
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYNA.(LL)-W/ACCESS
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781259633133
Author: BEER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4.3, Problem 4.93P
A small winch is used to raise a 120-lb load. Find (a) the magnitude of the vertical force P that should be applied at C to maintain equilibrium in the position shown, (b) the reactions at A and B, assuming that the bearing at B does not exert any axial thrust.
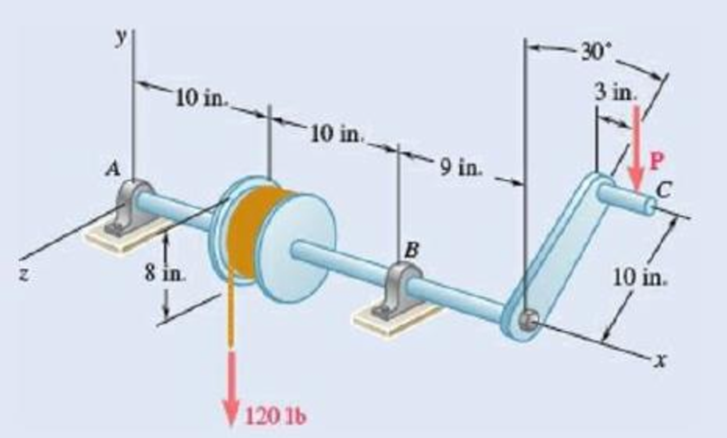
Fig. P4.93
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
calculate the total power required to go 80 mph in a VW Type 2 Samba Bus weighing 2310 lbs. with a Cd of 0.35 and a frontal area of 30ft^2. Consider the coefficient of rolling resistance to be 0.018. What is the increase in power required to go the same speed if the weight is increased by 2205 pounds (the rated carrying capacity of the vehicle). If the rated power for the vehicle is 49 bhp, will the van be able to reach 80 mph at full carrying capacity?
A distillation column with a total of 13 actual stages (including a partial condenser) is used to perform a separation which requires 7 ideal stages. Calculate the overall column efficiency, and report your answer in %
6. Consider a 10N step input to the mechanical system shown below, take M = 15kg, K = 135N/m, and
b = 0.4 Ns/m.
(a) Assume zero initial condition, calculate the
(i)
System pole
(ii)
System characterization, and
(iii) The time domain response
(b) Calculate the steady-state value of the system
b
[
www
K
个
х
M
-F(+)
Chapter 4 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYNA.(LL)-W/ACCESS
Ch. 4.1 - Two crates, each of mass 350 kg, are placed as...Ch. 4.1 - A lever AB is hinged at C and attached to a...Ch. 4.1 - A light rod AD is supported by frictionless pegs...Ch. 4.1 - A tension of 20 N is maintained in a tape as it...Ch. 4.1 - A gardener uses a 60 N wheelbarrow to transport a...Ch. 4.1 - The gardener of Prob. 4.1 wishes to transport a...Ch. 4.1 - A 2100-lb tractor is used to lift 900 lb of grave....Ch. 4.1 - For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 4.1 - A load of lumber of weight W = 25 kN is being...Ch. 4.1 - A load of lumber of weight W = 25 kN is being...
Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.7PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.8PCh. 4.1 - Three loads are applied as shown to a light beam...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.10PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.11PCh. 4.1 - For the beam of Sample Prob. 4.2, determine the...Ch. 4.1 - The maximum allowable value of each of the...Ch. 4.1 - For the beam and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 4.1 - 4.15 Two links AB and DE are connected by a bell...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.16PCh. 4.1 - 4.17 The required tension in cable AB is 200 lb....Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.18PCh. 4.1 - The bracket BCD is hinged at C and attached to a...Ch. 4.1 - The ladder AB, of length L and weight W, can be...Ch. 4.1 - 4.21 The 40-ft boom AB weighs 2 kips; the distance...Ch. 4.1 - A lever AB is hinged at C and attached to a...Ch. 4.1 - 4.23 and 4.24 For each of the plates and loadings...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.24PCh. 4.1 - A rod AB, hinged at A and attached at B to cable...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.26PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.27PCh. 4.1 - Determine the reactions at A and C when (a) = 0,...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.29PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.30PCh. 4.1 - Neglecting friction, determine the tension in...Ch. 4.1 - Fig. P4.31 and P4.32 4.32 Neglecting friction,...Ch. 4.1 - PROBLEM 4.33 A force P of magnitude 90 lb is...Ch. 4.1 - PROBLEM 4.34 Solve Problem 4,33 for a = 6 in,...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.35PCh. 4.1 - PROBLEM 4.36 A light bar AD is suspended from a...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.37PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.38PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.39PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.40PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.41PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.42PCh. 4.1 - The rig shown consists of a 1200-lb horizontal...Ch. 4.1 - Fig. P4.43 4.44 For the rig and crate of Prob....Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.45PCh. 4.1 - Knowing that the tension in wire BD is 1300 N,...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.47PCh. 4.1 - Beam AD carries the two 40-lb loads shown. The...Ch. 4.1 - Fig. P4.48 and P4.49 4.49 For the beam and loading...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.50PCh. 4.1 - A uniform rod AB with a length of l and weight of...Ch. 4.1 - Rod AD is acted upon by a vertical force P at end...Ch. 4.1 - A slender rod AB with a weigh of W is attached to...Ch. 4.1 - 4.54 and 4.55 A vertical load P is applied at end...Ch. 4.1 - 4.54 and 4.55 A vertical load P is applied at end...Ch. 4.1 - A collar B with a weight of W can move freely...Ch. 4.1 - A 400-lb weight is attached at A to the lever...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.58PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.59PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.60PCh. 4.2 - A 500-lb cylindrical tank, 8 ft in diameter, is to...Ch. 4.2 - 4.62 Determine the reactions at A and B when a =...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 4.63PCh. 4.2 - Prob. 4.64PCh. 4.2 - Determine the reactions at B and C when a = 30 mm.Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 4.66PCh. 4.2 - Determine the reactions at B and D when b = 60 mm....Ch. 4.2 - For the frame and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 4.2 - A 50-kg crate is attached to the trolley-beam...Ch. 4.2 - One end of rod AB rests in the corner A and the...Ch. 4.2 - For the boom and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 4.72PCh. 4.2 - Prob. 4.73PCh. 4.2 - Prob. 4.74PCh. 4.2 - Rod AB is supported by a pin and bracket at A and...Ch. 4.2 - Solve Prob. 4.75, assuming that the 170-N force...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 4.77PCh. 4.2 - Using the method of Sec. 4.2B, solve Prob. 4.22....Ch. 4.2 - Knowing that = 30, determine the reaction (a) at...Ch. 4.2 - Knowing that = 60, determine the reaction (a) at...Ch. 4.2 - Determine the reactions at A and B when = 50....Ch. 4.2 - Determine the reactions at A and B when = 80.Ch. 4.2 - Rod AB is bent into the shape of an arc of circle...Ch. 4.2 - A slender rod of length L is attached to collars...Ch. 4.2 - An 8-kg slender rod of length L is attached to...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 4.86PCh. 4.2 - A slender rod BC with a length of L and weight W...Ch. 4.2 - A thin ring with a mass of 2 kg and radius r = 140...Ch. 4.2 - A slender rod with a length of L and weight W is...Ch. 4.2 - Fig. P4.89 4.90 Knowing that for the rod of Prob....Ch. 4.3 - Two tape spools are attached to an axle supported...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.6FBPCh. 4.3 - A 20-kg cover for a roof opening is hinged at...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.91PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.92PCh. 4.3 - A small winch is used to raise a 120-lb load. Find...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.94PCh. 4.3 - A 250 400-mm plate of mass 12 kg and a...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.96PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.97PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.98PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.99PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.100PCh. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.101 Two steel pipes AB and BC, each...Ch. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.102 For the pipe assembly of Problem...Ch. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.103 The 24-lb square plate shown is...Ch. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.104 The table shown weighs 30 lb and has...Ch. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.105 A 10-ft boom is acted upon by the...Ch. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.106 The 6-m pole ABC is acted upon by a...Ch. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.107 Solve Problem 4.106 for a = 1.5 m....Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.108PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.109PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.110PCh. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.111 A 48-in. boom is held by a...Ch. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.112 Solve Problem 4.111, assuming that...Ch. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.114 The bent rod ABEF is supported by...Ch. 4.3 - The bent rod ABEF is supported by bearings at C...Ch. 4.3 - The horizontal platform ABCD weighs 60 lb and...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.116PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.117PCh. 4.3 - Solve Prob. 4.117, assuming that cable DCE is...Ch. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.119 Solve Prob. 4.113, assuming that the...Ch. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.120 Solve Prob. 4.115, assuming that the...Ch. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.121 The assembly shown is used to...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.122PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.123PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.124PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.125PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.126PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.127PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.128PCh. 4.3 - Frame ABCD is supported by a ball-and-socket joint...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.130PCh. 4.3 - The assembly shown consists of an 80-mm rod AF...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.132PCh. 4.3 - The frame ACD is supported by ball-and-socket...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.134PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.135PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.136PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.137PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.138PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.139PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.140PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.141PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.142RPCh. 4 - 4. 143 The lever BCD is hinged at C and attached...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.144RPCh. 4 - Neglecting friction and the radius of the pulley,...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.146RPCh. 4 - PROBLEM 4.147 A slender rod AB, of weight W, is...Ch. 4 - PROBLEM 4.148 Determine the reactions at A and B...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.149RPCh. 4 - PROBLEM 4.150 A 200-mm lever and a 240-mm-diameter...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.151RPCh. 4 - Prob. 4.152RPCh. 4 - A force P is applied to a bent rod ABC, which may...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
How does a computers main memory differ from its auxiliary memory?
