
Concept explainers
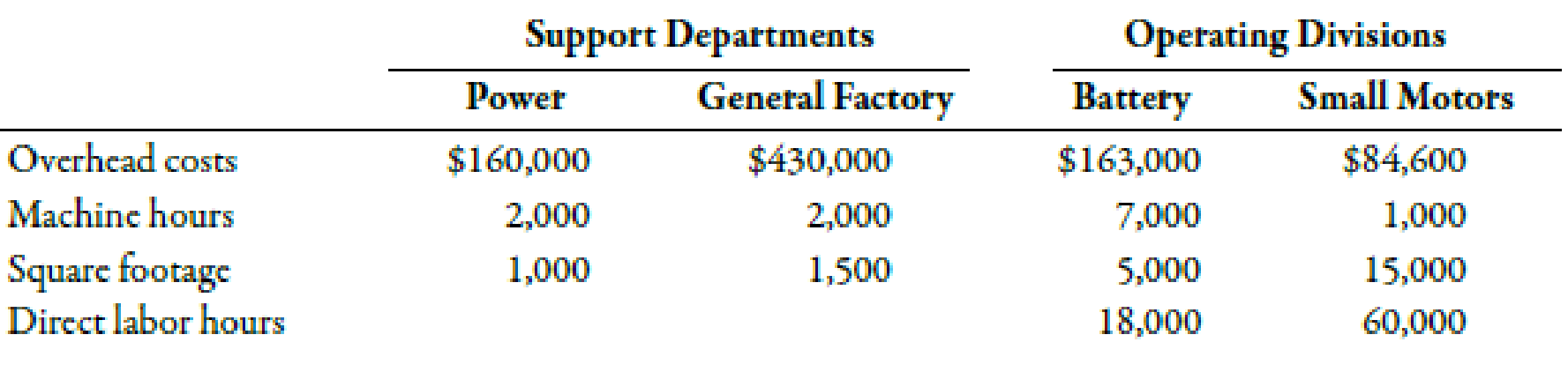
(Appendix 4B) Sequential Method of Support Department Cost Allocation
Refer to Exercise 4-51 for data. Now assume that Stevenson uses the sequential method to allocate support department costs to the operating divisions. General Factory is allocated first in the sequential method for the company.
Required:
- 1. Calculate the allocation ratios for Power and General Factory. (Note: Carry these calculations out to four decimal places.)
- 2. Allocate the support service costs to the operating divisions. (Note: Round all amounts to the nearest dollar.)
- 3. Assume divisional
overhead rates are based on direct labor hours. Calculate the overhead rate for the Battery Division and for the Small Motors Division. (Note: Round overhead rates to the nearest cent.)
1.
Computeallocation ratios for power and general factory under the sequential method.
Explanation of Solution
Sequential Method:
Sequential method recognizes that there is possible interaction between the support departments. However, it does notaccount for such interaction in full which makes it more accurate as compared to the direct method.
Use the following formula to calculate allocation ratios for general factory on the basis of number of square footage:
Power:
Substitute 1,000 for number of square footage in power and 21,000 for total square footage in the above formula.
Therefore, the cost assignment ratio for S2 is 0.0476.
Battery:
Substitute 5,000 for number ofsquare footage in battery and 21,000 for total square footage in the above formula.
Therefore, the cost assignment ratio for battery is 0.2381.
Small motors:
Substitute 15,000 for number ofsquare footage in small motors and 21,000 for total square footage in the above formula.
Therefore, the cost assignment ratio for painting department is 0.7143.
Use the following formula to calculate cost assignment ratios for power on the basis of number of machine hours:
Battery:
Substitute 7,000 for number of machine hoursofbattery and 8,000 for total machine hours ofoperating department in the above formula.
Therefore, the assignment ratio for assembly department is 0.8750.
Small motors:
Substitute 1,000 for number of machine hours of painting and 8,000 for total machine hours of operating department in the above formula.
Therefore, the assignment ratio for painting department is 0.1250.
2.
Apportion the support service costs to the operating divisions by using the sequential method:
Explanation of Solution
Allocation:
Allocation can be defined as the process of assigning the indirect costs to the cost object with the help of a convenient and reasonable method. It is essential to allocate indirect costs to the cost objects.
| Support departments | Operating departments | |||
| Power($) | General factory($) | Battery($) | Small motors($) | |
| Direct costs | 160,000 | 430,000 | 163,000 | 84,600 |
| Allocate: | ||||
| Power | 20,468 | (430,000) | 102,383 | 307,149 |
| General factory | (180,468) | 157,910 | 22,559 | |
| Total | 0 | 0 | 423,293 | 414,308 |
Table (1)
Working Note:
#. Allocation of support service costs to power:
1. Allocation of support servicecost to battery:
For power cost:
For general factory cost:
2. Allocation of support service cost to small motors:
For power cost:
For general factory cost:
3.
Compute overhead rate of battery and small motors divisions.
Answer to Problem 52E
The overhead rate of battery and small motors divisions is $23.52 and $6.91 respectively.
Explanation of Solution
Overhead Rate:
The amount which is calculate at the beginning of the accounting year for a related activity by dividing the total estimated annual overhead by estimated annual activity level is known as the overhead rate.
Use the following formula to calculate overhead rate for battery division:
Substitute $423,293 for estimated annual overhead and 18,000 DLH for estimated annual activity level in the above formula.
Therefore, overhead rate is $23.52.
Use the following formula to calculate overhead rate for small motors division:
Substitute $414,308 for estimated annual overhead and 60,000 DLH for estimated annual activity level in the above formula.
Therefore, overhead rate is $6.91.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Business Decision-Making
- general accountingarrow_forwardE3-17 (Algo) Calculating Equivalent Units, Unit Costs, and Cost Assigned (Weighted-Average Method) [LO 3-2] Vista Vacuum Company has the following production Information for the month of March. All materials are added at the beginning of the manufacturing process. Units . • Beginning Inventory of 3,500 units that are 100 percent complete for materials and 28 percent complete for conversion. 14,600 units started during the period. Ending Inventory of 4,200 units that are 14 percent complete for conversion. Manufacturing Costs Beginning Inventory was $20,500 ($10,100 materials and $10,400 conversion costs). Costs added during the month were $28,400 for materials and $51,500 for conversion ($26.700 labor and $24,800 applied overhead). Assume the company uses Weighted-Average Method. Required: 1. Calculate the number of equivalent units of production for materials and conversion for March. 2. Calculate the cost per equivalent unit for materials and conversion for March. 3. Determine the…arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,




