
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780133840544
Author: George F. Limbrunner, Craig D'Allaird, Leonard Spiegel
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 4.45SP
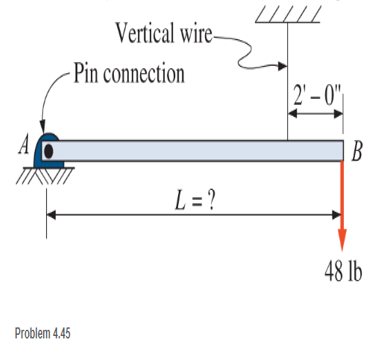
A rod of uniform cross section weighs 4 lb/ft and is pin-connected at point A, as shown. The rod supports a load of 48 lb at point B and is held horizontal by a vertical wire attached 2 ft from point B. With a force of 85 lb in the wire, determine the length of the rod.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Water in the glass tube is at a temperature of 40°C. Plot the height of the water as a function of the tube's inner diameter D for 0.5mm≤D≤3mm. Use increments of 0.5mm. Take sigma=69.6mN/m, and theta=0° for the contact angle.
Determine the distance h that the column of mercury in the tube will be depressed when the tube is inserted into the mercury at a room temperature of 68 F. Plot this relationship of h (vertical axis) versus D for 0.5 in≤D≤0.150in. Give values for increments of ΔD=0.025in. Discuss this result
Water is at a temperature of 30 C. Plot the height h of the water as a function of the gap w between the two glass plates for 0.4 mm ≤ w ≤ 2.4 mm. Use increments of 0.4mm. Take sigma=0.0718 N/m.
Chapter 4 Solutions
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
Ch. 4 - and 4.2 Sketch free-body diagram for the members...Ch. 4 - Sketch free-body diagram for the members shown.Ch. 4 - A steel cylinder having a mass of 120 kgis...Ch. 4 - A 50-lb block is supported by a pin support and a...Ch. 4 - A cylinder weighing 200 lb is supported on an...Ch. 4 - A weight W is supported by a flexible cable and an...Ch. 4 - The ladder shown is supported by a smooth...Ch. 4 - What horizontal force F applied at the center of...Ch. 4 - Calculate the force in cable AB and the angle (...Ch. 4 - Calculate the horizontal force F that should be...
Ch. 4 - Calculate the reactions of the two smooth inclined...Ch. 4 - Calculate the force in each cable for the...Ch. 4 - Three members of a truss intersect at joint B as...Ch. 4 - Four concurrent forces in equilibrium act at point...Ch. 4 - The beam shown carries vertical concentrated...Ch. 4 - Find the reactions at A and B for the beam shown....Ch. 4 - A simply supported beam spans 10 m. The beam...Ch. 4 - The beam shown carries vertical loads. Calculate...Ch. 4 - Calculate the reaction at each support for the...Ch. 4 - Calculate the reactions at A and B for the beam...Ch. 4 - Calculate the reactions at A and B for the beam...Ch. 4 - A 12-ft simple beam is supported at each end. It...Ch. 4 - The beam shown carries vertical loads as...Ch. 4 - Determine the reactions for the beam shown. The...Ch. 4 - Calculate the reaction at each support for the...Ch. 4 - Calculate the wall reactions for the cantilever...Ch. 4 - Determine the reactions at supports A and B of the...Ch. 4 - A mass M of 300 kg is supported by a boom, as...Ch. 4 - Rework Problem 4.28 assuming that point D has been...Ch. 4 - Calculate the force in the tie rod BC and the...Ch. 4 - The davit shown is used in pairs for...Ch. 4 - For the following computer problems, any...Ch. 4 - For the following computer problems, any...Ch. 4 - For the following computer problems, any...Ch. 4 - For the structure shown, draw free-body diagram...Ch. 4 - A 1200-lb load is supported by a cable that runs...Ch. 4 - For the pin-connected frame shown, sketch a...Ch. 4 - For the concurrent force system shown, calculate...Ch. 4 - A strut having a mass of 40 kg/m is supported by a...Ch. 4 - Calculate the reaction at each support for the...Ch. 4 - Calculate the reaction at each support for the...Ch. 4 - A beam supports a nonuniformly distributed load as...Ch. 4 - Calculate the reactions at each support for the...Ch. 4 - Compute reactions at each support for the beam...Ch. 4 - A rod of uniform cross section weighs 4 lb/ft and...Ch. 4 - A 12-ft-long weightiness member supports two...Ch. 4 - A uniform rod AB, having a weight of 5.00 lb and a...Ch. 4 - The plastic barrel tent anchor of Problem 2.11...Ch. 4 - Compute the reactions at A and B for the bracket...Ch. 4 - The truss shown is supported by a pin at A and a...Ch. 4 - Find the reactions at supports A and B for the...Ch. 4 - Find the reactions at supports A and B for the...Ch. 4 - Determine the reactions at A and B for the truss...Ch. 4 - A 40-ft ladder weighing 130 lb is pin-connected to...Ch. 4 - The frame shown is pin-connected at point A and...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.56SPCh. 4 - A horizontal beam is pin-connected to a wall at...Ch. 4 - Calculate the force in the cable for the structure...Ch. 4 - The Thenard shutter dam shown was originally...Ch. 4 - An inclined railway can be used to lift heavy...Ch. 4 - Two cylinders are supported in a box, as shown....
