
Concept explainers
A person pushes a 14.0-kg lawn mower at constant speed with a force of F = 88.0 N directed along the handle, which is at an angle of 45.0° to the horizontal (Fig. 4-58) (a) Draw the free-body diagram showing all forces acting on the mower. Calculate (b) the horizontal friction force on the mower, then (c) the normal force exerted vertically upward on the mower by the ground (d) What force must the person exert on the lawn mower to accelerate it from rest to 1.5 m/s in 2.5 seconds, assuming the same friction force?
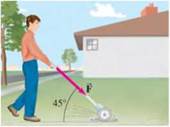
Figure 4-58 Problem 50.
Part (a) To Determine:
A free body diagram for the motion.:
Answer to Problem 48P
Solution:
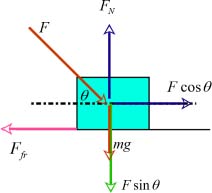
The free body diagram for the lawn mower is drawn as below:
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Mass of the lawn mower
Force acting on the mower
The angle at which the force acts
The initial speed of the mower
Final speed of the mower
Time taken to reach the final speed
Calculation:
The free body diagram for the lawn mower is given below:
The lawn mower of mass m is acted upon by a force F at an angle . The force is resolved into two components, parallel to the ground and perpendicular to the ground. The weight mg of the mower acts vertically downwards and the normal force acts vertically upwards. The force of friction acts along the ground in a direction opposite to the motion of the mower
Part (b)To determine:
The horizontal frictional force on the lawn mower
Answer to Problem 48P
Solution:
The frictional force when the lawn mover moves with constant speed is 62.2 N.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Mass of the lawn mower
Force acting on the mower
The angle at which the force acts
The initial speed of the mower
Final speed of the mower
Time taken to reach the final speed
Calculation:
The lawnmower moves with a constant speed under the action of the force F. Therefore, the net force on the mower is zero.
From the free body diagram, write the condition for the equilibrium in the horizontal direction.
Substitute the values of F and
from the given values and calculate the value of the frictional force.
Part (c)To determine:
The normal force acting on the mower
Answer to Problem 48P
Solution:
The normal force acting on the mower is199 N.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Mass of the lawn mower
Force acting on the mower
The angle at which the force acts
The initial speed of the mower
Final speed of the mower
Time taken to reach the final speed
Calculation:
Since there is no motion, either in the upward or in the downward directions, write the conditions for equilibrium in the vertical direction.
From the free body diagram,
Use the values for m, F and
from the given values and using 9.8m/s2 for g in the equation, calculate the value of the normal force.
Part (d) To Determine:
The force needed to accelerate the lawn mower from rest to 1.5 m/s in 2.5 s when the same frictional force acts on the lawnmower.
Answer to Problem 48P
Solution:
The force required to accelerate the lawn mover from rest to 1.5 m/s in 2.5 s when the same frictional force acts on the lawn mower is 99.6 N.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Mass of the lawn mower
Force acting on the mower
The angle at which the force acts
The initial speed of the mower
Final speed of the mower
Time taken to reach the final speed
Calculation:
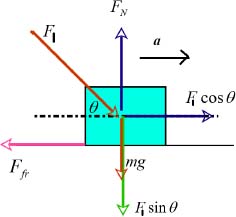
If the magnitude of the force changes to F1 and the lawn mower accelerates with an acceleration a, from rest to a speed v in a time t, with the frictional force having the same magnitude as in the previous case, the free body diagram, in this case, is drawn as is shown below:
In the horizontal direction, the equation for motion can be written as,
Calculate the acceleration using the equation of motion,
Substitute the values of , v and t and calculate a.
Use the calculated values of a and in the equation and calculate the value of .
Chapter 4 Solutions
Physics: Principles with Applications
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
- ! Required information The radius of the Moon is 1.737 Mm and the distance between Earth and the Moon is 384.5 Mm. The intensity of the moonlight incident on her eye is 0.0220 W/m². What is the intensity incident on her retina if the diameter of her pupil is 6.54 mm and the diameter of her eye is 1.94 cm? W/m²arrow_forwardRequired information An object is placed 20.0 cm from a converging lens with focal length 15.0 cm (see the figure, not drawn to scale). A concave mirror with focal length 10.0 cm is located 76.5 cm to the right of the lens. Light goes through the lens, reflects from the mirror, and passes through the lens again, forming a final image. Converging lens Object Concave mirror 15.0 cm -20.0 cm- 10.0 cm d cm d = 76.5. What is the location of the final image? cm to the left of the lensarrow_forward! Required information A man requires reading glasses with +2.15-D refractive power to read a book held 40.0 cm away with a relaxed eye. Assume the glasses are 1.90 cm from his eyes. His uncorrected near point is 1.00 m. If one of the lenses is the one for distance vision, what should the refractive power of the other lens (for close-up vision) in his bifocals be to give him clear vision from 25.0 cm to infinity? 2.98 Darrow_forward
- ! Required information Assume that the magnifier is held close to the eye. Use the standard near point of 25.0 cm to find the angular magnification. An insect that is 4.10 mm long is placed 10.3 cm from a simple magnifier with a focal length of 13.0 cm. What is the angular magnification?arrow_forward2arrow_forward3arrow_forward
- Imagine you are out for a stroll on a sunny day when you encounter a lake. Unpolarized light from the sun is reflected off the lake into your eyes. However, you notice when you put on your vertically polarized sunglasses, the light reflected off the lake no longer reaches your eyes. What is the angle between the unpolarized light and the surface of the water, in degrees, measured from the horizontal? You may assume the index of refraction of air is nair=1 and the index of refraction of water is nwater=1.33 . Round your answer to three significant figures. Just enter the number, nothing else.arrow_forwardDeduce what overvoltage is like in reversible electrodes.arrow_forwardpls help on thesearrow_forward
- pls help on thesearrow_forward20. Two small conducting spheres are placed on top of insulating pads. The 3.7 × 10-10 C sphere is fixed whie the 3.0 × 107 C sphere, initially at rest, is free to move. The mass of each sphere is 0.09 kg. If the spheres are initially 0.10 m apart, how fast will the sphere be moving when they are 1.5 m apart?arrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





