
Concept explainers
(a)
Find the symmetry of the points
(a)
Answer to Problem 86E
Rotated 180 deg counter clockwise about the origin.
Explanation of Solution
Given:Draw two points
Concept Used:
Mathematically, symmetrymeans that one shape becomes exactly like another when you move it in some way: turn, flip or slide. For two objects to be symmetrical, they must be the same size and shape, with one object having a different orientation from the first. There can also be symmetry in one object, such as a face. If you draw a line of symmetry down the centre of your face, you can see that the left side is a mirror image of the right side. Not all objects have symmetry; if an object is not symmetrical, it is called asymmetric
Calculation:
The graph of the points shown below: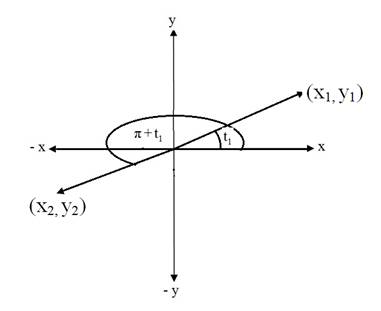 |
Let And the both points are rotated 180 deg counter clockwise about the origin. Therefore they are related as Hence the points are rotated 180 deg counter clockwise about the origin. |
Thus, the points arerotated 180 deg counter clockwise about the origin.
(b)
Make a conjecture about any relationship between
(b)
Answer to Problem 86E
Explanation of Solution
Given: Draw two points
Concept Used:
The line (or "axis") of symmetry is the y-axis, also known as the line x=0. This line is marked green in the picture. The graph is said to be "symmetric about the y-axis", and this line of symmetry is also called the "axis of symmetry"
Calculation:
The graph of the points shown below: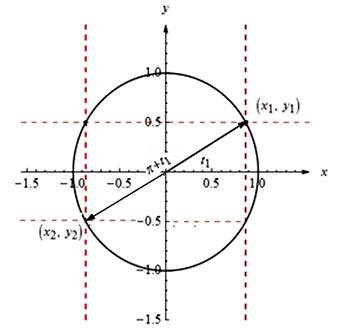 |
Draw two points And the both points are rotated 180 deg counter clockwise about the origin. Therefore they are related as Now we can see the points Since the graph has a rotational symmetry180 deg counter clockwise about the origin. which means |
Thus,
Make a conjecture about any relationship between
Answer to Problem 86E
Explanation of Solution
Given: Draw two points
Concept Used:The line (or "axis") of symmetry is the y-axis, also known as the line x=0. This line is marked green in the picture. The graph is said to be "symmetric about the y-axis", and this line of symmetry is also called the "axis of symmetry"
Calculation:
The graph of the points shown below: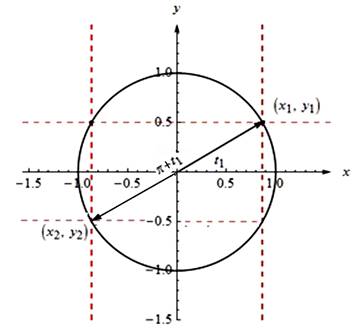 |
Draw two points And the both points are rotated 180 deg counter clockwise about the origin. Therefore they are related as Now we can see the points Since the graph has a rotational symmetry 180 deg counter clockwise about the origin. which means |
Thus,
Chapter 4 Solutions
PRECALCULUS W/LIMITS:GRAPH.APPROACH(HS)
- Find the accumulated amount A, if the principal P is invested at an interest rate of r per year for t years. (Round your answer to the nearest cent.) P = $3800, r = 4%, t = 10, compounded semiannually A = $ 5645.60 × Need Help? Read It SUBMIT ANSWER [3.33/6.66 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES REVIOUS ANSWERS ASK YOUR TEACHER TANAPCALC10 5.3.001.EP. PRACTICE ANOTHER Consider the following where the principal P is invested at an interest rate of r per year for t years. P = $3,100, r = 4%, t = 10, compounded semiannually Determine m, the number of conversion periods per year. 2 Find the accumulated amount A (in dollars). (Round your answer to the nearest cent.) A = $ 4604.44arrow_forwardForce with 800 N and 400 N are acting on a machine part at 30° and 60°, respectively with a positive x axis, Draw the diagram representing this situationarrow_forwardI forgot to mention to you to solve question 1 and 2. Can you solve it using all data that given in the pict i given and can you teach me about that.arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