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the reading on the vernier calipers? 7 6 0 5 10 8arrow_forwardDetermine the moments of the force about the x and the a axes. O 4 m F = {-40i +20j + 10k} N 3 m 6 m aarrow_forward6. A part of the structure for a factory automation system is a beam that spans 30.0 in as shown in Figure P5-6. Loads are applied at two points, each 8.0 in from a support. The left load F₁ = 1800 lb remains constantly applied, while the right load F₂ = 1800 lb is applied and removed fre- quently as the machine cycles. Evaluate the beam at both B and C. A 8 in F₁ = 1800 lb 14 in F2 = 1800 lb 8 in D RA B C 4X2X1/4 Steel tube Beam cross section RDarrow_forward
- 30. Repeat Problem 28, except using a shaft that is rotating and transmitting a torque of 150 N⚫m from the left bear- ing to the middle of the shaft. Also, there is a profile key- seat at the middle under the load.arrow_forward28. The shaft shown in Figure P5-28 is supported by bear- ings at each end, which have bores of 20.0 mm. Design the shaft to carry the given load if it is steady and the shaft is stationary. Make the dimension a as large as pos- sible while keeping the stress safe. Determine the required d = 20mm D = ? R = ?| 5.4 kN d=20mm Length not to scale -a = ?- +а= a = ? + -125 mm- -250 mm- FIGURE P5-28 (Problems 28, 29, and 30)arrow_forward12. Compute the estimated actual endurance limit for SAE 4130 WQT 1300 steel bar with a rectangular cross sec- tion of 20.0 mm by 60 mm. It is to be machined and subjected to repeated and reversed bending stress. A reli- ability of 99% is desired.arrow_forward
- 28. The shaft shown in Figure P5-28 is supported by bear- ings at each end, which have bores of 20.0 mm. Design the shaft to carry the given load if it is steady and the shaft is stationary. Make the dimension a as large as pos- sible while keeping the stress safe. Determine the required d = 20mm D = ? R = ?| 5.4 kN d=20mm Length not to scale -a = ?- +а= a = ? + -125 mm- -250 mm- FIGURE P5-28 (Problems 28, 29, and 30)arrow_forward2. A strut in a space frame has a rectangular cross section of 10.0 mm by 30.0 mm. It sees a load that varies from a tensile force of 20.0 kN to a compressive force of 8.0 kN.arrow_forwardfind stress at Qarrow_forward
- I had a theoretical question about attitude determination. In the attached images, I gave two axis and angles. The coefficient of the axes are the same and the angles are the same. The only difference is the vector basis. Lets say there is a rotation going from n hat to b hat. Then, you introduce a intermediate rotation s hat. So, I want to know if the DCM produced from both axis and angles will be the same or not. Does the vector basis affect the numerical value of the DCM? The DCM formula only cares about the coefficient of the axis and the angle. So, they should be the same right?arrow_forward3-15. A small fixed tube is shaped in the form of a vertical helix of radius a and helix angle y, that is, the tube always makes an angle y with the horizontal. A particle of mass m slides down the tube under the action of gravity. If there is a coefficient of friction μ between the tube and the particle, what is the steady-state speed of the particle? Let y γ 30° and assume that µ < 1/√3.arrow_forwardThe plate is moving at 0.6 mm/s when the force applied to the plate is 4mN. If the surface area of the plate in contact with the liquid is 0.5 m^2, deterimine the approximate viscosity of the liquid, assuming that the velocity distribution is linear.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
EVERYTHING on Axial Loading Normal Stress in 10 MINUTES - Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jQ-fNqZWrNg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY