
Concept explainers
Two electrostatic potential maps are shown, one of methyllithium (CH3Li) and the other of chloromethane (CH3Cl). Based on their polarity patterns, which do you think is which?

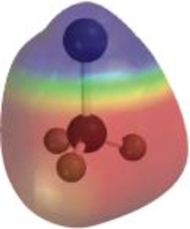
Interpretation:
From given electrostatic potential maps of methyllithium and chloromethane which is which has to be predicted based on polarity pattern.
Concept introduction:
The degree of electron transfer in polar covalent bond can be pictured with something called electrostatic potential maps which uses the colour to represent the electron distribution in an isolated gas-phase molecules.
In the electrostatic potential map colour of the parts are indicates given,
Yellow-green colour - nonpolar or neutral atom
Blue colour - an electron poor atom
Red colour- an electron rich atom.
Answer to Problem 4.26CP
(a) is found as chloromethane and (b) is found as methyllithium.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Given two electrostatic potential maps are,
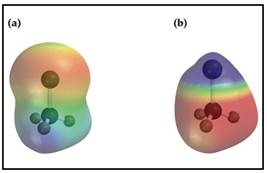
Figure 1
To predict: Methyllithium and chloromethane from given electrostatic potential maps
In electrostatic potential maps Lithium and Chlorine are placed at the top of each map.
Red colour area is for negatively polarized region hence which is accompanying with Chlorine.
The blue colour area is for passively polarized region hence it is accompanied with Lithium.
Thus, map (a) is for Methylchloride
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
General Chemistry: Atoms First
- Explain why acid chlorides are more reactive than amides in reactions with nucleophiles.arrow_forwardCalculating the pH of a weak base titrated with a strong acid An analytical chemist is titrating 101.7 mL of a 0.3500M solution of piperidine (C5H10NH) with a 0.05700M solution of HClO4. The pK of piperidine is 2.89. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 682.9 mL of the HClO solution to it. 4 Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HClO solution added. 4 Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pH = .11 00. 18 Ararrow_forwardThe following is a two groups (Regular tomato sauce & Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce) of data recorded by a team analysising salt content in tomato sauce using the MOHR titration method: Regular Tomato Sauce Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce 340.0 262.7 QUESTION: For both groups of data provide answers to the calculations attached in the imagearrow_forward
- 7. Concentration and uncertainty in the estimate of concentration (class data) Class mean for sample (Regular) |[Cl-] (mmol/L) class mean Sn za/2 95% Confidence Interval (mmol/L) [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 95% Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forwardThe following is a two groups (Regular tomato sauce & Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce) of data recorded by a team analysising salt content in tomato sauce using the MOHR titration method: Regular Tomato Sauce Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce 223.4 148.7 353.7 278.2 334.6 268.7 305.6 234.4 340.0 262.7 304.3 283.2 244.7 143.6 QUESTION: For both groups of data calculate the answers attached in the image.arrow_forwardGive reason(s) for six from the followings [using equations if possible] a. Addition of sodium carbonate to sulfanilic acid in the Methyl Orange preparation. b. What happened if the diazotization reaction gets warmed up by mistake. c. Addition of sodium nitrite in acidified solution in MO preparation through the diazotization d. Using sodium dithionite dihydrate in the second step for Luminol preparation. e. In nitroaniline preparation, addition of the acid mixture (nitric acid and sulfuric acid) to the product of step I. f. What is the main reason of the acylation step in nitroaniline preparation g. Heating under reflux. h. Fusion of an organic compound with sodium. HAND WRITTEN PLEASEarrow_forward
- edict the major products of the following organic reaction: u A + ? CN Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Te LMUNDARYarrow_forwardSketch the intermediates for A,B,C & D.arrow_forwardCan the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? O ? A . If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. . If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ㅇ 80 F5 F6 A 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Cente FIGarrow_forward
- In methyl orange preparation, if the reaction started with 0.5 mole of sulfanilic acid to form the diazonium salt of this compound and then it converted to methyl orange [0.2 mole]. If the efficiency of the second step was 50%, Calculate: A. Equation(s) of Methyl Orange synthesis: Diazotization and coupling reactions. B. How much diazonium salt was formed in this reaction? C. The efficiency percentage of the diazotization reaction D. Efficiency percentage of the whole reaction.arrow_forwardHand written equations pleasearrow_forwardHand written equations pleasearrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





