
(a)
The variables in the graph and the relation of variables at various points on the graph are to be determined.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The graph given in the question is,
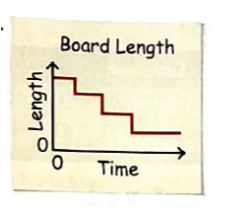
The graph is between length and time.
The given graph represents the variation of length of a board with time. The time is plotted on the x-axis while length is plotted on the y-axis.
The variables in the graph are length and time.
The length of the board remains constant over a shot time interval and as the length keeps on decreasing the time interval in which the length of the board remainsconstant,increases.
The variation of length of board in the different timeinterval is shown below:
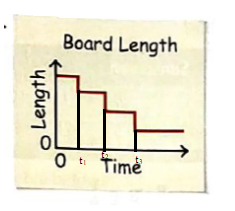
After a time interval (t3-t2) the length of the board remains constant with respect to time.
(b)
The variables in the graph and the relation of variables at various points on the graph are to be determined.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The graph given in the question is,
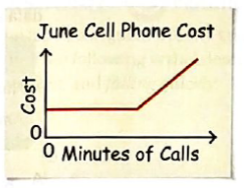
The given graph represents the cell phone cost of June month with respect to minutes of calls.
The variables are cost and minutes of calls.
The graph represents that the cell phone cost is fixed up to half month of June with respect to number of calls and the cost starts to rise linearly in the rest of the month with respect to minutes of calls.
Chapter 4 Solutions
EP ALGEBRA 1-ETEXT ACCESS
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Elementary Statistics
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
- For each graph below, state whether it represents a function. Graph 1 24y Graph 2 Graph 3 4 2 -8 -6 -4 -2 -2 2 4 6 Function? ○ Yes ○ No ○ Yes ○ No Graph 4 Graph 5 8 Function? Yes No Yes No -2. ○ Yes ○ No Graph 6 4 + 2 4 -8 -6 -4 -2 2 4 6 8 Yes -4++ Noarrow_forwardPractice k Help ises A 96 Anewer The probability that you get a sum of at least 10 is Determine the number of ways that the specified event can occur when two number cubes are rolled. 1. Getting a sum of 9 or 10 3. Getting a sum less than 5 2. Getting a sum of 6 or 7 4. Getting a sum that is odd Tell whether you would use the addition principle or the multiplication principle to determine the total number of possible outcomes for the situation described. 5. Rolling three number cubes 6. Getting a sum of 10 or 12 after rolling three number cubes A set of playing cards contains four groups of cards designated by color (black, red, yellow, and green) with cards numbered from 1 to 14 in each group. Determine the number of ways that the specified event can occur when a card is drawn from the set. 7. Drawing a 13 or 14 9. Drawing a number less than 4 8. Drawing a yellow or green card 10. Drawing a black, red, or green car The spinner is divided into equal parts. Find the specified…arrow_forwardAnswer the questionsarrow_forward
- Solve the problems on the imagearrow_forwardAsked this question and got a wrong answer previously: Third, show that v3 = (−√3, −3, 3)⊤ is an eigenvector of M3 . Also here find the correspondingeigenvalue λ3 . Just from looking at M3 and its components, can you say something about the remaining twoeigenvalues? If so, what would you say?arrow_forwardDetermine whether the inverse of f(x)=x^4+2 is a function. Then, find the inverse.arrow_forward
- The 173 acellus.com StudentFunctions inter ooks 24-25/08 R Mastery Connect ac ?ClassiD-952638111# Introduction - Surface Area of Composite Figures 3 cm 3 cm 8 cm 8 cm Find the surface area of the composite figure. 2 SA = [?] cm² 7 cm REMEMBER! Exclude areas where complex shapes touch. 7 cm 12 cm 10 cm might ©2003-2025 International Academy of Science. All Rights Reserved. Enterarrow_forwardYou are given a plane Π in R3 defined by two vectors, p1 and p2, and a subspace W in R3 spanned by twovectors, w1 and w2. Your task is to project the plane Π onto the subspace W.First, answer the question of what the projection matrix is that projects onto the subspace W and how toapply it to find the desired projection. Second, approach the task in a different way by using the Gram-Schmidtmethod to find an orthonormal basis for subspace W, before then using the resulting basis vectors for theprojection. Last, compare the results obtained from both methodsarrow_forwardPlane II is spanned by the vectors: - (2) · P² - (4) P1=2 P21 3 Subspace W is spanned by the vectors: 2 W1 - (9) · 1 W2 1 = (³)arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





