
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
E or Z configuration has to be identified for the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Cis–trans isomerism (or) geometric isomerism or configurational isomerism:
The two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are in same side in double bond of
Example:
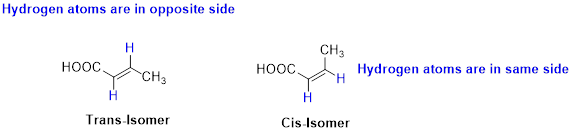
(b)
Interpretation:
E or Z configuration has to be identified for the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Cis–trans isomerism (or) geometric isomerism or configurational isomerism:
The two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are in same side in double bond of alkenes is called as cis isomer (or Z-isomer). Two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are opposite side in double bond of alkenes is called as trans isomer (or E-isomer).
Example:

(c)
Interpretation:
E or Z configuration has to be identified for the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Cis–trans isomerism (or) geometric isomerism or configurational isomerism:
The two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are in same side in double bond of alkenes is called as cis isomer (or Z-isomer). Two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are opposite side in double bond of alkenes is called as trans isomer (or E-isomer).
Example:

(d)
Interpretation:
E or Z configuration has to be identified for the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Cis–trans isomerism (or) geometric isomerism or configurational isomerism:
The two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are in same side in double bond of alkenes is called as cis isomer (or Z-isomer). Two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are opposite side in double bond of alkenes is called as trans isomer (or E-isomer).
Example:

(e)
Interpretation:
E or Z configuration has to be identified for the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Cis–trans isomerism (or) geometric isomerism or configurational isomerism:
The two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are in same side in double bond of alkenes is called as cis isomer (or Z-isomer). Two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are opposite side in double bond of alkenes is called as trans isomer (or E-isomer).
Example:

(f)
Interpretation:
E or Z configuration has to be identified for the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Cis–trans isomerism (or) geometric isomerism or configurational isomerism:
The two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are in same side in double bond of alkenes is called as cis isomer (or Z-isomer). Two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are opposite side in double bond of alkenes is called as trans isomer (or E-isomer).
Example:

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK ESSENTIAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY

 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


