
(a)
Interpretation:
The standard free energy of activation of reaction B is to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
The rate of the reaction is affected by the activation free energy of the reaction. The relationship between the activation free energy and
Where,
•
•
•
Answer to Problem 4.29P
The standard free energy of activation for reaction B is
Explanation of Solution
It is given that standard free energy of activation of reaction A is
The relative rates of two reactions are expressed as,
Where,
•
•
•
Substitute the activation energy for reaction A, the relative rate of A and B, gas constant and temperature in the given formula.
Rearrange the above equation for the calculation of activation energy of B as shown below.
Thus, standard free energy of activation for reaction B is
The standard free energy of activation for reaction B is
(b)
Interpretation:
The reaction free energy diagram for the two reactions showing the two values of
Concept introduction:
The transition state is formed during the conversion of reactants into products in the
Answer to Problem 4.29P
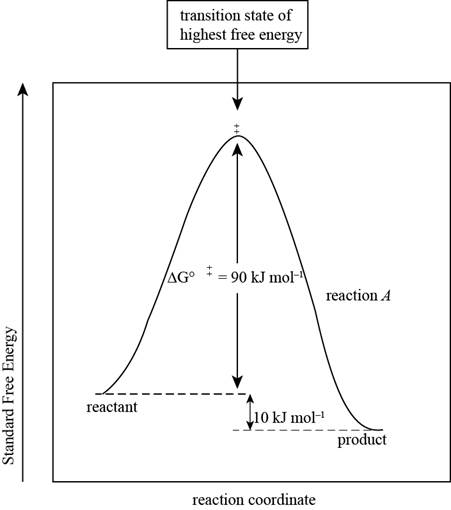
The reaction free-energy diagram for the reaction A showing the two values of
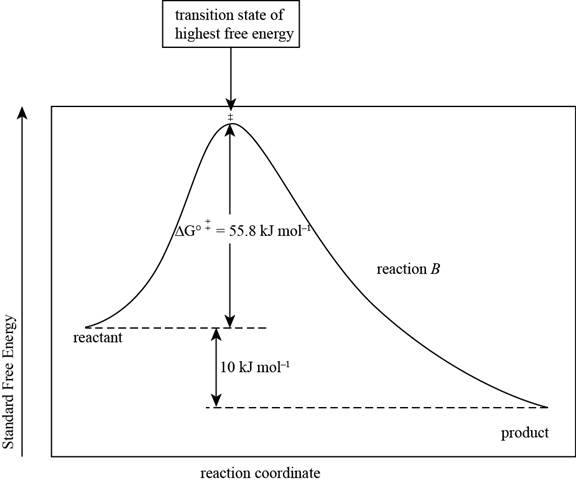
The reaction free-energy diagram for the reaction B showing the two values of
Explanation of Solution
It is given that standard free energy of activation of reaction A is
The reaction free-energy diagram for the reaction A showing the two values of
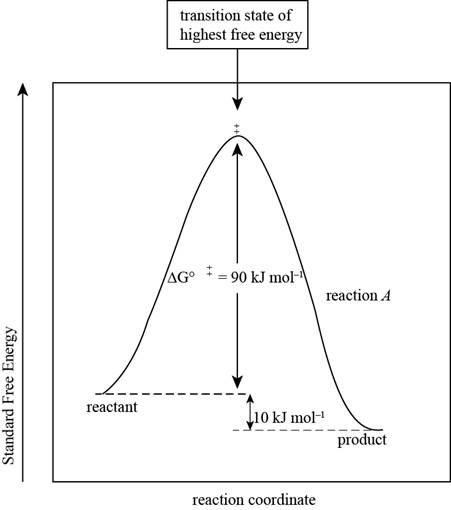
Figure 1
This diagram represents the plot between standard free energy and the reaction coordinates. The point at which the energy is maximum represents the transition state of the reaction.
The reaction free energy diagram for the reaction B showing the two values of
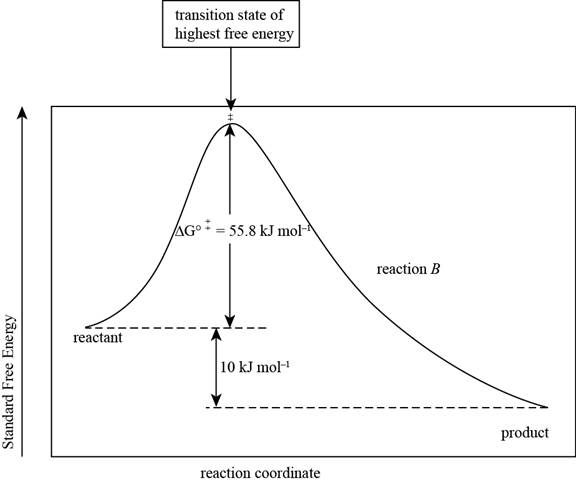
Figure 2
The reaction free-energy diagram for the two reactions showing the two values of
(c)
Interpretation:
The standard free energy of activation of the reverse reaction in both reactions A and B is to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
The free energy diagram represents the plot between standard free energy and the reaction coordinates. The point at which the energy is maximum represents the transition state of the reaction.
Answer to Problem 4.29P
The standard free energy of activation of the reverse reaction in both reactions A and B is
Explanation of Solution
It is given that standard free energy of activation of reaction A is
The products of each reaction are
The standard free energy of activation of the reverse reaction A is,
Thus, the standard free energy of activation of the reverse reaction A is
The standard free energy of activation of the reverse reaction B is,
Thus, the standard free energy of activation of the reverse reaction A is
The standard free energy of activation of the reverse reaction in both reactions A and B is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions
- Predict the major products of this reaction: excess H+ NaOH ? A Note that the first reactant is used in excess, that is, there is much more of the first reactant than the second. If there won't be any products, just check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privarrow_forward1. For each of the reaction "railroads" below, you are either asked to give the structure(s) of the starting material(s) or product(s), or provide reagents/conditions to accomplish the transformation, as indicated by the boxes. a. NaOMe H+ .CO,H HO₂C MeOH (excess) MeOH H3C Br يع CH3 1. LiAlH4 2. H3O+ 3. PBг3 H3C 1. Et-Li 2. H3O+ -CO₂Me -CO₂Me OH CH3 CH3 ল CH3arrow_forwardPredict the intermediate 1 and final product 2 of this organic reaction: NaOMe ག1, ད།་, - + H You can draw 1 and 2 in any arrangement you like. 2 work up Note: if either 1 or 2 consists of a pair of enantiomers, just draw one structure using line bonds instead of 3D (dash and wedge) bonds at the chiral center. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Parrow_forward
- What is the total energy cost associated with the compound below adopting the shown conformation? CH3 HH DH CH3arrow_forwardΗΝ, Draw Final Product C cyclohexanone pH 4-5 Edit Enamine H3O+ CH3CH2Br THF, reflux H Edit Iminium Ionarrow_forwardHow many hydrogen atoms are connected to the indicated carbon atom?arrow_forward
- Identify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forwardIdentify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forwardH H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forwardchoose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
