
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781259989452
Author: Hayt
Publisher: Mcgraw Hill Publishers
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4.1, Problem 1P
For the circuit of Fig. 4.3, determine the nodal voltages v1 and v2.
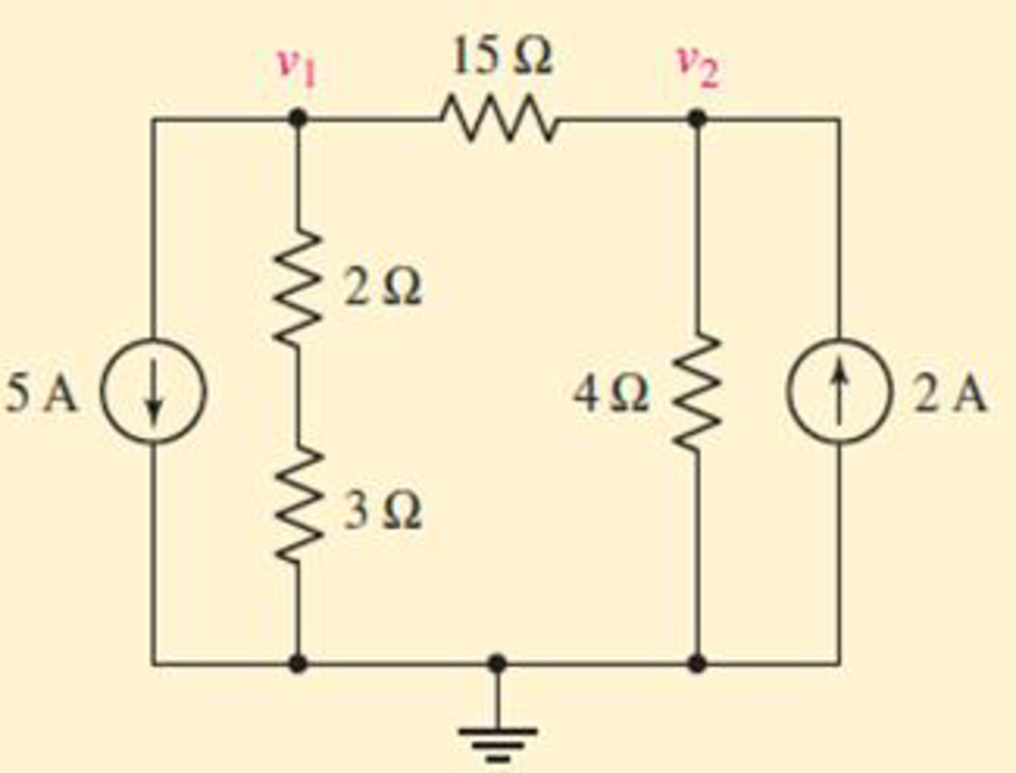
FIGURE 4.3
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A Si step junction maintained at room temperature under equilibrium conditions has a p-side doping of
NA 2X1015/cm³ and an n-side doping of ND=1015/cm³. Compare
a) Vbi
b) Xp, Xn, and W
c) ɛ at x=0
d) V at x=0
Make sketches that are roughly to scale of the charge density, electric field, and electrostatic
potential as a function of position.
Can you show how this answer was found?
Can you show how this answer was found?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
Ch. 4.1 - For the circuit of Fig. 4.3, determine the nodal...Ch. 4.1 - For the circuit of Fig. 4.5, compute the voltage...Ch. 4.1 - For the circuit of Fig. 4.8, determine the nodal...Ch. 4.2 - For the circuit of Fig. 4.11, compute the voltage...Ch. 4.3 - Determine i1 and i2 in the circuit in Fig. 4.19....Ch. 4.3 - Determine i1 and i2 in the circuit of Fig 4.21....Ch. 4.3 - Determine i1 in the circuit of Fig. 4.24 if the...Ch. 4.4 - Determine the current i1 in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 4.4 - Determine v3 in the circuit of Fig. 4.28. FIGURE...Ch. 4 - Solve the following systems of equations: (a) 2v2 ...
Ch. 4 - (a) Solve the following system of equations:...Ch. 4 - (a) Solve the following system of equations:...Ch. 4 - Correct (and verify by running) the following...Ch. 4 - In the circuit of Fig. 4.35, determine the current...Ch. 4 - Calculate the power dissipated in the 1 resistor...Ch. 4 - For the circuit in Fig. 4.37, determine the value...Ch. 4 - With the assistance of nodal analysis, determine...Ch. 4 - Prob. 9ECh. 4 - For the circuit of Fig. 4.40, determine the value...Ch. 4 - Use nodal analysis to find vP in the circuit shown...Ch. 4 - Prob. 12ECh. 4 - Prob. 13ECh. 4 - Determine a numerical value for each nodal voltage...Ch. 4 - Prob. 15ECh. 4 - Using nodal analysis as appropriate, determine the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 17ECh. 4 - Determine the nodal voltages as labeled in Fig....Ch. 4 - Prob. 19ECh. 4 - Prob. 20ECh. 4 - Employing supernode/nodal analysis techniques as...Ch. 4 - Prob. 22ECh. 4 - Prob. 23ECh. 4 - Prob. 24ECh. 4 - Repeat Exercise 23 for the case where the 12 V...Ch. 4 - Prob. 26ECh. 4 - Prob. 27ECh. 4 - Determine the value of k that will result in vx...Ch. 4 - Prob. 29ECh. 4 - Prob. 30ECh. 4 - Prob. 31ECh. 4 - Determine the currents flowing out of the positive...Ch. 4 - Obtain numerical values for the two mesh currents...Ch. 4 - Use mesh analysis as appropriate to determine the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 35ECh. 4 - Prob. 36ECh. 4 - Find the unknown voltage vx in the circuit in Fig....Ch. 4 - Prob. 38ECh. 4 - Prob. 39ECh. 4 - Determine the power dissipated in the 4 resistor...Ch. 4 - (a) Employ mesh analysis to determine the power...Ch. 4 - Define three clockwise mesh currents for the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 43ECh. 4 - Prob. 44ECh. 4 - Prob. 45ECh. 4 - Prob. 46ECh. 4 - Prob. 47ECh. 4 - Prob. 48ECh. 4 - Prob. 49ECh. 4 - Prob. 50ECh. 4 - Prob. 51ECh. 4 - Prob. 52ECh. 4 - For the circuit represented schematically in Fig....Ch. 4 - The circuit of Fig. 4.80 is modified such that the...Ch. 4 - The circuit of Fig. 4.81 contains three sources....Ch. 4 - Solve for the voltage vx as labeled in the circuit...Ch. 4 - Consider the five-source circuit of Fig. 4.83....Ch. 4 - Replace the dependent voltage source in the...Ch. 4 - After studying the circuit of Fig. 4.84, determine...Ch. 4 - Prob. 60ECh. 4 - Employ LTspice (or similar CAD tool) to verify the...Ch. 4 - Employ LTspice (or similar CAD tool) to verify the...Ch. 4 - Employ LTspice (or similar CAD tool) to verify the...Ch. 4 - Verify numerical values for each nodal voltage in...Ch. 4 - Prob. 65ECh. 4 - Prob. 66ECh. 4 - Prob. 67ECh. 4 - Prob. 68ECh. 4 - Prob. 69ECh. 4 - (a) Under what circumstances does the presence of...Ch. 4 - Referring to Fig. 4.88, (a) determine whether...Ch. 4 - Consider the LED circuit containing a red, green,...Ch. 4 - The LED circuit in Fig. 4.89 is used to mix colors...Ch. 4 - A light-sensing circuit is in Fig. 4.90, including...Ch. 4 - Use SPICE to analyze the circuit in Exercise 74 by...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The solid steel shaft AC has a diameter of 25 mm and is supported by smooth bearings at D and E. It is coupled ...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
The ____________ is always transparent.
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
What types of coolant are used in vehicles?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
How does a computers main memory differ from its auxiliary memory?
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
What is an uninitialized variable?
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
How are relationships between tables expressed in a relational database?
Modern Database Management
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Can you show how this answer was found:arrow_forwardQ1 [2 point] Perform 13+10 in the following Adder- Subtractor: A= |B= A3 B3 IB2 B1 A0 BO FAH FAH FAH FA M CO Q2 [2 point] Perform 13-10 in the following Adder- Subtractor: A= B= A3 B3 A2 B2 A1 B1 A0 BO A = = BC= AB FA FA FA FA M COarrow_forwardMatlab Homework (20ps) A BFSK signal is transmitted through a channel with AWGN. Generate similar BFSK received signal plots as shown on next page. (20 pts) BFSK for eb-1 and npower=0.01 with 500 samples BFSK for eb=1 and npower=0.1 with 500 samples 2.5 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 -0.5 -1 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 0.5 -1 -1.5 1.5 -1.5 -1 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 -1.5 -1 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5arrow_forward
- Can you show how this answer was found?arrow_forward1. You are to design a 9-volt battery operated baseband PAM communication system that must last great than 10 years without replacing the batteries. The application requires a BER of <10^-4 and a data rate of 200bps. The channel can be modeled as AWGN with a noise power spectral density of 10^-9 W/Hz and a channel loss of 10 dB. (a) Estimate the required capacity of the batteries. (The battery life (hours) is equal to the battery volts times of the battery capacity (Amps* hours) divided by the total load (Watts)) and (b) Can you easily find this battery? If not, what would you suggest be done?arrow_forward3. You are on a design team tasked to design a system of remote sensors that use PAM. Here is what the team knows/assumptions: The remote sensor will use a single AA battery required to power the sensors. The system has a bandwidth of 2KHz and requires a data rate of 12 Kbps and a BER of less than 1*10^-4. The typical channel has maximum losses of 35 dB and a noise power spectral density is 10^-9 W/Hz. Your boss assigns you with the task of estimating how long the battery will last.arrow_forward
- 2. The noise power (in watts) measured in a baseband PAM communication channel is 230*10^-6 Watts. The transmitter output power is 600 mW and has a data rate of 300 Kbps. The channel bandwidth is 100 KHz with losses that can be modeled as 0.5dB/meter. The application requires a BER ofarrow_forwardQ27arrow_forwardQ25arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Nodal Analysis for Circuits Explained; Author: Engineer4Free;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f-sbANgw4fo;License: Standard Youtube License