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
The solid steel shaft AC has a diameter of 25 mm and is supported by smooth bearings at D and E. It is coupled ...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
The job of the _____ is to fetch instructions, carry out the operations commanded by the instructions, and prod...
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Write a summary list of the problem-solving steps identified in the chapter, using your own words.
BASIC BIOMECHANICS
How is the hydrodynamic entry length defined for flow in a pipe? Is the entry length longer in laminar or turbu...
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. Solve the following linear time invariant differential equations using Laplace transforms subject to different initial conditions (a) y-y=t for y(0) = 1 and y(0) = 1 (b) ÿ+4y+ 4y = u(t) for y(0) = 0 and y(0) = 1 (c) y-y-2y=0 for y(0) = 1 and y(0) = 0arrow_forward3. For the mechanical systems shown below, the springs are undeflected when x₁ = x2 = x3 = 0 and the input is given as fa(t). Draw the free-body diagrams and write the modeling equations governing each of the systems. K₁ 000 K₂ 000 M₁ M2 -fa(t) B₂ B₁ (a) fa(t) M2 K₂ 000 B K₁ x1 000 M₁ (b)arrow_forwardThis question i m uploading second time . before you provide me incorrect answer. read the question carefully and solve accordily.arrow_forward
- 1. Create a table comparing five different analogous variables for translational, rotational, electrical and fluid systems. Include the standard symbols for each variable in their respective systems.arrow_forward2) Suppose that two unequal masses m₁ and m₂ are moving with initial velocities v₁ and v₂, respectively. The masses hit each other and have a coefficient of restitution e. After the impact, mass 1 and 2 head to their respective gaps at angles a and ẞ, respectively. Derive expressions for each of the angles in terms of the initial velocities and the coefficient of restitution. m1 m2 8 m1 m2 βarrow_forward4. Find the equivalent spring constant and equivalent viscous-friction coefficient for the systems shown below. @ B₁ B₂ H B3 (b)arrow_forward
- 5. The cart shown below is inclined 30 degrees with respect to the horizontal. At t=0s, the cart is released from rest (i.e. with no initial velocity). If the air resistance is proportional to the velocity squared. Analytically determine the initial acceleration and final or steady-state velocity of the cart. Take M= 900 kg and b 44.145 Ns²/m². Mg -bx 2 отarrow_forward9₁ A Insulated boundary Insulated boundary dx Let's begin with the strong form for a steady-state one-dimensional heat conduction problem, without convection. d dT + Q = dx dx According to Fourier's law of heat conduction, the heat flux q(x), is dT q(x)=-k dx. x Q is the internal heat source, which heat is generated per unit time per unit volume. q(x) and q(x + dx) are the heat flux conducted into the control volume at x and x + dx, respectively. k is thermal conductivity along the x direction, A is the cross-section area perpendicular to heat flux q(x). T is the temperature, and is the temperature gradient. dT dx 1. Derive the weak form using w(x) as the weight function. 2. Consider the following scenario: a 1D block is 3 m long (L = 3 m), with constant cross-section area A = 1 m². The left free surface of the block (x = 0) is maintained at a constant temperature of 200 °C, and the right surface (x = L = 3m) is insulated. Recall that Neumann boundary conditions are naturally satisfied…arrow_forward1 - Clearly identify the system and its mass and energy exchanges between each system and its surroundings by drawing a box to represent the system boundary, and showing the exchanges by input and output arrows. You may want to search and check the systems on the Internet in case you are not familiar with their operations. A pot with boiling water on a gas stove A domestic electric water heater A motor cycle driven on the roadfrom thermodynamics You just need to draw and put arrows on the first part a b and carrow_forward
- 7. A distributed load w(x) = 4x1/3 acts on the beam AB shown in Figure 7, where x is measured in meters and w is in kN/m. The length of the beam is L = 4 m. Find the moment of the resultant force about the point B. w(x) per unit length L Figure 7 Barrow_forward4. The press in Figure 4 is used to crush a small rock at E. The press comprises three links ABC, CDE and BG, pinned to each other at B and C, and to the ground at D and G. Sketch free-body diagrams of each component and hence determine the force exerted on the rock when a vertical force F = 400 N is applied at A. 210 80 80 C F 200 B 80 E 60% -O-D G All dimensions in mm. Figure 4arrow_forward2. Figure 2 shows a device for lifting bricks and concrete blocks. It comprises two compo- nents ABC and BD, with a frictionless pin at B. Determine the minimum coefficient of friction required at A and D if the device is to work satisfactorily. W all dimensions in inches Figure 2 Darrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
EVERYTHING on Axial Loading Normal Stress in 10 MINUTES - Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jQ-fNqZWrNg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY