
Explain how σ and
Interpretation:
The similarity and difference between s and p bonds is to be explained.
Concept Introduction:
- There are two types of bonds that are formed between the atoms-
- Electron in atoms occupy atomic orbitals while in molecule, electrons occupy molecular orbitals. These molecular orbitals are formed by the combination of the atomic orbitals and they can be bonding molecular orbitals and ant-bonding molecular orbitals.
- The process of mixing of atomic orbitals of similar energy to produce new molecular orbitals of equivalent energy is known as hybridization.
a) Covalent bond- the bond formed by the sharing of electrons between the atoms.
b) Ionic bond- When atoms gain/loss electrons and become ions, the electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions is known as ionic bond.
Answer to Problem 1E
Similarity-They both are chemical covalent bonds and are formed by the overlapping of the atomic orbitals.
Differences-
| s- bond | ?-bond |
| Formed by the axial overlap of the atomic orbitals. | Formed by the side-ways overlap of the atomic orbitals. |
| It can be formed by the overlap of s-s, s-p or p-p orbitals. | It can only be formed by the overlap of p orbitals |
| Oriented along the internuclear axis. | Oriented perpendicular to the internuclear axis. |
| Exists independently. | Exist along with sigma bond. |
| Stronger than pi-bond. | Weaker than sigma bond. |
| More reactive. | Less reactive. |
| Determines the shape of the molecule. | Does not determine the shape of the molecule. |
Explanation of Solution
- Sigma (s) bonds- It is a type of covalent bond which is formed by the end to end overlapping of the atomic orbitals of the atoms involved in bonding.
- Pi (p)bonds -It is a type of covalent bond which is formed by the side wise overlapping of the atomic orbitals of the atoms involved in bonding.
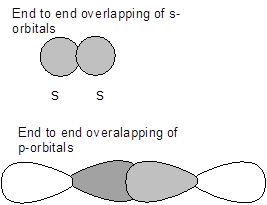

Therefore, differences between sigma and pi bonds are-
| s- bond | ?-bond |
| Formed by the axial overlap of the atomic orbitals. | Formed by the side-ways overlap of the atomic orbitals. |
| It can be formed by the overlap of s-s, s-p or p-p orbitals. | It can only be formed by the overlap of p orbitals |
| Oriented along the internuclear axis. | Oriented perpendicular to the internuclear axis. |
| Exists independently. | Exist along with sigma bond. |
| Stronger than pi-bond. | Weaker than sigma bond. |
| More reactive. | Less reactive. |
| Determines the shape of the molecule. | Does not determine the shape of the molecule. |
However, the only similarity between these two are that they both are chemical covalent bonds and are formed by the overlapping the atomic orbitals, and the main difference is that sigma bond is formed by the axial overlap of the atomic orbitals, whereas, pi bond is formed by the sideways overlapping of atomic orbitals.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Chemistry Atoms First2e
- Identify the missing organic reactants in the following reaction: H+ X + Y OH H+ O O Note: This chemical equation only focuses on the important organic molecules in the reaction. Additional inorganic or small-molecule reactants or products (like H₂O) are not shown. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactants X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Cente ? Earrow_forwardCalculate the solubility of CaF2 in g/L (Kp = 4.0 x 10-8). sparrow_forwardFor the following reaction with excess reagent, predict the product. Be sure your answer accounts for stereochemistry. If multiple stereocenters are formed, be sure to draw all products using appropriate wedges and dashes. 1. EtLi, Et₂O CH₁ ? 2. H₂O*arrow_forward
- Write the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure 요 OH ہو۔ HO OH name X S ☐ ☐arrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren't any products, because nothing will happen, check the box under the drawing area instead. D ㄖˋ ید H No reaction. + 5 H₂O.* Click and drag to start drawing a structure. OH H₂Oarrow_forwardDraw one product of an elimination reaction between the molecules below. Note: There may be several correct answers. You only need to draw one of them. You do not need to draw any of the side products of the reaction 'O 10 + x 也 HO + 义 Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
- What are the angles a and b in the actual molecule of which this is a Lewis structure? H- :0: C=N: b Note for advanced students: give the ideal angles, and don't worry about small differences from the ideal that might be caused by the fact that different electron groups may have slightly different sizes. a = 0° b=0 Xarrow_forwardA student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more products missing from the right-hand side, but there are no reagents missing from the left-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow. • Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area. • If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing products to the right-hand side, and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow. • You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown. + This transformation can't be done in one step. T iarrow_forwardDetermine the structures of the missing organic molecules in the following reaction: H+ O OH H+ + H₂O ☑ ☑ Note: Molecules that share the same letter have the exact same structure. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the missing organic molecule X. Molecule X shows up in multiple steps, but you only have to draw its structure once. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X § ©arrow_forward
- Table 1.1 Stock Standard Solutions Preparation. The amounts shown should be dissolved in 100 mL. Millipore water. Calculate the corresponding anion concentrations based on the actual weights of the reagents. Anion Amount of reagent (g) Anion Concentration (mg/L) 0.1649 Reagent Chloride NaCl Fluoride NaF 0.2210 Bromide NaBr 0.1288 Nitrate NaNO3 0.1371 Nitrite NaNO2 0.1500 Phosphate KH2PO4 0.1433 Sulfate K2SO4 0.1814arrow_forwardDraw the structure of the pound in the provided CO as a 300-1200 37(2), 11 ( 110, and 2.5 (20arrow_forwardPlease help me with # 4 and 5. Thanks in advance!arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning


