maximizing shareholder equity? Do you think there’s a way to measure and track this balance effectively?arrow_forward$5,000 received each year for five years on the first day of each year if your investments pay 6 percent compounded annually. $5,000 received each quarter for five years on the first day of each quarter if your investments pay 6 percent compounded quarterly. Can you show me either by hand or using a financial calculator please.arrow_forwardCan you solve these questions on a financial calculator: $5,000 received each year for five years on the last day of each year if your investments pay 6 percent compounded annually. $5,000 received each quarter for five years on the last day of each quarter if your investments pay 6 percent compounded quarterly.arrow_forward
- Now suppose Elijah offers a discount on subsequent rooms for each house, such that he charges $40 for his frist room, $35 for his second, and $25 for each room thereafter. Assume 30% of his clients have only one room cleaned, 25% have two rooms cleaned, 30% have three rooms cleaned, and the remaining 15% have four rooms cleaned. How many houses will he have to clean before breaking even? If taxes are 25% of profits, how many rooms will he have to clean before making $15,000 profit? Answer the question by making a CVP worksheet similar to the depreciation sheets. Make sure it works well, uses cell references and functions/formulas when appropriate, and looks nice.arrow_forward1. Answer the following and cite references. • what is the whole overview of Green Markets (Regional or Sectoral Stock Markets)? • what is the green energy equities, green bonds, and green financing and how is this related in Green Markets (Regional or Sectoral Stock Markets)? Give a detailed explanation of each of them.arrow_forwardCould you help explain “How an exploratory case study could be goodness of work that is pleasing to the Lord?”arrow_forward
- What are the case study types and could you help explain and make an applicable example.What are the 4 primary case study designs/structures (formats)?arrow_forwardThe Fortune Company is considering a new investment. Financial projections for the investment are tabulated below. The corporate tax rate is 24 percent. Assume all sales revenue is received in cash, all operating costs and income taxes are paid in cash, and all cash flows occur at the end of the year. All net working capital is recovered at the end of the project. Year 0 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Investment $ 28,000 Sales revenue $ 14,500 $ 15,000 $ 15,500 $ 12,500 Operating costs 3,100 3,200 3,300 2,500 Depreciation 7,000 7,000 7,000 7,000 Net working capital spending 340 390 440 340 ?arrow_forwardWhat are the six types of alternative case study compositional structures (formats)used for research purposes, such as: 1. Linear-Analytical, 2. Comparative, 3. Chronological, 4. Theory Building, 5. Suspense and 6. Unsequenced. Please explainarrow_forward
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





